Sodium butyrate

Sodium butyrate structure
|
Common Name | Sodium butyrate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 156-54-7 | Molecular Weight | 110.087 | |
| Density | 0.987g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 164.3ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H7NaO2 | Melting Point | 250-253 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 69.7ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Sodium butyrateButyric acid is a histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor, with anti-tumor effects in several cancers. |
| Name | sodium butyrate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Butyric acid is a histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor, with anti-tumor effects in several cancers. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
HDAC |
| In Vitro | Sodium Butyrate induces morphological changes, inhibits cell proliferation and impairs cell viability in NPC cells. Sodium Butyrate (1, 5, 10 mM) is cytotoxic to NPC cells, inducing a dose- and time-dependent decrease in cell viability, in both 5-8F and 6-10B cells. Sodium Butyrate induces nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell apoptosis by activating the mitochondrial apoptotic axis. Moreover, SOCE inhibition and disruption of the CRAC channel can attenuate the apoptosis induced by Sodium Butyrate[1]. Sodium butyrate significantly decreases cell viability, accompanied by reduced levels of p-mTOR and PCNA protein. Sodium butyrate, in a dose-dependent manner, induces cell cycle arrest in G0/G1 phase and reduces the numbers of cells in S phase. In addition, relative expression of p21, p27, and pro-apoptosis bak genes, and protein levels of p21Waf1/Cip1, p27Kip1, cyclinD3, CDK4, and Cleave-caspase3 are increased by higher concentrations of sodium butyrate (1, 5, 10 mM), and the levels of cyclinD1 and CDK6 are reduced by 5 and 10 mM butyrate[3]. |
| In Vivo | Sodium Butyrate (300 mg/kg, s.c.) administration immediately after HI provided almost complete neuroprotection in comparison with non-treated animals. Sodium butyrate administration results in an increased number of microglial cells to 150% of vehicle-treated animals in the ipsilateral side. Sodium butyrate promotes the polarization of microglia from M1- to M2-like phenotype after neonatal hypoxia-ischemia[2]. Sodium butyrate (300 mg/kg, s.c.) in combination with AK-7 (20 mg/kg, i.p.) significantly alleviates this reduction of the time spent exploring new objects, ameliorates the reduction of the number of Ki67-positive cells and DCX-immunoreactive neuroblasts in the dentate gyrus of the mice. In addition, sodium butyrate reverses SIRT2-related age phenotypes[4]. |
| Cell Assay | Cells are seeded at a density of 2,000 cells/well in 96-well plates with 200 µL culture medium containing Sodium Butyrate at different concentrations. Then, the cells are consecutively cultured for 72 h. Every 24 h, 20 µL 5 mg/mL MTT solution is added into the corresponding well, and the cells are cultured for another 4 h. Then, the solution is replaced with 150 µL dimethylsulfoxide, followed by gentle agitation of the plates for 15 min at room temperature. Finally, the absorbance at 492 nm is measured to represent the cell viability. |
| Animal Admin | Seven-day-old rat pups are subjected to unilateral carotid artery ligation followed by 60 min of hypoxia (7.6% O2). Sodium Butyrate (300 mg/kg) is administered in a 5-day regime with the first injection given immediately after hypoxic exposure. The damage of the ipsilateral hemisphere is evaluated by hematoxylin-eosin staining 6 days after the insult. Samples are collected at 24 and 48 h and 6 days. |
| References |
| Density | 0.987g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 164.3ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 250-253 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C4H7NaO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 110.087 |
| Flash Point | 69.7ºC |
| Exact Mass | 110.034370 |
| PSA | 40.13000 |
| Vapour Pressure | 1.35mmHg at 25°C |
| InChIKey | MFBOGIVSZKQAPD-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
| SMILES | CCCC(=O)[O-].[Na+] |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong acids. |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATAMUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S37/39-S26-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | 2820 |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | ET6400000 |
| HS Code | 2915600000 |
|
~% 
Sodium butyrate CAS#:156-54-7
Detail
|
| Literature: Tetrahedron Asymmetry, , vol. 22, # 13 p. 1473 - 1478 |
|
~% 
Sodium butyrate CAS#:156-54-7 |
| Literature: Journal of Fluorine Chemistry, , vol. 132, # 2 p. 107 - 113 |
|
~% 
Sodium butyrate CAS#:156-54-7 |
| Literature: Journal of Fluorine Chemistry, , vol. 132, # 2 p. 107 - 113 |
|
~% 
Sodium butyrate CAS#:156-54-7 |
| Literature: Journal of the American Chemical Society, , vol. 61, p. 100 |
| Precursor 6 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2915600000 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2915600000 butanoic acids and pentanoic acids and their salts and esters VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:5.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Epigenetic reprogramming of the type III interferon response potentiates antiviral activity and suppresses tumor growth.
PLoS Biol. 12(1) , e1001758, (2014) Type III interferon (IFN-λ) exhibits potent antiviral activity similar to IFN-α/β, but in contrast to the ubiquitous expression of the IFN-α/β receptor, the IFN-λ receptor is restricted to cells of ep... |
|
|
Short-chain fatty acids and acidic pH upregulate UT-B, GPR41, and GPR4 in rumen epithelial cells of goats.
Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 308(4) , R283-93, (2015) Currently, the mechanism(s) responsible for the regulation of urea transporter B (UT-B) expression levels in the epithelium of the rumen remain unclear. We hypothesized that rumen fermentation product... |
|
|
The PHD finger of p300 influences its ability to acetylate histone and non-histone targets.
J. Mol. Biol. 426(24) , 3960-72, (2014) In enzymes that regulate chromatin structure, the combinatorial occurrence of modules that alter and recognise histone modifications is a recurrent feature. In this study, we explored the functional r... |
| MFCD00002816 |
| Butyrate sodium salt |
| Natriumbutyrat |
| Na butyrate |
| EINECS 205-857-6 |
| SODIUM BUTYRATE pure |
| NAB |
| BUTYRIC ACID NA |
| Sodium butanoate |
| SODIUM N-BUTYLATE |
| SODIUMBUTYRATE,USP |
| Sodium Butyrate |
| sodium n-butyrate |
| butyratesodium |
| butyric acid sodium salt |

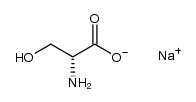
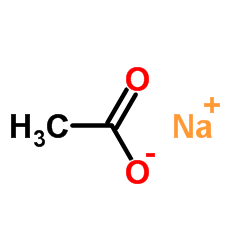
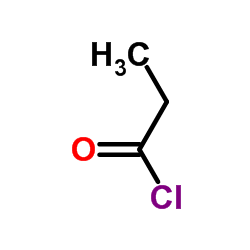
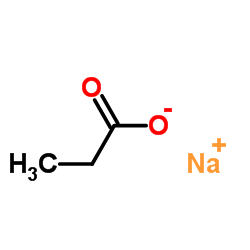



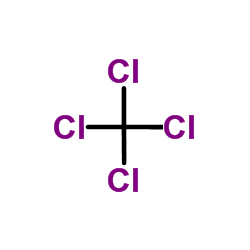

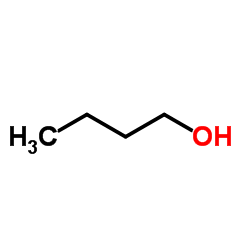
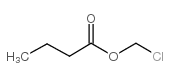 CAS#:33657-49-7
CAS#:33657-49-7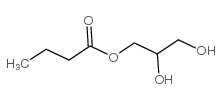 CAS#:557-25-5
CAS#:557-25-5 CAS#:504-63-2
CAS#:504-63-2 CAS#:110-54-3
CAS#:110-54-3 CAS#:64-17-5
CAS#:64-17-5 CAS#:78-83-1
CAS#:78-83-1 CAS#:141-78-6
CAS#:141-78-6 CAS#:105-54-4
CAS#:105-54-4 CAS#:123-19-3
CAS#:123-19-3
