anacardic acid
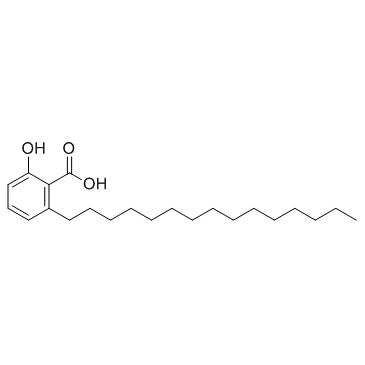
anacardic acid structure
|
Common Name | anacardic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 16611-84-0 | Molecular Weight | 348.519 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 474.8±33.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C22H36O3 | Melting Point | 90-91℃ | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 255.1±21.9 °C | |
Use of anacardic acidAnacardic Acid, extracted from cashew nut shell liquid, is a histone acetyltransferase inhibitor, inhibits HAT activity of p300 and PCAF, with IC50s of ∼8.5 μM and ∼5 μM, respectively. |
| Name | 2-hydroxy-6-pentadecylbenzoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Anacardic Acid, extracted from cashew nut shell liquid, is a histone acetyltransferase inhibitor, inhibits HAT activity of p300 and PCAF, with IC50s of ∼8.5 μM and ∼5 μM, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
p300:8.5 μM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Anacardic Acid is a histone acetyltransferase, inhibits HAT activity of p300 and PCAF, with IC50s of ∼8.5 μM and ∼5 μM, respectively[1]. Anacardic Acid (300 μM) inhibits mycelial growth. Anacardic Acid (50 μM) induces apoptosis-like characteristics in M. oryzae, and the effect is caspase independent. Anacardic Acid (1-80 μM) leads to loss of mitochondrial potential. Anacardic Acid (1-60 μM) also exhibits antioxidant activity in M. oryzae[3]. |
| In Vivo | Anacardic acid (5 mg/kg, i.p.) attenuates the binding of HATs to the promoter of MEF2A and reverse hyperacetylation of H3K9ac caused by phenylephrine in C57BL/6 mice. Anacardic acid inhibits the level of transcription on MEF2A and cardiac development-related downstream genes, attenuates the protein overexpression of cardiac downstream genes caused by phenylephrine, reverses and attenuates cardiac hypertrophy in the hearts of mice exposed to phenylephrine, and attenuates the left ventricular pressure and improves cardiac function in the cardiac hypertrophy mice[2]. |
| Kinase Assay | Briefly, indicated amounts of proteins/peptide are incubated in HAT assay buffer containing 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, 10% (v/v) glycerol, 1 mM dithiothreitol, 1 mM phenylmethyl sulfonyl fluoride, 0.1 mM EDTA, pH 8.0, 10 mM sodium butyrate at 30°C for 10 min in the presence or absence of compound followed by the addition of 1 μL of 6.2 Ci/mmol [3H]acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) and are further incubated for another 10 min. The final reaction volume is 30 μL. The reaction mixture is then blotted onto P-81 filter papers, and radioactive counts are recorded on a Wallac 1409 liquid scintillation counter. To characterize the inhibition kinetics of anacardic acid, filter binding assays are done using a constant amount of HeLa core histones in the presence or absence of AA with increasing concentrations of [3H]acetyl-CoA[1]. |
| Cell Assay | Mycelial cell death assay is performed to evaluate the number of colony-forming units in treated and untreated samples. M. oryzae conidia (106 conidia/mL) are allowed to germinate in 100-mL flasks with 20 mL complete medium broth (CM) at 28°C in a rotary shaker (200 rpm) for 12 h. The cultures are exposed to different concentrations of anacardic acid for 2 h. The germinated conidia are washed with sterile water, diluted to 104 conidia/mL, and plated on oat meal agar and incubated at 28°C for 3 days. Colony-forming units (CFUs) are counted in each of the three ndividual experiments performed, and values are plotted in the graph as average of three replicates. The data in each sample is expressed as the percentage of the total number of CFUs observed in untreated or 0.1 % DMSO treated control[3]. |
| Animal Admin | Pathogen-free male and female 11-13 week-old C57BL/6 mice (18-20 g) are randomly selected to inject phenylephrine (20 mg/kg) (control groups receive equivalent normal saline). In some cases, phenylephrine-treated C57BL/6 mice are administered with a Chinese herbal extract anacardic acid (5 mg/kg). Anacardic acid is dissolved in sterile DMSO at a concentration of 1 mg/ml and stored at 4°C. Phenylephrine is administered by a subcutaneous injection at a dose of 20 mg per kg per day continuously for 30 days. Moreover, anacardic acid is administered by an intraperitoneal injection at a dose of 5 mg/kg every 3rd day intraperitoneal injection at a dose of 5 mg/kg every 3rd day. After modeling, mice are euthanized using 20% carbon dioxide in an anesthesia chamber until they are unresponsive to nose pinch and the hearts are isolated[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 474.8±33.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 90-91℃ |
| Molecular Formula | C22H36O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 348.519 |
| Flash Point | 255.1±21.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 348.266449 |
| PSA | 57.53000 |
| LogP | 9.96 |
| Appearance of Characters | white to beige |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.515 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | DMSO: ≥20mg/mL |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 9 | |
| HS Code | 2918290000 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS: 2918290000 other carboxylic acids with phenol function but without other oxygen function, their anhydrides, halides, peroxides, peroxyacids and their derivatives Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward) VAT:17.0% MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Acetylation mediates Cx43 reduction caused by electrical stimulation.
J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 87 , 54-64, (2015) Communication between cardiomyocytes depends upon gap junctions (GJ). Previous studies have demonstrated that electrical stimulation induces GJ remodeling and modifies histone acetylase (HAT) and deac... |
|
|
Genotoxic and cytostatic effects of 6-pentadecyl salicylic anacardic acid in transformed cell lines and peripheral blood mononuclear cells.
Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 777 , 43-53, (2015) In Mexico, as in many other countries, traditional medicine is used for the treatment of several diseases. In particular, Amphipterygium adstringens infusion is used for gastritis, gastric ulcers, and... |
|
|
Ehrlichia chaffeensis exploits host SUMOylation pathways to mediate effector-host interactions and promote intracellular survival.
Infect. Immun. 82(10) , 4154-68, (2014) Ehrlichia chaffeensis is an obligately intracellular Gram-negative bacterium that selectively infects mononuclear phagocytes. We recently reported that E. chaffeensis utilizes a type 1 secretion (T1S)... |
| 2-Hydroxy-6-pentadecyl-benzoic acid |
| 2-pentadecyl-6-hydroxybenzoic acid |
| Benzoic acid, 2-hydroxy-6-pentadecyl- |
| 22:0-Anacardic acid |
| 6-(pentadecenyl)salicylic acid |
| 6-n-pentadecylsalicylic acid |
| (15:0)-Anacardic acid |
| ANACARDIC ACID |
| 6-pentadecylsalicylic acid |
| Anarcadic Acid |
| Pentadecylsalicylic acid, 6- |
| Cyclogallipharic acid |
| 2-Hydroxy-6-pentadecylbenzoic acid |
| salicylic acid, 6-pentadecyl- |
| 22:0-Anacardic acid,2-Hydroxy-6-pentadecylbenzoic acid,6-Pentadecylsalicylic acid |
 CAS#:103904-74-1
CAS#:103904-74-1 CAS#:103904-73-0
CAS#:103904-73-0 CAS#:38449-25-1
CAS#:38449-25-1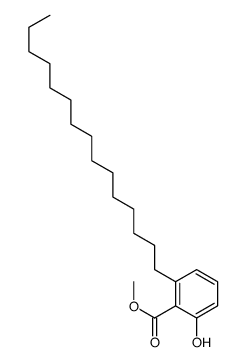 CAS#:38449-27-3
CAS#:38449-27-3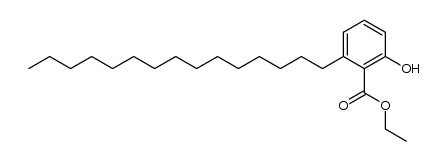 CAS#:217449-10-0
CAS#:217449-10-0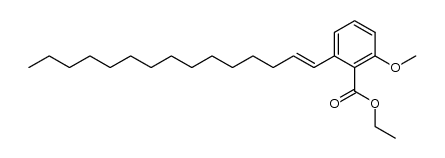 CAS#:110202-79-4
CAS#:110202-79-4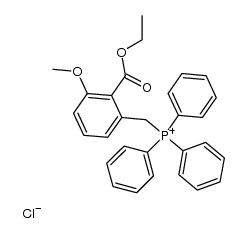 CAS#:110202-78-3
CAS#:110202-78-3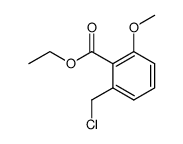 CAS#:81625-30-1
CAS#:81625-30-1 CAS#:110202-81-8
CAS#:110202-81-8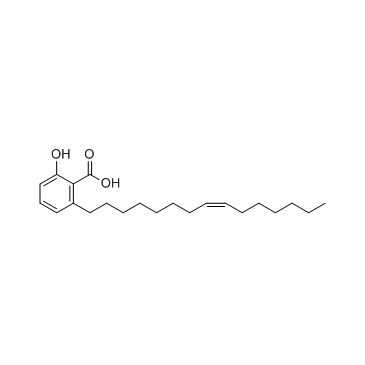 CAS#:22910-60-7
CAS#:22910-60-7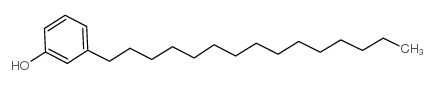 CAS#:501-24-6
CAS#:501-24-6 CAS#:35151-93-0
CAS#:35151-93-0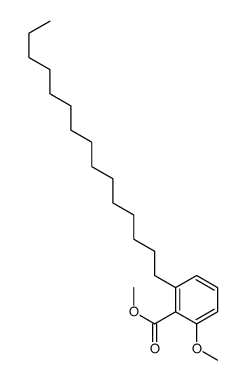 CAS#:65446-29-9
CAS#:65446-29-9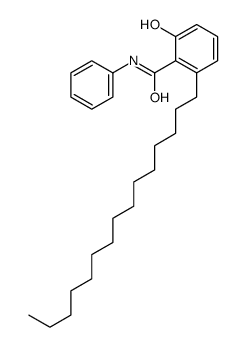 CAS#:79688-36-1
CAS#:79688-36-1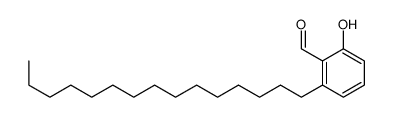 CAS#:79688-37-2
CAS#:79688-37-2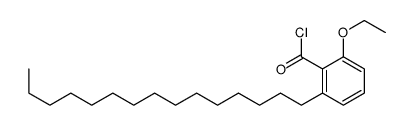 CAS#:485386-83-2
CAS#:485386-83-2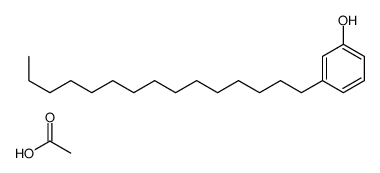 CAS#:52122-74-4
CAS#:52122-74-4
