SB 747651A dihydrochloride
Modify Date: 2025-08-25 17:45:44
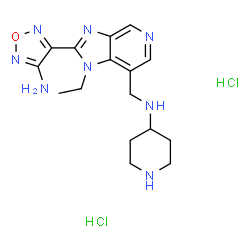
SB 747651A dihydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | SB 747651A dihydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1781882-72-1 | Molecular Weight | 415.32 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C16H24Cl2N8O | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of SB 747651A dihydrochlorideSB-747651A dihydrochloride is an ATP-competitive mitogen- and stress-activated kinase 1 (MSK1) inhibitor with an IC50 of 11 nM. SB-747651A dihydrochloride also inhibits PRK2, RSK1, p70S6K and ROCK-II. SB-747651A dihydrochloride can be used for inflammation research[1]. |
| Name | N-{[2-(4-Amino-1,2,5-oxadiazol-3-yl)-1-ethyl-1H-imidazo[4,5-c]pyridin-7-yl]methyl}-4-piperidinamine dihydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | SB-747651A dihydrochloride is an ATP-competitive mitogen- and stress-activated kinase 1 (MSK1) inhibitor with an IC50 of 11 nM. SB-747651A dihydrochloride also inhibits PRK2, RSK1, p70S6K and ROCK-II. SB-747651A dihydrochloride can be used for inflammation research[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 11 nM (MSK1)[1] |
| In Vitro | SB-747651A dihydrochloride (5 μM; neutrophils) affects CXCL2-induced intraluminal crawling of neutrophils in a Mac-1-dependent manner. SB-747651A dihydrochloride thwarts the intraluminal crawling of adherent neutrophils to optimal sites of emigration. SB-747651A dihydrochloride (5 μM; neutrophils) significantly increases transmigration time and detachment time. SB-747651A dihydrochloride affects mechanisms that regulate transendothelial migration of neutrophils in response to CXCL2 chemotactic gradient. SB-747651A dihydrochloride inhibits the migration speed of extravascular chemotaxing neutrophils but does not affect their directionality in response to CXCL2 chemotactic gradient[2]. |
| In Vivo | SB747651A (3 mg/kg; intrascrotal injection) dihydrochloride results in increased neutrophil adhesion 3.5~4.5 hours following stimulation with CXCL2 as compared to the effect of CXCL2[3]. SB-747651A (3 mg/kg; i.p.) dihydrochloride affects neutrophil extravasation by increasing neutrophil emigration only at 3 and 4 hours in mouse peritonitis model of acute inflammation[3]. Animal Model: Male C57BL/6N mice (8~16 weeks)[3] Dosage: 3 mg/kg Administration: Intrascrotal injection Result: Resulted in increased neutrophil adhesion 3.5~4.5 hours following stimulation with CXCL2 as compared to the effect of CXCL2. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C16H24Cl2N8O |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 415.32 |
| Exact Mass | 414.145020 |
| InChIKey | NRRCQHARLPNLHJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CCn1c(-c2nonc2N)nc2cncc(CNC3CCNCC3)c21.Cl.Cl |
| 1H-Imidazo[4,5-c]pyridine-7-methanamine, 2-(4-amino-1,2,5-oxadiazol-3-yl)-1-ethyl-N-4-piperidinyl-, hydrochloride (1:2) |
| N-{[2-(4-Amino-1,2,5-oxadiazol-3-yl)-1-ethyl-1H-imidazo[4,5-c]pyridin-7-yl]methyl}-4-piperidinamine dihydrochloride |