Coenzyme A Lithiumsalt
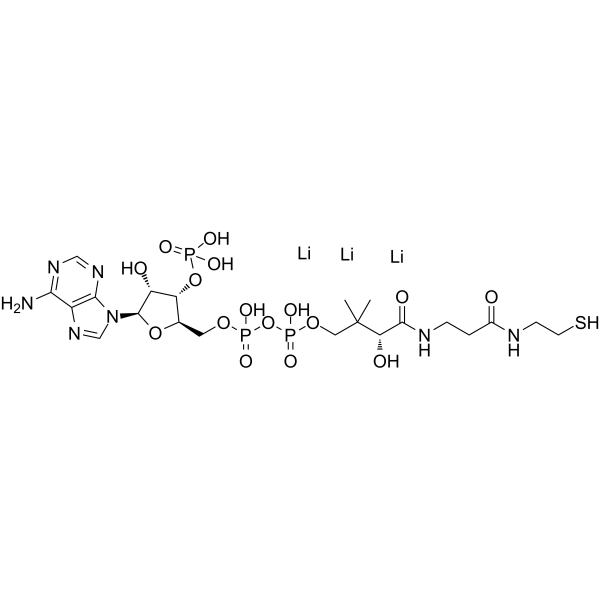
Coenzyme A Lithiumsalt structure
|
Common Name | Coenzyme A Lithiumsalt | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 18439-24-2 | Molecular Weight | 785.333 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C21H33Li3N7O16P3S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Coenzyme A LithiumsaltCoenzyme A (trilithium), a ubiquitous essential cofactor, is an acyl group carrier and carbonyl-activating group for the citric acid cycle and fatty acid metabolism. Coenzyme A (trilithium) plays a central role in the metabolism of carboxylic acids, including short- and long-chain fatty acids[1]. |
| Name | Coenzyme A Trilithium Salt |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Coenzyme A (trilithium), a ubiquitous essential cofactor, is an acyl group carrier and carbonyl-activating group for the citric acid cycle and fatty acid metabolism. Coenzyme A (trilithium) plays a central role in the metabolism of carboxylic acids, including short- and long-chain fatty acids[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
[1]. Roberta Leonardi, et al. Coenzyme A: back in action. Prog Lipid Res. 2005 Mar-May;44(2-3):125-53. |
| Molecular Formula | C21H33Li3N7O16P3S |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 785.333 |
| Exact Mass | 785.139771 |
| PSA | 423.28000 |
| LogP | 1.01230 |
| InChIKey | QSCBPHBAFBVXRK-FWPADLEJSA-K |
| SMILES | CC(C)(COP(=O)([O-])OP(=O)([O-])OCC1OC(n2cnc3c(N)ncnc32)C(O)C1OP(=O)([O-])O)C(O)C(=O)NCCC(=O)NCCS.[Li+].[Li+].[Li+] |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Safety Phrases | S22;S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
Characterization of an acyl-coA thioesterase that functions as a major regulator of peroxisomal lipid metabolism.
J. Biol. Chem. 277 , 1128-1138, (2002) Peroxisomes function in beta-oxidation of very long and long-chain fatty acids, dicarboxylic fatty acids, bile acid intermediates, prostaglandins, leukotrienes, thromboxanes, pristanic acid, and xenob... |
|
|
Central role of mitochondria in drug-induced liver injury.
Drug Metab. Rev. 44(1) , 34-87, (2011) A frequent mechanism for drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is the formation of reactive metabolites that trigger hepatitis through direct toxicity or immune reactions. Both events cause mitochondrial m... |
|
|
Hereditary and acquired diseases of acyl-coenzyme A metabolism.
Mol. Genet. Metab. 94 , 4-15, (2008) Coenzyme A (CoA) sequestration, toxicity or redistribution (CASTOR) is predicted to occur in many hereditary and acquired conditions in which the degradation of organic acyl esters of CoA is impaired.... |
| MFCD00075848 |
| COENZYME A TRILITHIUM SALT |
| Coenzyme A (lithium salt) |
| EINECS 242-317-9 |