Acotiamide hydrochloride
Modify Date: 2025-08-20 11:08:17
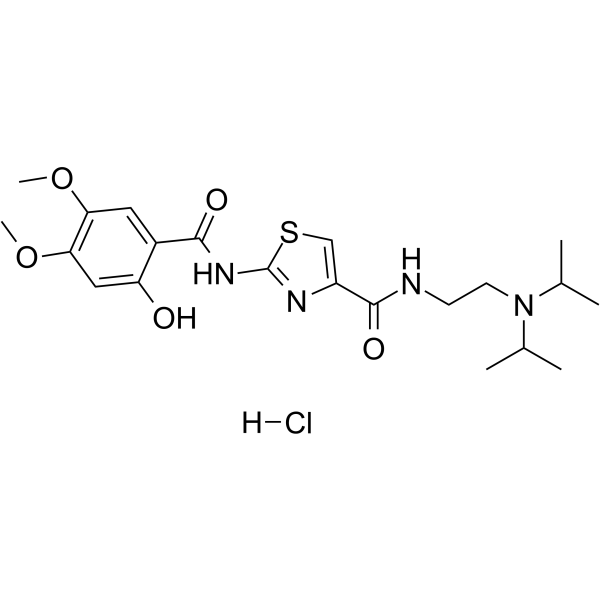
Acotiamide hydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | Acotiamide hydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 185104-11-4 | Molecular Weight | 487.013 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C21H31ClN4O5S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Acotiamide hydrochlorideAcotiamide hydrochloride is an orally active, selective and reversible acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor, with IC50 of 1.79 μM. Acotiamide hydrochloride can enhance gastric contractility and accelerate delayed gastric emptying. Acotiamide hydrochloride has the potential for the research of functional dyspepsia involving gastric motility dysfunction and intestinal inflammatory[1][2][3]. |
| Name | N-[2-[di(propan-2-yl)amino]ethyl]-2-[(2-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxybenzoyl)amino]-1,3-thiazole-4-carboxamide,hydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Acotiamide hydrochloride is an orally active, selective and reversible acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor, with IC50 of 1.79 μM. Acotiamide hydrochloride can enhance gastric contractility and accelerate delayed gastric emptying. Acotiamide hydrochloride has the potential for the research of functional dyspepsia involving gastric motility dysfunction and intestinal inflammatory[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 1.79 μM (AChE) |
| In Vitro | Acotiamide hydrochloride (10, 30, 100 μM; 1 hour) reduces expression levels of IκB-α phosphorylation in LPS- and MCP-1-stimulated macrophage cell lines[1]. Cell Viability Assay[1] Cell Line: NR8383, macrophage Concentration: 10, 30, 100 μM Incubation Time: 1 hour Result: Significantly reduced both TNF-α and IL-6 productions in LPS/MCP-1-stimulated NR8383 cells. |
| In Vivo | Acotiamide hydrochloride (0.3, 1, 3 mg/kg; i.v./3, 10, 30 mg/kg; p.o.) increases the postprandial gastric motility index in a dose-dependent manner[2]. Acotiamide hydrochloride (0.83 mg/kg; i.v.; once) inhibits AChE in rat stomach with IC50 of 1.79 μM[3]. Animal Model: Male mongrel dogs (9-11 kg), Male beagle dogs (9.6-12.9 kg)[2] Dosage: 0.3, 1, 3, 10, 30 mg/kg Administration: Intravenous injection; once. Result: Increased the postprandial gastric motility. Animal Model: Male Sprague-Dawley rats (aged 6-7 weeks)[3]. Dosage: 0.83 mg/kg Administration: Intravenous injection; once. Result: Effectively improved functional dyspepsia by inhibiting AChE in rat stomach. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C21H31ClN4O5S |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 487.013 |
| Exact Mass | 486.170380 |
| PSA | 148.24000 |
| LogP | 4.72760 |
| InChIKey | VQEKQYLTAIVCBW-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | COc1cc(O)c(C(=O)Nc2nc(C(=O)NCCN(C(C)C)C(C)C)cs2)cc1OC.Cl |
| N-[2-(Diisopropylamino)ethyl]-2-[(2-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxybenzoyl)amino]-1,3-thiazole-4-carboxamide hydrochloride (1:1) |
| Acotiamide hydrochloride |
| UNII:510791NN30 |
| Z338 |
| YM 443 |
| 4-Thiazolecarboxamide, N-[2-[bis(1-methylethyl)amino]ethyl]-2-[(2-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxybenzoyl)amino]-, hydrochloride (1:1) |

