| Description |
Sinapine is an alkaloid from seeds of the cruciferous species which shows favorable biological activities such as antioxidant and radio-protective activities.
|
| Related Catalog |
|
| Target |
P-glycoprotein[1]
|
| In Vitro |
Sinapine increases the sensitivity of Caco-2 cells to doxorubicin in a dose-dependent manner, whereas no or less effect is observed in the cells treated with doxorubicin alone. The combination of Sinapine and doxorubicin has a synergistic effect and increased the cytotoxicity of doxorubicin against Caco-2 cells. Results indicate that Sinapine plays an important role in the down-regulation of P-glycoprotein expression through suppression of FGFR4-FRS2a-ERK1/2 signaling pathway[1]. Sinapine can effectively protect against OH-induced damages to DNA and MSCs, thereby it may have a therapeutic potential in MSCs transplantation[2].
|
| In Vivo |
During the first 8 days, the dry matter intake and live weight gain of the rats are significantly reduced by the intake of sinapine and other phenolic compounds. However, after this adaptation period their performances are similar to those of the control group[3].
|
| Cell Assay |
The Caco-2 cells are seeded into a 96-well plate with 8000 cells/well for 24 h. After incubation with different doses of Sinapine (0-200 μM), doxorubicin, or both for 24 h, the medium is discarded. Cell survival after exposure to Sinapine alone or a combination of Sinapine and the anti-tumor agent doxorubicin is examined by MTT colorimetric assay[1].
|
| Animal Admin |
Rats[3] Sixty male Sprague-Dawley rats (95 g) are randomly allotted to 6 groups of 10 rats each and reared in individual cages. Six groups of 10 growing rats each are fed ad libitum for 15 days one of six diets: diet A, rapeseed (3.80 g of sinapine/kg DM); diet B, ethanol/water-extracted rapeseed (0.48 g of sinapine); diet C, control diet; diet G, control diet+3.74 g of extracted sinapine; diet H, control diet + 3.72 g of sinapine+other phenolic compounds; or diet I, control diet+the hydrolysis products of sinapine and other phenolic compounds. The rats are weighed at 8 a.m. on days 1, 4, 8, 11 and 15 of the trial. After sacrifice the gut contents are eliminated to permit determination of empty body weight gain (EBWG). The distribution, refusal and intake of each rat are recorded every day[3].
|
| References |
[1]. Guo Y, et al. Sinapine as an active compound for inhibiting the proliferation of Caco-2 cells via downregulation of P-glycoprotein. Food Chem Toxicol. 2014 May;67:187-92. [2]. Li X, et al. Protective Effect of Sinapine against Hydroxyl Radical-Induced Damage to Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Possible Mechanisms. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2016;64(4):319-25. [3]. Vermorel M, et al. Valorization of rapeseed meal. 5. Effects of sinapine and other phenolic compounds on food intake and nutrient utilization in growing rats. Reprod Nutr Dev. 1987;27(4):781-90.
|
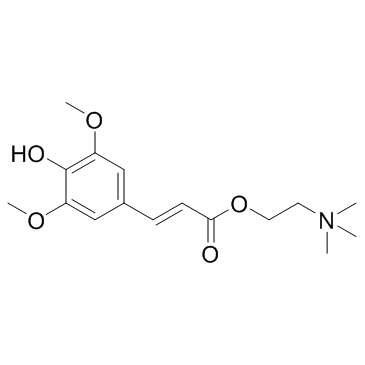
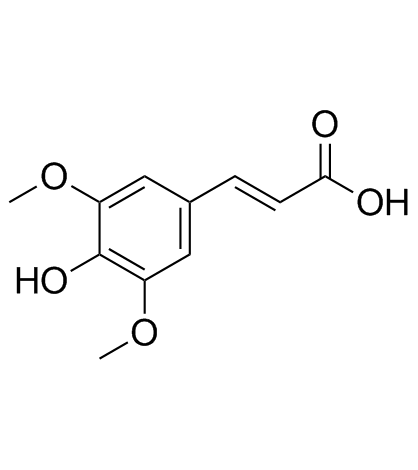 CAS#:530-59-6
CAS#:530-59-6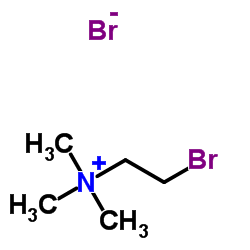 CAS#:2758-06-7
CAS#:2758-06-7
