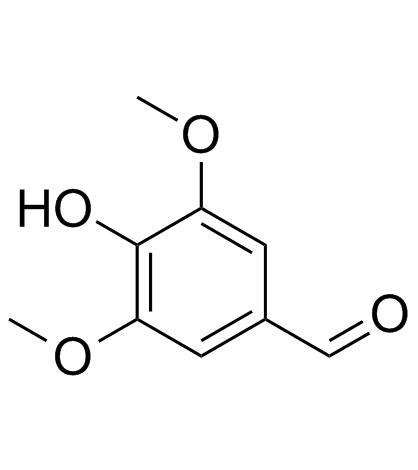
Sinapic acid
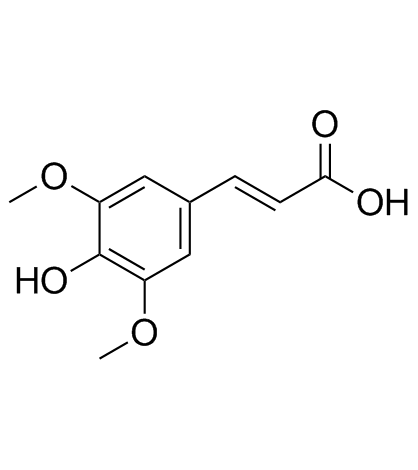
Sinapic acid structure
|
Common Name | Sinapic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 530-59-6 | Molecular Weight | 224.210 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 403.4±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C11H12O5 | Melting Point | 203-205 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 158.6±20.8 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Sinapic acidSinapinic acid (Sinapic acid) is a phenolic compound isolated from Hydnophytum formicarum Jack. Rhizome, acts as an inhibitor of HDAC, with an IC50 of 2.27 mM[1], and also inhibits ACE-I activity[2]. Sinapinic acid posssess potent anti-tumor activity, induces apoptosis of tumor cells[1]. Sinapinic acid shows antioxidant and antidiabetic activities[2]. Sinapinic acid reduces total cholesterol, triglyceride, and HOMA-IR index, and also normalizes some serum parameters of antioxidative abilities and oxidative damage in ovariectomized rats[3]. |
| Name | trans-sinapic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Sinapinic acid (Sinapic acid) is a phenolic compound isolated from Hydnophytum formicarum Jack. Rhizome, acts as an inhibitor of HDAC, with an IC50 of 2.27 mM[1], and also inhibits ACE-I activity[2]. Sinapinic acid posssess potent anti-tumor activity, induces apoptosis of tumor cells[1]. Sinapinic acid shows antioxidant and antidiabetic activities[2]. Sinapinic acid reduces total cholesterol, triglyceride, and HOMA-IR index, and also normalizes some serum parameters of antioxidative abilities and oxidative damage in ovariectomized rats[3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
HDAC:2.27 mM (IC50) ACE-I |
| In Vitro | Sinapinic acid acts as an inhibitor of HDAC, with an IC50 of 2.27 mM[1]. Sinapinic acid also inhibits ACE-I activity[2]. Sinapinic acid inhibits HDAC activity in HeLa cells, suppresses the growth of HeLa and HT29 cells with IC50s of 0.91 ± 0.02 mM and 1.6 ± 0.02 mM at 72 h, respectively, induces apoptosis of these cancer cells[1]. |
| In Vivo | Sinapinic acid (5 or 25 mg/kg, p.o. daily for 4 weeks) increases the serum estradiol concentration; decreases insulin resistance and the triglyceride and total cholesterol concentrations; and favorably affects the parameters of antioxidant abilities (reduces glutathione, superoxide dismutase) and oxidative damage in rats[3]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 403.4±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 203-205 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C11H12O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 224.210 |
| Flash Point | 158.6±20.8 °C |
| Exact Mass | 224.068466 |
| PSA | 75.99000 |
| LogP | 1.29 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.604 |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong bases. Combustible. |
| Water Solubility | insoluble |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36-S37/39 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 2918990090 |
|
~% 
Sinapic acid CAS#:530-59-6 |
| Literature: Journal of the American Chemical Society, , vol. 70, p. 57 |
|
~% 
Sinapic acid CAS#:530-59-6 |
| Literature: EP1604643 A1, ; Page/Page column 10-11 ; |
|
~72% 
Sinapic acid CAS#:530-59-6 |
| Literature: Chimichi, Stefano; Sio, Francesco De; Donati, Donato; Fina, Giuseppe; Pepino, Roberto; Sarti-Fantoni, Piero Heterocycles, 1983 , vol. 20, # 2 p. 263 - 267 |
|
~% 
Sinapic acid CAS#:530-59-6 |
| Literature: Phytochemistry (Elsevier), , vol. 12, p. 893 - 897 |
|
~% 
Sinapic acid CAS#:530-59-6 |
| Literature: Chemistry and Biodiversity, , vol. 9, # 1 p. 91 - 98 |
|
~% 
Sinapic acid CAS#:530-59-6 |
| Literature: Phytochemistry (Elsevier), , vol. 29, # 9 p. 2999 - 3001 |
|
~% 
Sinapic acid CAS#:530-59-6 |
| Literature: Heterocycles, , vol. 20, # 2 p. 263 - 267 |
|
~% 
Sinapic acid CAS#:530-59-6 |
| Literature: Journal of the Chinese Chemical Society, , vol. 56, # 6 p. 1186 - 1190 |
| HS Code | 2918990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2918990090. other carboxylic acids with additional oxygen function and their anhydrides, halides, peroxides and peroxyacids; their halogenated, sulphonated, nitrated or nitrosated derivatives. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Methionine oxidation accelerates the aggregation and enhances the neurotoxicity of the D178N variant of the human prion protein.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1842(12 Pt A) , 2345-56, (2014) The D178N mutation of the prion protein (PrP) results in the hereditary prion disease fatal familial insomnia (FFI). Little is known regarding the effects of methionine oxidation on the pathogenesis o... |
|
|
Dimethyl sulphoxide and Ca2+ stimulate assembly of Vibrio cholerae FtsZ.
Biochimie 105 , 64-75, (2014) We cloned, overexpressed and purified Vibrio cholerae FtsZ protein for the first time. We used several complementary techniques to probe and compare the comparative assembly properties of recombinant ... |
|
|
Antimicrobial activity of natural products from the flora of Northern Ontario, Canada.
Pharm. Biol. 53(6) , 800-6, (2015) The number of multidrug resistant (MDR) microorganisms is increasing and the antimicrobial resistance expressed by these pathogens is generating a rising global health crisis. In fact, there are only ... |
| 4-Hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxycinnamic acid |
| 2-Propenoic acid, 3-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-, (E)- |
| Sinapic acid |
| 3,5-Dimethoxy-4-hydroxycinnamic Acid |
| Sinapic acid, trans- |
| 3-(4-Hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)acrylic acid |
| 3 5-dimethoxy-4-hydroxycinnamic acid |
| (2E)-3-(4-Hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)acrylic acid |
| (2E)-3-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-enoic acid |
| Sinapinic acid |
| 2-propenoic acid, 3-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)- |
| 3,5-DIMETHOXY-4-HYDROXY-TRANS-CINNAMIC ACID |
| (E)-sinapic acid |
| 2-Propenoic acid, 3-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-, (2E)- |
| EINECS 208-487-3 |
| MFCD00004401 |
| trans-3,5-Dimethoxy-4-hydroxycinnamic Acid |
| trans-sinapic acid |

![3-methyl-4-nitro-5-[2-(3,5-dimethoxy-4-hydroxyphenyl)ethenyl]isoxazole structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/304/85364-71-2.png)