Diflunisal
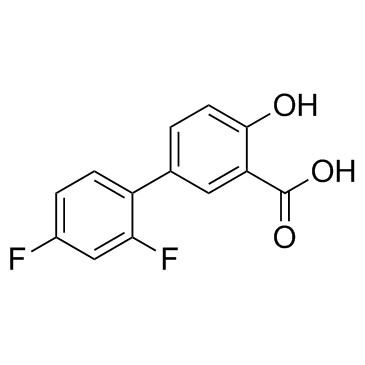
Diflunisal structure
|
Common Name | Diflunisal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 22494-42-4 | Molecular Weight | 250.198 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 386.9±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C13H8F2O3 | Melting Point | 32-36 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 187.8±27.9 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of DiflunisalDiflunisal (MK-647) is a salicylate derivative with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory and uricosuric properties, which is used alone as an analgesic and in rheumatoid arthritis patients. The mechanism of action of diflunisal is as a Cyclooxygenase (COX) Inhibitor. |
| Name | diflunisal |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Diflunisal (MK-647) is a salicylate derivative with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory and uricosuric properties, which is used alone as an analgesic and in rheumatoid arthritis patients. The mechanism of action of diflunisal is as a Cyclooxygenase (COX) Inhibitor. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
COX |
| In Vivo | Administration of increasing doses of Diflunisal to rats shows that the effect of the dose on the pharmacokinetics of Diflunisal is quite complicated. The plasma concentrations of Diflunisal decline exponentially with time, albeit with a half-life that increases with increasing dose. The CLP is reduced considerably when the dose increases from 3 to 10 mg/kg and then remains relatively constant over the dose range of 10 to 60 mg/kg. Diflunisal has been shown to be highly bound to rat plasma protein and dependent on concentration. The fraction of unbound Diflunisal is increased about 10-fold over the concentration range of 5 to 300 μg/mL[1]. Diflunisal exhibits activity after oral administration with potency about 25 times greater than that of aspirin, about 3 times that of glafenine and twice that of zomepirac[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats[1] For the study of dose dependency, Diflunisal is administered by i.a. injection in doses of 3, 10, 30 and 60 mg/kg (1.5, 5, 15 and 30 mg/mL dosing solution in 0.1 M NaHCO3). The infusion studies consist of a bolus injection of Diflunisal followed immediately by a 7-hr infusion at a constant rate. Seven groups of rats are included in the infusion studies. The loading doses used are 2, 3, 5, 10, 25, 50 and 80 mg/kg and their corresponding infusion rates are 3, 4.5, 9, 18, 36, 72 and 144 μg/min (0.576 mL/hr of seven different dosing solutions: 0.31, 0.47, 0.94, 1.88, 3.75, 7.5 and 15 mg/mL in 0.1 M NaHCO3). Blood samples are collected serially at appropriate times for the dose-dependency studies, but collected hourly for the infusion studies. Plasma is obtained immediately by centrifugation of blood samples and extracted with acetonitrile and then frozen (-20°C) until assay[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 386.9±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 32-36 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C13H8F2O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 250.198 |
| Flash Point | 187.8±27.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 250.044144 |
| PSA | 57.53000 |
| LogP | 4.44 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.601 |
| Storage condition | Refrigerator |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319-H335-H361 |
| Precautionary Statements | P280-P301 + P312 + P330-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R22;R36/37/38;R63 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S26-S36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | DV2030000 |
| HS Code | 2918290000 |
|
~93% 
Diflunisal CAS#:22494-42-4 |
| Literature: DeVasher, Rebecca B.; Moore, Lucas R.; Shaughnessy, Kevin H. Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2004 , vol. 69, # 23 p. 7919 - 7927 |
|
~% 
Diflunisal CAS#:22494-42-4 |
| Literature: US4131618 A1, ; |
|
~88% 
Diflunisal CAS#:22494-42-4 |
| Literature: Kim, Seung-Hoi; Kim, Jong-Gyu Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society, 2011 , vol. 32, # 1 p. 341 - 343 |
|
~% 
Diflunisal CAS#:22494-42-4 |
| Literature: Science (Washington, DC, United States), , vol. 337, # 6102 p. 1644 - 1648,5 |
|
~% 
Diflunisal CAS#:22494-42-4 |
| Literature: Science (Washington, DC, United States), , vol. 337, # 6102 p. 1644 - 1648,5 |
|
~% 
Diflunisal CAS#:22494-42-4 |
| Literature: Science (Washington, DC, United States), , vol. 337, # 6102 p. 1644 - 1648,5 |
|
~% 
Diflunisal CAS#:22494-42-4 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 21, p. 1093 - 1100 |
|
~% 
Diflunisal CAS#:22494-42-4 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 21, p. 1093 - 1100 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 7 | |
| HS Code | 2922299090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2922299090. other amino-naphthols and other amino-phenols, other than those containing more than one kind of oxygen function, their ethers and esters; salts thereof. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Synthesis and biological evaluation of amide derivatives of diflunisal as potential anti-tumor agents.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 19(15) , 4399-402, (2009) To discover the new medicinal activity, the structure of diflunisal has been modified. Forty amide derivatives of diflunisal were synthesized starting from diflunisal in three steps. Their inhibition ... |
|
|
Evaluation of the drug-polymer interaction in calcium alginate beads containing diflunisal.
Pharmazie 65(2) , 106-9, (2010) Calcium alginate gel beads have been developed in recent years as a unique vehicle for oral drug delivery due to their excellent biocompatibility, biodegradability, simple method of preparation, abund... |
|
|
Simultaneous determination of ezetimibe and simvastatin in pharmaceutical preparations by MEKC.
J. Chromatogr. Sci. 48(2) , 95-9, (2010) A micellar electrokinetic capillary chromatography method was developed and validated for the simultaneous determination of ezetimibe and simvastatin in pharmaceutical preparations. The influence of b... |
| Dolobil |
| Difludol |
| Dolisal |
| 2',4'-Difluoro-4-hydroxy-3-biphenylcarboxylic acid |
| Flustar |
| 4',6'-difluoro-4-hydroxybiphenyl-3-carboxylic acid |
| Dolobis |
| [1,1'-Biphenyl]-3-carboxylic acid, 2',4'-difluoro-4-hydroxy- |
| Diflunisal |
| EINECS 245-034-9 |
| Fluodonil |
| Adomal |
| [14C]-Diflunisal |
| MFCD00057834 |
| 5-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-2-hydroxybenzoic acid |
| 2-hydroxy-5-(2',4'-difluorophenyl)benzoic acid |
| Diflunisalum |
| Fluniget |
| Dolobid |
| Flovacil |
| 2',4'-difluoro-4-hydroxy-[1,1'-biphenyl]-3-carboxylic acid |
| 2',4'-Difluoro-4-hydroxybiphenyl-3-carboxylic acid |
| 5-(2,4-Difluorophenyl)salicylic acid |

![2',4'-difluoro[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl acetate structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/151/59089-67-7.png)



![5-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-2-hydroxy-N-[4-nitro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]benzamide structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/111/1058742-35-0.png) CAS#:1058742-35-0
CAS#:1058742-35-0![[4-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-2-(4-methylpiperazine-1-carbonyl)phenyl] benzoate structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/493/1095208-64-2.png) CAS#:1095208-64-2
CAS#:1095208-64-2![[2-(diethylcarbamoyl)-4-(2,4-difluorophenyl)phenyl] benzoate structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/069/1095208-40-4.png) CAS#:1095208-40-4
CAS#:1095208-40-4![[4-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-2-(phenylcarbamoyl)phenyl] benzoate structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/331/1095208-46-0.png) CAS#:1095208-46-0
CAS#:1095208-46-0![[4-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-2-(morpholine-4-carbonyl)phenyl] acetate structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/386/1186025-55-7.png) CAS#:1186025-55-7
CAS#:1186025-55-7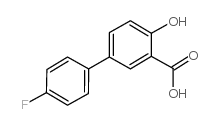 CAS#:22510-33-4
CAS#:22510-33-4![[4-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-2-(methylcarbamoyl)phenyl] acetate structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/418/950984-92-6.png) CAS#:950984-92-6
CAS#:950984-92-6
