Agmatine sulfate

Agmatine sulfate structure
|
Common Name | Agmatine sulfate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2482-00-0 | Molecular Weight | 228.270 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 281.4ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H16N4O4S | Melting Point | 234-238 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 124ºC | |
Use of Agmatine sulfateAgmatine sulfate exerts modulatory action at multiple molecular targets, such as neurotransmitter systems, ion channels and nitric oxide synthesis. It is an endogenous agonist at imidazoline receptor and a NO synthase inhibitor. |
| Name | 2-(4-aminobutyl)guanidine,sulfuric acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Agmatine sulfate exerts modulatory action at multiple molecular targets, such as neurotransmitter systems, ion channels and nitric oxide synthesis. It is an endogenous agonist at imidazoline receptor and a NO synthase inhibitor. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Agmatine binds to alpha 2-adrenergic and imidazoline receptors and stimulates release of catecholamines from adrenal chromaffin cells. Its biosynthetic enzyme, arginine decarboxylase, is present in brain. Agmatine, locally synthesized, is an endogenous agonist at imidazoline receptors, a noncatecholamine ligand at alpha 2-adrenergic receptors and may act as a neurotransmitter[1]. Agmatine is synthesized in the brain, stored in synaptic vesicles in regionally selective neurons, accumulated by uptake, released by depolarization, and inactivated by agmatinase. Agmatine inhibits nitric oxide synthase, and induces the release of some peptide hormones[2]. Agmatine, 4-(aminobutyl)guanidine, is produced by decarboxylation of L-arginine by the enzyme arginine decarboxylase. Agmatine is a competitive inhibitor of all NOS isoenzymes but not an NO precursor. Ki values are approximately 660 µM (NOS I), 220 µM (NOS II) and 7.5 mM (NOS III)[3]. Agmatine stimulates nitrite production three-fold above basal nitrite formation by endothelial cells. Agmatine displaces [3H]-idazoxan from endothelial cellmembranes and is found to induce transients in the cytosolic calcium of endothelial cells. The transients could be downregulated by repeated exposure to agmatine but are not affected by pretreatment with norepinephrine[4]. |
| In Vivo | Agmatine produces an antidepressant-like effect when assessed in the forced swimming test and in the tail suspension test in mice (dose range 0.01-50 mg/kg, i.p.), without accompanying changes in ambulation in an open-field[5]. In ischemic stroke, agmatine protects the blood-brain barrier, which can be monitored in vivo by quantification of permeability by using dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging[6]. Agmatine substantially augments the antidepressant-like effect of MK-801, reinforcing the notion that this compound modulates NMDA receptor activation[7]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats: Thirty-four male Sprague-Dawley rats are subjected to transient MCA occlusion for 90 minutes. Immediately after reperfusion, agmatine (100 mg/kg) or normal saline is injected intraperitoneally into the agmatine-treated group (n= 17) or the control group, respectively. MR imaging is performed after reperfusion[6]. Mice: Mice are pretreated with a range of sub-effective doses of either fluoxetine (1, 2.5 and 5 mg/kg, p.o.; a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor), imipramine (0.01, 0.05 and 0.1 mg/kg, p.o.; a tricyclic antidepressant), bupropion (0.1, 0.5 and 1 mg/kg, p.o.; dopamine reuptake inhibitor with subtle activity on noradrenergic reuptake), or MK-801 (0.0001, 0.0005 and 0.001 mg/kg, p.o.; noncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonist) and immediately after, a sub-effective dose of either agmatine (0.0001 mg/kg p.o.) or vehicle is administered. After 60 min, the animals are subjected to behavioral testing[7]. |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 281.4ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 234-238 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C5H16N4O4S |
| Molecular Weight | 228.270 |
| Flash Point | 124ºC |
| Exact Mass | 228.089218 |
| PSA | 170.90000 |
| LogP | 1.52760 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.00357mmHg at 25°C |
| InChIKey | PTAYFGHRDOMJGC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | NCCCCN=C(N)N.O=S(=O)(O)O |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Water Solubility | H2O: 50 mg/mL |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 2925290090 |
|
~% 
Agmatine sulfate CAS#:2482-00-0 |
| Literature: DE463576 ; Fortschr. Teerfarbenfabr. Verw. Industriezweige, vol. 16, p. 2510 |
|
~% 
Agmatine sulfate CAS#:2482-00-0 |
| Literature: DE463576 ; Fortschr. Teerfarbenfabr. Verw. Industriezweige, vol. 16, p. 2510 |
| HS Code | 2925290090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2925290090 other imines and their derivatives; salts thereof。Supervision conditions:None。VAT:17.0%。Tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:6.5%。General tariff:30.0% |
|
Interaction of myo-inositol hexakisphosphate with biogenic and synthetic polyamines.
Org. Biomol. Chem. 13 , 7500-12, (2015) Within all the eukaryotic cells myo-inositol phosphates (InsPs) are an important group of biomolecules that are potentially related to signaling functions. The most abundant member of this family in n... |
|
|
Chemical genetics reveals a complex functional ground state of neural stem cells.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 3(5) , 268-273, (2007) The identification of self-renewing and multipotent neural stem cells (NSCs) in the mammalian brain holds promise for the treatment of neurological diseases and has yielded new insight into brain canc... |
|
|
Effect of Novel Starter Culture on Reduction of Biogenic Amines, Quality Improvement, and Sensory Properties of Doenjang, a Traditional Korean Soybean Fermented Sauce Variety.
J. Food Sci. 80 , M1794-803, (2015) To select appropriate microorganisms as starter cultures for the reliable and reproducible fermentation of soybean fermented products of Korean Doenjang, various ratios of fungi (Aspergillus oryzae J,... |
| 4-Guanidinobutane sulfate |
| N-(4-Aminobutyl)guanidine sulfate |
| (4-aminobutyl)guanidinium sulphate |
| 1-(4-Aminobutyl)guanidine sulfate (1:1) |
| Agmatine sulfate |
| agmatine |
| Guanidine, N-(4-aminobutyl)-, sulfate (1:1) |
| Guanidine, (4-aminobutyl)-, sulfate (1:1) |
| 1-(4-Aminobutyl)guanidine sulfate |
| 1-Amino-4-guanidinobutane sulfate |
| 4-aminobutylguanidine sulfate |
| 1-Amino-4-guanidinobutane sulfate salt |
| MFCD00013109 |
| Prestwick_710 |
| EINECS 219-617-3 |
| (4-Aminobutyl)guanadine sulfate |
| 1-Amino-4-guanidobutane Sulfate |
| Agmatine sulphate |
| Agmatine sulfate salt |
| Agmatine (sulfate) |

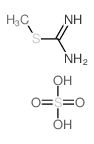
 CAS#:333-93-7
CAS#:333-93-7![N-[4-(hydrazinylmethylideneamino)butyl]prop-2-enamide structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/004/181147-64-8.png) CAS#:181147-64-8
CAS#:181147-64-8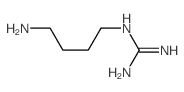 CAS#:306-60-5
CAS#:306-60-5
