Ascochlorin
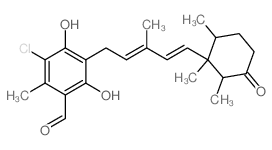
Ascochlorin structure
|
Common Name | Ascochlorin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 26166-39-2 | Molecular Weight | 404.92700 | |
| Density | 1.199g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 556.9ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C23H29ClO4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 290.6ºC | |
Use of AscochlorinAscochlorin (Ilicicolin D), an isoprenoid antibiotic, mediates its anti-tumor effects predominantly through the suppression of STAT3 signaling cascade. Ascochlorin induces apoptosis. Anti-inflammatory activity[1][2][3]. |
| Name | 5-chloro-2,4-dihydroxy-6-methyl-3-[(2E,4E)-3-methyl-5-(1,2,6-trimethyl-3-oxocyclohexyl)penta-2,4-dienyl]benzaldehyde |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Ascochlorin (Ilicicolin D), an isoprenoid antibiotic, mediates its anti-tumor effects predominantly through the suppression of STAT3 signaling cascade. Ascochlorin induces apoptosis. Anti-inflammatory activity[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
STAT3 Apoptosis |
| In Vitro | Ascochlorin (Ilicicolin D) (10-50 μM; 24-72 hours) inhibits the viability of HepG2, HCCLM3 and Huh7 cells in a time and dose dependent manner[3]. Ascochlorin (50 μM; 48 hours) induces apoptosis in HCC cells[3]. Ascochlorin (1-50 μM) significantly suppresses the production of nitric oxide (NO) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and decreases the gene expression of inducible NO synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in a dose-dependent manner. Ascochlorin inhibits the mRNA expression and the protein secretion of interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-6 but not tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. Ascochlorin suppresses nuclear translocation and DNA binding affinity of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB). Ascochlorin down-regulates phospho-extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (p-ERK1/2) and p-p38[2]. Cell Viability Assay[3] Cell Line: HepG2, HCCLM3, Huh7 cells Concentration: 10, 25, 50 μM Incubation Time: 24, 48, 72 hours Result: Inhibit the viability of three different HCC cell lines tested (HepG2, HCCLM3 and Huh7) in a time and dose dependent manner. Western Blot Analysis[3] Cell Line: HepG2 cells Concentration: 50 μM Incubation Time: 48 hours Result: Inhibited expression of the cell cycle regulator protein cyclin D1, the anti-apoptotic proteins Bcl-2, Mcl-1, survivin and XIAP, and the invasive gene product MMP-9. |
| In Vivo | Ascochlorin (Ilicicolin D) (2.5-5 mg/kg; i.p.; day 0, 1, 2, 3, 13, 15, 17, 20, 22, 24, 27, 29 and 31) inhibits tumor growth in an orthotopic HCC mouse model[1]. Animal Model: Eight week-old athymic balb/c nude female mice (HCCLM3-Luc2 tumors)[3] Dosage: 2.5 mg/kg, 5 mg/kg Administration: I.p.; day 0, 1, 2, 3, 13, 15, 17, 20, 22, 24, 27, 29 and 31 Result: Induced significant inhibition of tumor growth. |
| References |
| Density | 1.199g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 556.9ºC at 760mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C23H29ClO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 404.92700 |
| Flash Point | 290.6ºC |
| Exact Mass | 404.17500 |
| PSA | 74.60000 |
| LogP | 5.55850 |
| Vapour Pressure | 5.2E-13mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.603 |
| InChIKey | SETVRSKZJJWOPA-FLDGXQSCSA-N |
| SMILES | CC(C=CC1(C)C(C)CCC(=O)C1C)=CCc1c(O)c(Cl)c(C)c(C=O)c1O |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|
|
Silibinin suppresses PMA-induced MMP-9 expression by blocking the AP-1 activation via MAPK signaling pathways in MCF-7 human breast carcinoma cells.
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 354(1) , 165-71, (2007) Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) plays an important role in the invasion and metastasis of cancer cells. In this study, we examined the inhibitory effect of silibinin, a flavonoid antioxidant from m... |
| Ascochlorin |
| Ilicicolin D |
| ascochlorin |