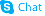Torcetrapib
Torcetrapib structure
|
Common Name | Torcetrapib | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 262352-17-0 | Molecular Weight | 600.47 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 504.8±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C26H25F9N2O4 | Melting Point | 54-58ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 259.1±30.1 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of TorcetrapibTorcetrapib(CP-529414) is a CETP inhibitor with IC50 of 37 nM, elevates HDL-C and reduces nonHDL-C in plasma.IC50 value: 37 nM [1]Target: CETP inhibitorin vitro: Torcetrapib dose-dependently increases aldosterone release from H295R cells after either 24 or 48 h of treatment with an EC50 of approximately 80 nM, this effect is mediated by calcium channel as calcium channel blockers completely blocks torcetrapib-induced corticoid release and calcium increase. Torcetrapib (1 μM) significantly increases the expression of steroidogenic gene, CYP11B2 and CYP11B1, in H295R cell lines [2].in vivo: Torcetrapib (< 100 mg, daily) changes the plasma distribution of CETP, as the apparent molecular weight of the CETP has shifted to a larger form, by 2 hours after the dose in healthy young subjects. Torcetrapib treatment with 10 mg, 30 mg, 60 mg, and 120 mg daily and 120 mg twice daily results in 16%, 28%, 62%, 73%, and 91% increases in plasma HDL-C, respectively, with no significant changes in TPC in healthy young subjects. [1] Torcetrapib results in an increase of 72.1% in high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and a decrease of 24.9% in low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, in addition to an increase of 5.4 mm Hg in systolic blood pressure, a decrease in serum potassium, and increases in serum sodium, bicarbonate, and aldosterone, in patients at high cardiovascular risk after 12 months' treatment [3]. Torcetrapib (90 mg/kg/day) results in a 70% inhibition of CE transfer in rabbits fed an atherogenic diet. Torcetrapib (90 mg/kg/day) increases mean HDL-C levels by above 3-fold and apoA-I levels by 2.5-fold in plasma in rabbits fed an atherogenic diet. Torcetrapib-treated animal has a multiple-fold increase in HDL-C AUC and a corresponding reduction in aortic lesion area with 60% reduction of aortic free cholesterol (FC) and cholesteryl ester (EC) in rabbits fed an atherogenic diet. Torcetrapib-treated rabbits stimulate free cholesterol efflux to a significantly greater extent than does sera from control rabbits [4]. |
| Name | torcetrapib |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Torcetrapib(CP-529414) is a CETP inhibitor with IC50 of 37 nM, elevates HDL-C and reduces nonHDL-C in plasma.IC50 value: 37 nM [1]Target: CETP inhibitorin vitro: Torcetrapib dose-dependently increases aldosterone release from H295R cells after either 24 or 48 h of treatment with an EC50 of approximately 80 nM, this effect is mediated by calcium channel as calcium channel blockers completely blocks torcetrapib-induced corticoid release and calcium increase. Torcetrapib (1 μM) significantly increases the expression of steroidogenic gene, CYP11B2 and CYP11B1, in H295R cell lines [2].in vivo: Torcetrapib (< 100 mg, daily) changes the plasma distribution of CETP, as the apparent molecular weight of the CETP has shifted to a larger form, by 2 hours after the dose in healthy young subjects. Torcetrapib treatment with 10 mg, 30 mg, 60 mg, and 120 mg daily and 120 mg twice daily results in 16%, 28%, 62%, 73%, and 91% increases in plasma HDL-C, respectively, with no significant changes in TPC in healthy young subjects. [1] Torcetrapib results in an increase of 72.1% in high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and a decrease of 24.9% in low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, in addition to an increase of 5.4 mm Hg in systolic blood pressure, a decrease in serum potassium, and increases in serum sodium, bicarbonate, and aldosterone, in patients at high cardiovascular risk after 12 months' treatment [3]. Torcetrapib (90 mg/kg/day) results in a 70% inhibition of CE transfer in rabbits fed an atherogenic diet. Torcetrapib (90 mg/kg/day) increases mean HDL-C levels by above 3-fold and apoA-I levels by 2.5-fold in plasma in rabbits fed an atherogenic diet. Torcetrapib-treated animal has a multiple-fold increase in HDL-C AUC and a corresponding reduction in aortic lesion area with 60% reduction of aortic free cholesterol (FC) and cholesteryl ester (EC) in rabbits fed an atherogenic diet. Torcetrapib-treated rabbits stimulate free cholesterol efflux to a significantly greater extent than does sera from control rabbits [4]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 504.8±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 54-58ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C26H25F9N2O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 600.47 |
| Flash Point | 259.1±30.1 °C |
| PSA | 59.08000 |
| LogP | 7.76 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.512 |
| Storage condition | Store at RT |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
|
Cholesteryl ester-transfer protein inhibitors stimulate aldosterone biosynthesis in adipocytes through Nox-dependent processes.
J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 353(1) , 27-34, (2015) Hyperaldosteronism and hypertension were unexpected side effects observed in trials of torcetrapib, a cholesteryl ester-transfer protein (CETP) inhibitor that increases high-density lipoprotein. Given... |
|
|
Effect on cardiovascular risk of high density lipoprotein targeted drug treatments niacin, fibrates, and CETP inhibitors: meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials including 117,411 patients.
BMJ 349 , g4379, (2014) To investigate the effects on cardiovascular outcomes of drug interventions that increase high density lipoprotein levels.Meta-analysis.Therapeutic benefit of niacin, fibrates, and cholesteryl ester t... |
|
|
Identification of a novel, non-tetrahydroquinoline variant of the cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) inhibitor torcetrapib, with improved aqueous solubility.
Xenobiotica 44(7) , 591-605, (2014) 1. Elaborate studies of cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) polymorphisms and genetic deficiency in humans suggest direct links between CETP, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-c) levels ... |
| 1(2H)-Quinolinecarboxylic acid, 4-[[[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]methyl](methoxycarbonyl)amino]-2-ethyl-3,4-dihydro-6-(trifluoromethyl)-, ethyl ester, (2R,4S)- |
| Torcetrapib |
| Ethyl (2R,4S)-4-{[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzyl](methoxycarbonyl)amino}-2-ethyl-6-(trifluoromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-1(2H)-quinolinecarboxylate |
| MFCD08063631 |
| Ethyl (2R,4S)-4-{[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzyl](methoxycarbonyl)amino}-2-ethyl-6-(trifluoromethyl)-3,4-dihydroquinoline-1(2H)-carboxylate |
| ethyl (2R,4S)-4-[[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]methyl-methoxycarbonylamino]-2-ethyl-6-(trifluoromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-quinoline-1-carboxylate |
 CAS#:474645-94-8
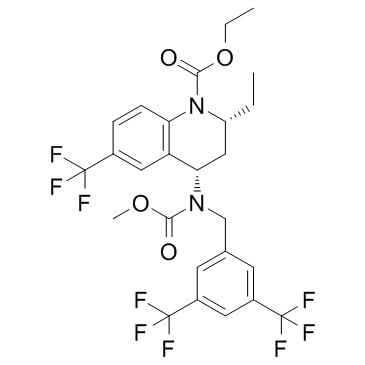
CAS#:474645-94-8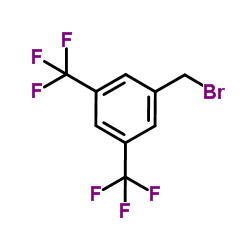 CAS#:32247-96-4
CAS#:32247-96-4 CAS#:455-14-1
CAS#:455-14-1![(3R)-[3-(4-trifluoromethylphenylamino)pentanoyl]carbamic acid methyl ester Structure](https://www.chemsrc.com/caspic/365/474645-92-6.png) CAS#:474645-92-6
CAS#:474645-92-6![methyl N-[2-ethyl-6-(trifluoromethyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinolin-4-yl]carbamate Structure](https://www.chemsrc.com/caspic/327/474645-93-7.png) CAS#:474645-93-7
CAS#:474645-93-7 CAS#:343798-02-7
CAS#:343798-02-7 CAS#:400090-60-0
CAS#:400090-60-0![Carbamic acid, [(1R)-1-(cyanomethyl)propyl]-, 1,1-dimethylethyl ester (9CI) Structure](https://www.chemsrc.com/caspic/242/198493-28-6.png) CAS#:198493-28-6
CAS#:198493-28-6 CAS#:474645-97-1
CAS#:474645-97-1