5-Bromovanillin
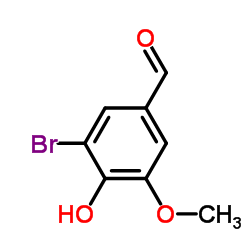
5-Bromovanillin structure
|
Common Name | 5-Bromovanillin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2973-76-4 | Molecular Weight | 231.043 | |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 289.5±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H7BrO3 | Melting Point | 164-166 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 128.9±25.9 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
| Name | 5-Bromovanillin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 289.5±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 164-166 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C8H7BrO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 231.043 |
| Flash Point | 128.9±25.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 229.957855 |
| PSA | 46.53000 |
| LogP | 2.40 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.623 |
| InChIKey | KLSHZDPXXKAHIJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | COc1cc(C=O)cc(Br)c1O |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S37/39-S36/37/39-S22-S24/25-S20/21 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 2913000090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2913000090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS: 2913000090 halogenated, sulphonated, nitrated or nitrosated derivatives of products of heading 2912 Educational tariff:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Regulatory conditions:none Most favored nation tariff:5.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Dechlorination of chlorocatechols by stable enrichment cultures of anaerobic bacteria.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 57(1) , 77-84, (1991) Metabolically stable anaerobic cultures obtained by enrichment with 5-bromovanillin, 5-chlorovanillin, catechin, and phloroglucinol were used to study dechlorination of chlorocatechols. A high degree ... |
|
|
Enzymatic release of halogens or methanol from some substituted protocatechuic acids.
J. Bacteriol. 162(2) , 693-7, (1985) Four strains of gram-negative bacteria capable of growing at the expense of 5-chlorovanillate were isolated from soil, and the metabolism of one strain was studied in particular detail. In the presenc... |
|
|
Hydroxylation reaction catalyzed by the Burkholderia cepacia AC1100 bacterial strain. Involvement of the chlorophenol-4-monooxygenase.
Eur. J. Biochem. 261(2) , 533-9, (1999) The Burkholderia cepacia AC1100 strain, known to degrade the herbicide, 2,4,5-Trichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4,5-T), is able to metabolize 4-hydroxyarylaldehyde, not only into the corresponding acid, ... |
| 5-Bromo-4-Hydroxy-3-Methoxybenzaldehyde |
| 3-methoxy-4-hydroxy-5-bromo-benzaldehyde |
| EINECS 221-016-6 |
| 3-Bromo-4-hydroxy-5-methoxybenzaldehyde |
| 3-bromo4-hydroxy-5-methoxy-benzaldehyde |
| 5-Bromovanillin |
| 5-bromovanilin |
| VHR DQ CE EO1 |
| 3-BROMO-4-HYDROXY-5-METHOXY-BENZALDEHYDE |
| 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxy bromobenzaldehyde |
| Benzaldehyde, 3-bromo-4-hydroxy-5-methoxy- |
| Bromovanillin |
| Vanillin, 5-bromo- |
| MFCD00006940 |
 CAS#:121-33-5
CAS#:121-33-5 CAS#:71119-08-9
CAS#:71119-08-9 CAS#:108-20-3
CAS#:108-20-3 CAS#:881-68-5
CAS#:881-68-5 CAS#:2556-04-9
CAS#:2556-04-9 CAS#:2426-87-1
CAS#:2426-87-1![4-[tert-butyl(dimethyl)silyl]oxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/266/69404-94-0.png) CAS#:69404-94-0
CAS#:69404-94-0 CAS#:2316-61-2
CAS#:2316-61-2 CAS#:458-35-5
CAS#:458-35-5 CAS#:110642-42-7
CAS#:110642-42-7 CAS#:400070-31-7
CAS#:400070-31-7 CAS#:5424-43-1
CAS#:5424-43-1 CAS#:3934-87-0
CAS#:3934-87-0 CAS#:52805-45-5
CAS#:52805-45-5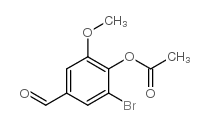 CAS#:308088-29-1
CAS#:308088-29-1 CAS#:91335-52-3
CAS#:91335-52-3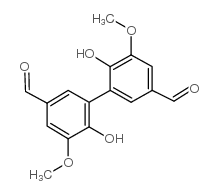 CAS#:2092-49-1
CAS#:2092-49-1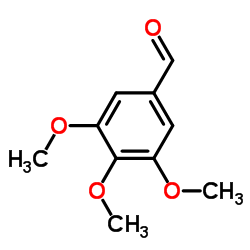 CAS#:86-81-7
CAS#:86-81-7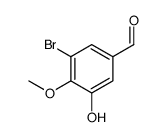 CAS#:23354-30-5
CAS#:23354-30-5
