Carnosic acid
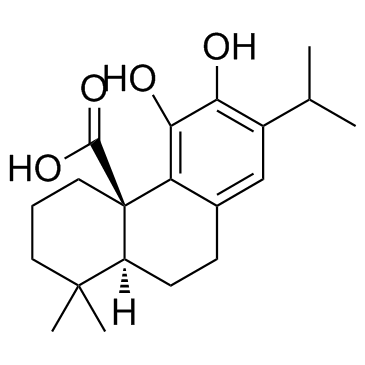
Carnosic acid structure
|
Common Name | Carnosic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 3650-09-7 | Molecular Weight | 332.434 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 506.4±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H28O4 | Melting Point | 190 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 274.2±26.6 °C | |
Use of Carnosic acidCarnosic acid has demonstrated inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation, suppression of cell proliferation, and antibacterial activity. |
| Name | carnosic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Carnosic acid has demonstrated inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation, suppression of cell proliferation, and antibacterial activity. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Carnosic acid, a phenolic diterpene, is enriched in the leaves of Lamiaceae plants, and is particularly high in dried leaves of Rosmarinus officinalis L. and Salvia officinalis. Carnosic acid has demonstrated inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation, suppression of cell proliferation, and antibacterial activity. It is widely reported that Carnosic acid has a therapeutic potential in different types of cancer, mostly based on in vitro experiments. Carnosic acid has also shown neuroprotective effects in experimental models of neurodegenerative diseases, mainly through activation of the antioxidant NRF2/ARE pathway[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 506.4±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 190 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C20H28O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 332.434 |
| Flash Point | 274.2±26.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 332.198761 |
| PSA | 77.76000 |
| LogP | 4.93 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.576 |
| InChIKey | QRYRORQUOLYVBU-VBKZILBWSA-N |
| SMILES | CC(C)c1cc2c(c(O)c1O)C1(C(=O)O)CCCC(C)(C)C1CC2 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
~70% 
Carnosic acid CAS#:3650-09-7 |
| Literature: Tada, Masahiro; Ohkanda, Tomoyuki; Kurabe, Jun Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 2010 , vol. 58, # 1 p. 27 - 29 |
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 3 | |
|
Redox-dependent induction of antioxidant defenses by phenolic diterpenes confers stress tolerance in normal human skin fibroblasts: Insights on replicative senescence.
Free Radic. Biol. Med. 83 , 262-72, (2015) Mild stress-induced hormesis represents a promising strategy for targeting the age-related accumulation of molecular damage and, therefore, for preventing diseases and achieving healthy aging. Fruits,... |
|
|
Carnosol Is a Potent Lung Protective Agent: Experimental Study on Mice.
Transplant. Proc. 47 , 1657-61, (2015) Oxidative stress has been implicated in various disease states and ischemia/reperfusion injury is a direct consequence of oxidative stress in lung transplantation. Because the success rate of organ tr... |
|
|
Enhanced Eryptosis Following Exposure to Carnosic Acid.
Cell Physiol. Biochem. 37 , 1779-91, (2015) The phenolic abietane diterpene component of rosemary and sage, carnosic acid, may either induce or inhibit apoptosis of nucleated cells. The mechanisms involved in the effects of carnosic acid includ... |
| Salvin |
| 4a(2H)-Phenanthrenecarboxylic acid, 1,3,4,9,10,10a-hexahydro-5,6-dihydroxy-1,1-dimethyl-7-(1-methylethyl)-, (4aR,10aS)- |
| Carnosic acid |
| RoseOx |
| 11,12-Dihydroxyabieta-8,11,13-trien-20-oic acid |
| Carnosic acid |
| (4aR,10aS)-5,6-dihydroxy-1,1-dimethyl-7-propan-2-yl-2,3,4,9,10,10a-hexahydrophenanthrene-4a-carboxylic acid |
| MFCD02259459 |
| Carsonic acid |
| Carnosolic Acid |
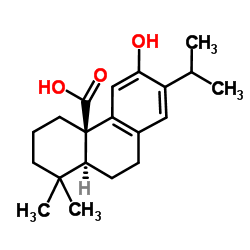
 CAS#:5957-80-2
CAS#:5957-80-2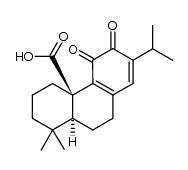 CAS#:380429-82-3
CAS#:380429-82-3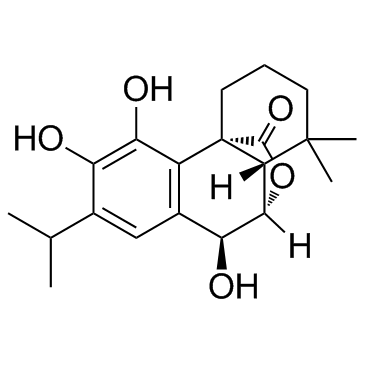 CAS#:80225-53-2
CAS#:80225-53-2
