Dovitinib (TKI-258, CHIR-258)
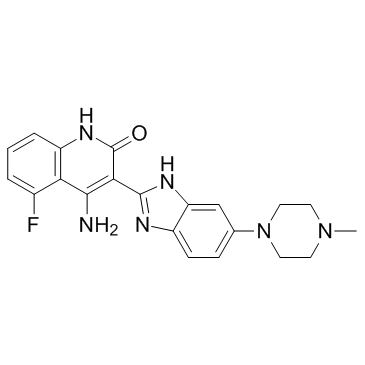
Dovitinib (TKI-258, CHIR-258) structure
|
Common Name | Dovitinib (TKI-258, CHIR-258) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 405169-16-6 | Molecular Weight | 392.429 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C21H21FN6O | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Dovitinib (TKI-258, CHIR-258)Dovitinib is a multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor with IC50s of 1, 2, 8/9, 10/13/8, 27/210 nM for FLT3, c-Kit, FGFR1/3, VEGFR1/2/3 and PDGFRα/β, respectively. |
| Name | 4-Amino-5-fluoro-3-[5-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl]quinolin-2(1H)-one |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Dovitinib is a multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor with IC50s of 1, 2, 8/9, 10/13/8, 27/210 nM for FLT3, c-Kit, FGFR1/3, VEGFR1/2/3 and PDGFRα/β, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
FGFR1:8 nM (IC50) FGFR3:9 nM (IC50) VEGFR1:1 nM (IC50) VEGFR2:13 nM (IC50) VEGFR3:8 nM (IC50) PDGFRα:27 nM (IC50) PDGFRβ:210 nM (IC50) FLT3:1 nM (IC50) c-Kit:2 nM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Dovitinib potently inhibits the FGF-stimulated growth of WT and F384L-FGFR3-expressing B9 cells with IC50 values of 25 nM. B9-MINV cells are resistant to the inhibitory activity of Dovitinib at concentrations up to 1 μM. Dovitinib inhibits cell proliferation of KMS11 (FGFR3-Y373C), OPM2 (FGFR3-K650E), and KMS18 (FGFR3-G384D) cells with IC50 of values of 90 nM (KMS11 and OPM2) and 550 nM, respectively[1]. Dovitinib significantly reduces the basal phosphorylation levels of FGFR-1, FGFR substrate 2α (FRS2-α) and ERK1/2 but not Akt in both SK-HEP1 and 21-0208 cells[2]. Dovitinib enhances the BMP-2-induced alkaline phosphatase (ALP) induction, which is a representative marker of osteoblast differentiation. Dovitinib also stimulates the translocation of phosphorylated Smad1/5/8 into the nucleus and phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinases, including ERK1/2 and p38[3]. Dovitinib strongly inhibits both the interaction of TNIK with ATP (Ki, 13 nM) and the activation of Wnt signaling effectors such as β-catenin and TCF4. Dovitinib also induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in IM-9 cells without significant cytotoxicity in PBMCs[4]. |
| In Vivo | Dovitinib (10 mg/kg, 30 mg/kg, 60 mg/kg, p.o.) shows significant antitumor effect in the KMS11-bearing mice model, and the growth inhibition is 48%, 78.5%, and 94% in the 10 mg/kg, 30 mg/kg, and 60 mg/kg treatment arms, respectively, compared with the placebo-treated mice[1]. Dovitinib (50 and 75 mg/kg) results in 97% and 98% tumor growth inhibition, respectively, and the maximal efficacy is at 50 mg/kg[2]. |
| Kinase Assay | The inhibitory concentration of 50% (IC50) values for the inhibition of RTKs by Dovitinib are determined in a time-resolved fluorescence (TRF) or radioactive format, measuring the inhibition by Dovitinib of phosphate transfer to a substrate by the respective enzyme. The kinase domains of FGFR3, FGFR1, PDGFR-β, and VEGFR1-3 are assayed in 50 mM HEPES (N-2-hydroxyethylpiperazine-N′-2-ethanesulfonic acid), pH 7.0, 2 mM MgCl2, 10 mM MnCl2 1 mM NaF, 1 mM dithiothreitol (DTT), 1 mg/mL bovine serum albumin (BSA), 0.25 μM biotinylated peptide substrate (GGGGQDGKDYIVLPI), and 1 to 30 μM adenosine triphosphate (ATP) depending on the Km for the respective enzyme. ATP concentrations are at or just below Km. For c-KIT and FLT3 reactions the pH is raised to 7.5 with 0.2 to 8 μM ATP in the presence of 0.25 to 1 μM biotinylated peptide substrate (GGLFDDPSYVNVQNL). Reactions are incubated at room temperature for 1 to 4 hours and the phosphorylated peptide captured on streptavidin-coated microtiter plates containing stop reaction buffer (25 mM EDTA [ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid], 50 mM HEPES, pH 7.5). Phosphorylated peptide is measured with the DELFIA TRF system using a Europium-labeled antiphosphotyrosine antibody PT66. The concentration of Dovitinib for IC50 is calculated using nonlinear regression with XL-Fit data analysis software version 4.1. Inhibition of colony-stimulating factor-1 receptor (CSF-1R), PDGFR-α, insulin receptor (InsR), and insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 (IGFR1) kinase activity is determined using the IC50 Profiler Express service. |
| Cell Assay | Cell viability is assessed by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium (MTT) dye absorbance according to the manufacturer's instructions. Cells are seeded in 96-well plates at a density of 5000 (B9 cells) or 20 000 (MM cell lines) cells per well. Cells are incubated with 30 ng/mL aFGF and 100 μg/mL heparin or 1% IL-6 where indicated and increasing concentrations of Dovitinib. For each concentration of Dovitinib, 10-μL aliquots of drug or DMSO diluted in culture medium is added. For drug combination studies, cells are incubated with 0.5 μM dexamethasone, 100 nM Dovitinib, or both simultaneously where indicated. To evaluate the effect of Dovitinib on growth of MM cells adherent to BMSCs, 10 000 KMS11 cells are cultured on BMSC-coated 96-well plates in the presence or absence of Dovitinib. Plates are incubated for 48 to 96 hours. For assessment of macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF)-mediated growth, 5000 M-NFS-60 cells/well are incubated with serial dilutions of CHIR-25 ZS8 with 10 ng/mL M-CSF and without granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF). After 72 hours cell viability is determined using Cell Titer-Glo Assay. Each experimental condition is performed in triplicate. |
| Animal Admin | The xenograft mouse model is prepared as previously described.27 Briefly, 6- to 8-week-old female BNX mice are inoculated subcutaneously into the right flank with 3×107 KMS11 cells in 150 μL IMDM, together with 150 μL Matrigel basement membrane matrix. Treatment is initiated when tumors reach volumes of 200 mm3 at which time mice are randomized to receive 10, 30, or 60 mg/kg Dovitinib or 5 mM citrate buffer. Dosing is performed daily for 21 days by gavage. Eight to 10 mice are included in each treatment group. Caliper measurements are performed twice weekly to estimate tumor volume, using the formula: 4π/3 × (width/2)2 × (length/2). One-way analysis of variance is used to compare differences between vehicle- and Dovitinib-treated groups. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H21FN6O |
| Molecular Weight | 392.429 |
| Exact Mass | 392.176086 |
| PSA | 94.04000 |
| LogP | 1.59 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.691 |
| InChIKey | PIQCTGMSNWUMAF-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CN1CCN(c2ccc3nc(-c4c(N)c5c(F)cccc5[nH]c4=O)[nH]c3c2)CC1 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
| 4-amino-5-fluoro-3-[6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl]quinolin-2(1H)-one |
| 2(1H)-Quinolinone, 4-amino-5-fluoro-3-[6-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl]- |
| Dovitinib |
| 4-Amino-5-fluoro-3-[5-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl]quinolin-2(1H)-one |
| 4-Amino-5-fluor-3-[5-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl]chinolin-2(1H)-on |
| Dovitinib (TKI-258,CHIR-258) |
| 4-amino-5-fluoro-3-[6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl]-1H-quinolin-2-one |
| Unii-I35H55G906 |
| Dovitinib (TKI-258, CHIR-258) |
| CHIR-258 |
| 4-amino-5-fluoro-3-(5-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)quinolin-2(1H)-one |
| 4-amino-5-fluoro-3-[6-(4-methyl-piperazin-1-yl)-1H-benzoimidazol-2-yl]-1H-quinolin-2-one |
| 4-Amino-5-fluoro-3-[5-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl]-2(1H)-quinolinone |
| 4-amino-5-fluoro-3-(5-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)quinolin-2(1H)-one |
| TKI-258 |
| CHIR-258(Dovitinib,TKI258) |
| Dovitinib (TKI-258) |
| CHIR258 7.7G |
| CHIR-258(Dovitinib) |
![Ethyl 2-(5-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)acetate Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/247/402948-37-2.png) CAS#:402948-37-2
CAS#:402948-37-2 CAS#:77326-36-4
CAS#:77326-36-4 CAS#:109-01-3
CAS#:109-01-3 CAS#:1635-61-6
CAS#:1635-61-6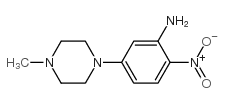 CAS#:23491-48-7
CAS#:23491-48-7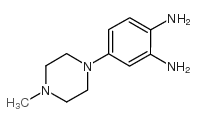 CAS#:54998-08-2
CAS#:54998-08-2