Niflumic acid
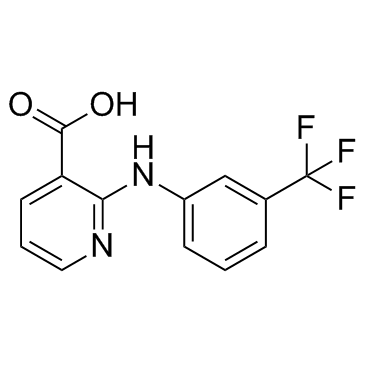
Niflumic acid structure
|
Common Name | Niflumic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 4394-00-7 | Molecular Weight | 282.218 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 378.0±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C13H9F3N2O2 | Melting Point | 203-204ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 182.4±27.9 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Niflumic acidNiflumic acid, a Ca2+-activated Cl- channel blocker, is an analgesic and anti-inflammatory agent used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.Target: Othersniflumic acid, an inhibitor of calcium-activated chloride currents. Niflumic acid does not block directly calcium channels or activate potassium channels. Niflumic acid selectively reduces a component of noradrenaline- and 5-HT-induced pressor responses by inhibiting a mechanism which leads to the opening of voltage-gated calcium channels [1]. Niflumic acid molecule is completely buried in the substrate-binding hydrophobic channel. The conformations of the binding site in PLA(2) as well as that of niflumic acid are not altered upon binding [2]. Niflumic acid (NFA) produces biphasic behavior on human CLC-K channels that suggests the presence of two functionally different binding sites: an activating site and a blocking site [3]. |
| Name | Niflumic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Niflumic acid, a Ca2+-activated Cl- channel blocker, is an analgesic and anti-inflammatory agent used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.Target: Othersniflumic acid, an inhibitor of calcium-activated chloride currents. Niflumic acid does not block directly calcium channels or activate potassium channels. Niflumic acid selectively reduces a component of noradrenaline- and 5-HT-induced pressor responses by inhibiting a mechanism which leads to the opening of voltage-gated calcium channels [1]. Niflumic acid molecule is completely buried in the substrate-binding hydrophobic channel. The conformations of the binding site in PLA(2) as well as that of niflumic acid are not altered upon binding [2]. Niflumic acid (NFA) produces biphasic behavior on human CLC-K channels that suggests the presence of two functionally different binding sites: an activating site and a blocking site [3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 378.0±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 203-204ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C13H9F3N2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 282.218 |
| Flash Point | 182.4±27.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 282.061615 |
| PSA | 62.22000 |
| LogP | 4.94 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.589 |
| InChIKey | JZFPYUNJRRFVQU-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=C(O)c1cccnc1Nc1cccc(C(F)(F)F)c1 |
| Storage condition | Store at RT |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in ethanol (~50 mg/ml), acetone (50 mg/ml, Clear to Slightly Hazy, Yellow), methanol (~50 mg/ml), DMSO (56 mg/ml at 25°C), and acetonitrile (~50 mg/ml). |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 + H312 + H332-H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P280-P301 + P312 + P330-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R20/21/22;R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36/37/39 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | QT2999100 |
| Packaging Group | Ⅲ |
| HS Code | 2933399090 |
| HS Code | 2933399090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933399090. other compounds containing an unfused pyridine ring (whether or not hydrogenated) in the structure. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
An orphan esterase ABHD10 modulates probenecid acyl glucuronidation in human liver.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 42(12) , 2109-16, (2014) Probenecid, a widely used uricosuric agent, is mainly metabolized to probenecid acyl glucuronide (PRAG), which is considered a causal substance of severe allergic or anaphylactoid reactions. PRAG can ... |
|
|
Role of anoctamin-1 and bestrophin-1 in spinal nerve ligation-induced neuropathic pain in rats.
Mol. Pain 11 , 41, (2015) Calcium-activated chloride channels (CaCCs) activation induces membrane depolarization by increasing chloride efflux in primary sensory neurons that can facilitate action potential generation. Previou... |
|
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental... |
| EINECS 224-516-2 |
| MFCD00010569 |
| 2-(3-Trifluoromethyl-phenylamino)-; nicotinic acid |
| 3-Pyridinecarboxylic acid, 2-[[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]amino]- |
| Niflumic acid |
| 2-(a,a,a-Trifluoro-m-toluidino)nicotinic Acid |
| 2-{[3-(Trifluoromethyl)phenyl]amino}nicotinic acid |
| 2-[[3-(Trifluoromethyl)phenyl]amino]-3-pyridinecarboxylic Acid |
| 2-(3-TrifluoroMethylanilino)nicotinic Acid |
| 2-((3-(Trifluoromethyl)phenyl)amino)nicotinic acid |
| 2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)anilino]pyridine-3-carboxylic acid |
| 2-[(3-Trifluoromethylphenyl)amino]nicotinic Acid |
 CAS#:2942-59-8
CAS#:2942-59-8 CAS#:98-16-8
CAS#:98-16-8![1-(3'-trifluoromethylphenyl)-2-methyl-4H-1,2-dihydro-pyrido-[2,3-d]-[1,3]-oxazin-4-one Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/495/137488-50-7.png) CAS#:137488-50-7
CAS#:137488-50-7![1-(3'-trifluoromethylphenyl)-2-chloromethyl-4H-1,2-dihydro-pyrido-[2,3-d]-[1,3]-oxazin-4-one Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/350/137488-49-4.png) CAS#:137488-49-4
CAS#:137488-49-4![1-(3'-trifluoromethylphenyl)-2-ethoxy-4H-1,2-dihydro-pyrido-[2,3-d]-[1,3]-oxazin-4-one Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/388/137488-48-3.png) CAS#:137488-48-3
CAS#:137488-48-3 CAS#:735318-84-0
CAS#:735318-84-0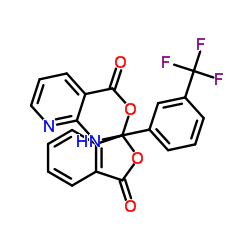 CAS#:66898-62-2
CAS#:66898-62-2![2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)anilino]pyridine-3-carbonyl chloride structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/307/70458-49-0.png) CAS#:70458-49-0
CAS#:70458-49-0
