Ribitol
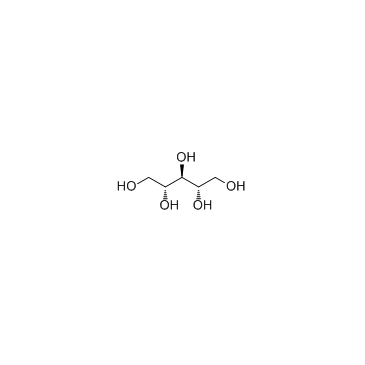
Ribitol structure
|
Common Name | Ribitol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 488-81-3 | Molecular Weight | 152.146 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 494.5±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H12O5 | Melting Point | 101-104ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 261.9±21.9 °C | |
Use of RibitolRibitol is a crystalline pentose alcohol formed by the reduction of ribose. Enhancing the flux of D-glucose to the pentose phosphate pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae for the production of D-ribose and ribitol. |
| Name | D-ribitol |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Ribitol is a crystalline pentose alcohol formed by the reduction of ribose. Enhancing the flux of D-glucose to the pentose phosphate pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae for the production of D-ribose and ribitol. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | Ribitol is a reduced sugar[1]. Phosphoglucose isomerase-deficient (pgi1) strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae are studied for the production of D-ribose and Ribitol from D-glucose via the intermediates of the pentose phosphate pathway. Overexpression of the gene encoding sugar phosphate phosphatase (DOG1) of S. cerevisiae is needed for the production of D-ribose and Ribitol. The engineered strains are compared for their ability to produce the PPP-derived 5-carbon compounds Ribitol and D-ribose from D-glucose[2]. |
| Kinase Assay | The high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analyses are carried out using a Fast Acid Column (100×7.8 mm) and a HPX-87H Ion Exclusion Column (300 mm×7.8 mm) in series with 2.5 mM H2SO4 in water as the mobile phase at a flow rate of 0.3 mL/min, at 55°C. This method enabled quantification of D-glucose, ethanol, glycerol, D-xylulose, Ribitol, and xylitol. D-ribose, D-ribulose, and D-arabitol coeluted on the Aminex HPX-87H column. The CarboPac MA-1 column of Dionex ICS-3000 is used to analyze representative culture supernatant samples for the presence of arabitol and xylitol. Samples are run at column temperature of 30°C with 480 mM NaOH at flow rate 0.4 mL/min. The CarboPac MA-1 column separated D-arabitol from D-ribose and D-ribulose, but the alkaline conditions degraded D-ribulose interfering with the quantification of D-ribose.Yeast cells are disrupted with glass beads in 100 mM sodium phosphate buffer pH 7.0 containing phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride and pepstatin A in final concentrations of 0.17 mg/mL and 0.01 mg/mL, respectively.The activity of NAD+-dependent Gdh2p is measured in a reaction buffer of 0.5 M triethanol amine pH 7.7 and 2 mM NADH. After addition of the cell lysate, the reaction is started by adding a mixture of α-ketoglutarate (100 mM) and NH4Cl (200 mM) to a final concentration of 2.4 mM and 4.9 mM, respectively. The GapB activity is measured. Shortly, the reaction mixture is 500 mM triethanol amine pH 7.8, 1 mM ATP, 2 mM MgCl2, 200 μM NADPH, and 10 μg/mL of phosphoglycerate kinase. 3-phosphoglycerate is added to a final concentration of 5 mM to start the reaction. Activity measurements are performed with a Cobas Mira Plus automated analyzer[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 494.5±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 101-104ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C5H12O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 152.146 |
| Flash Point | 261.9±21.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 152.068466 |
| PSA | 101.15000 |
| LogP | -3.77 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.571 |
| InChIKey | HEBKCHPVOIAQTA-NGQZWQHPSA-N |
| SMILES | OCC(O)C(O)C(O)CO |
| Storage condition | Store at RT. |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Precursor 5 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
|
Urinary metabolic fingerprinting of mice with diet-induced metabolic derangements by parallel dual secondary column-dual detection two-dimensional comprehensive gas chromatography.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1361 , 265-76, (2014) This study investigates the potential of a parallel dual secondary column-dual detection two-dimensional comprehensive GC platform (GC×2GC-MS/FID) for metabolic profiling and fingerprinting of mouse u... |
|
|
Proteomic and metabolomic analysis of the carotenogenic yeast Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous using different carbon sources.
BMC Genomics 16 , 289, (2015) Astaxanthin is a potent antioxidant with increasing biotechnological interest. In Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous, a natural source of this pigment, carotenogenesis is a complex process regulated throug... |
|
|
Selective removal of phosphate for analysis of organic acids in complex samples.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1388 , 1-8, (2015) Accurate quantitation of compounds in samples of biological origin is often hampered by matrix interferences one of which occurs in GC-MS analysis from the presence of highly abundant phosphate. Conse... |
| (2R,3s,4S)-1,2,3,4,5-Pentanpentol |
| adonitol |
| ADONIT |
| ADONITE |
| ADONITOL(RG) |
| (2R,3s,4S)-pentane-1,2,3,4,5-pentol |
| RIBITO |
| Adonito |
| D-erythro-Pentitol |
| MFCD00064291 |
| D-Ribitol |
| meso ribitol |
| Ribitol |
| (2R,3s,4S)-1,2,3,4,5-Pentanepentol |
| Adonite Ribitol |
| EINECS 207-685-7 |
| Adonite,Ribitol |
| meso-ribitol |
| D-(+)-Arabitol |
| Adonitrol |
 CAS#:50-70-4
CAS#:50-70-4 CAS#:488-84-6
CAS#:488-84-6 CAS#:81076-13-3
CAS#:81076-13-3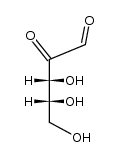 CAS#:3445-24-7
CAS#:3445-24-7![3-(1,4-dioxaspiro[4.5]decan-3-yl)prop-2-en-1-ol Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/123/88367-50-4.png) CAS#:88367-50-4
CAS#:88367-50-4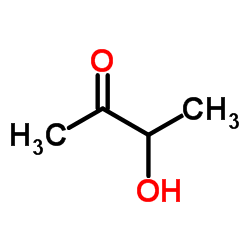 CAS#:513-86-0
CAS#:513-86-0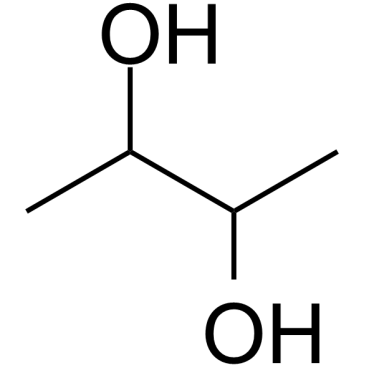 CAS#:513-85-9
CAS#:513-85-9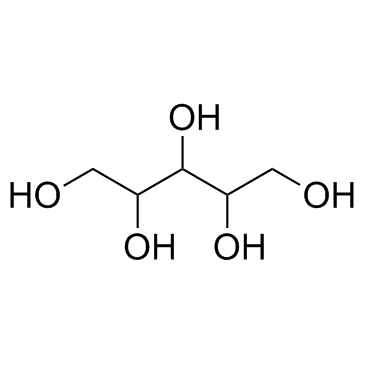 CAS#:488-82-4
CAS#:488-82-4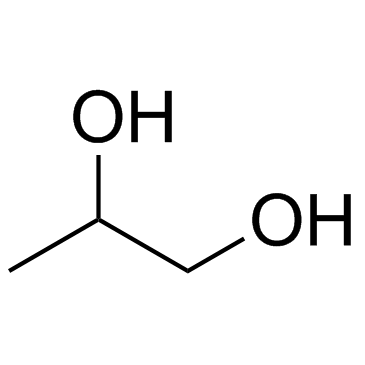 CAS#:57-55-6
CAS#:57-55-6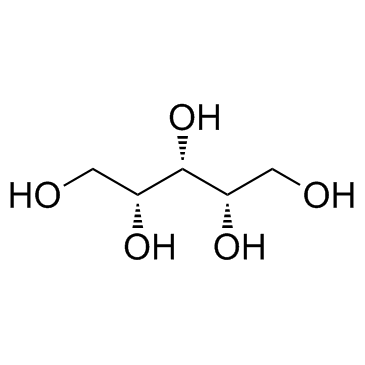 CAS#:87-99-0
CAS#:87-99-0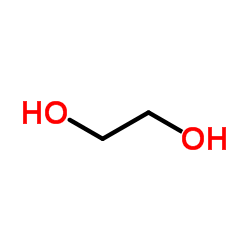 CAS#:107-21-1
CAS#:107-21-1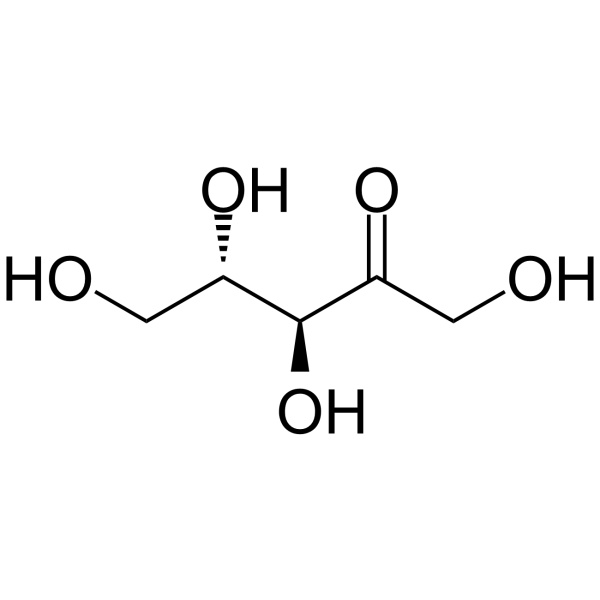 CAS#:2042-27-5
CAS#:2042-27-5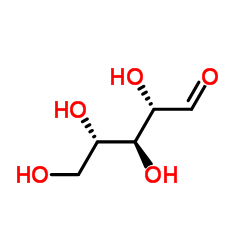 CAS#:24259-59-4
CAS#:24259-59-4 CAS#:5348-85-6
CAS#:5348-85-6
