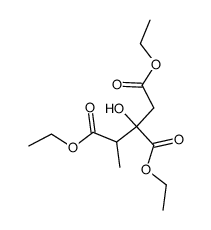
2-Methylcitric acid
Modify Date: 2025-08-26 19:13:53
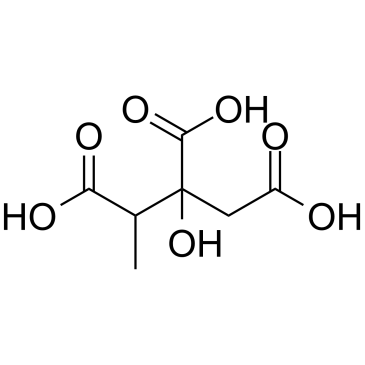
2-Methylcitric acid structure
|
Common Name | 2-Methylcitric acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 6061-96-7 | Molecular Weight | 206.15000 | |
| Density | 1.178g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 464.4ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H10O7 | Melting Point | 79°C (lit.) | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 234.7ºC | |
Use of 2-Methylcitric acid2-Methylcitric acid (Methylcitric acid) is an endogenous metabolite in the 2-methylcitric acid cycle. 2-Methylcitric acid accumulates in methylmalonic and propionic acidemias and acts as a marker metabolite. 2-Methylcitric acid markedly inhibits ADP-stimulated and uncoupled respiration in mitochondria supported by glutamate[1]. |
| Name | 2-methylcitric acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 2-Methylcitric acid (Methylcitric acid) is an endogenous metabolite in the 2-methylcitric acid cycle. 2-Methylcitric acid accumulates in methylmalonic and propionic acidemias and acts as a marker metabolite. 2-Methylcitric acid markedly inhibits ADP-stimulated and uncoupled respiration in mitochondria supported by glutamate[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | 2-Methylcitric acid (Methylcitric acid) impairs glutamate metabolism and induces permeability transition in brain mitochondria. 2-Methylcitric acid inhibits glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) activity at concentrations as low as 0.5 mM[1]. 2-Methylcitric acid (1-3 mM; 150 seconds) provokes a significant decrease in mitochondrial membrane potential and induced swelling in Ca2+-loaded mitochondria supported by different substrates[1]. 2-Methylcitric acid behaves as a potent inhibitor of glutamate oxidation by inhibiting glutamate dehydrogenase activity and as a permeability transition inducer, disturbing mitochondrial energy homeostasis. 2-Methylcitric acid does not significantly impair mitochondrial glutamate transport. 2-Methylcitric acid does not significantly impair glutamate mitochondrial transport in liver mitochondria[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.178g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 464.4ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 79°C (lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C7H10O7 |
| Molecular Weight | 206.15000 |
| Flash Point | 234.7ºC |
| Exact Mass | 206.04300 |
| PSA | 132.13000 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.586 |
| InChIKey | YNOXCRMFGMSKIJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CC(C(=O)O)C(O)(CC(=O)O)C(=O)O |
| HS Code | 2918199090 |
|---|
|
~% 
2-Methylcitric acid CAS#:6061-96-7 |
| Literature: Habicht; Schneeberger Helvetica Chimica Acta, 1956 , vol. 39, p. 1316,1318 |
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| HS Code | 2918199090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2918199090 other carboxylic acids with alcohol function but without other oxygen function, their anhydrides, halides, peroxides, peroxyacids and their derivatives。Supervision conditions:None。VAT:17.0%。Tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:6.5%。General tariff:30.0% |
| 2-hydroxy-butane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid |
| 1,2,3-Butanetricarboxylic acid,2-hydroxy |
| 2-Hydroxy-butan-1,2,3-tricarbonsaeure |
| 2-hydroxybutane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate |
| 2-methylcitrate |
| 2-hydroxy-1,2,3-butantricarbons |
| Methylcitronensaeure |
| 2-hydroxybutane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid |
| 2-hydroxy-1,2,3-butanetricarboxylic acid |
| 2-Methylcitric acid |