Quinine Hydrochloride Dihydrate
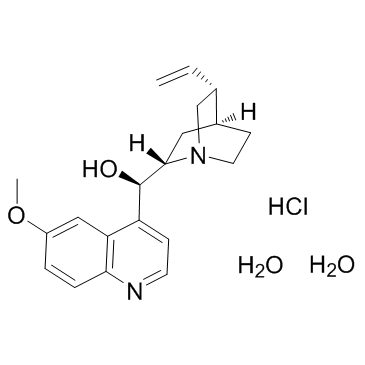
Quinine Hydrochloride Dihydrate structure
|
Common Name | Quinine Hydrochloride Dihydrate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 6119-47-7 | Molecular Weight | 396.908 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 633ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H29ClN2O4 | Melting Point | 115-116 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 122 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of Quinine Hydrochloride DihydrateQuinine Hydrochloride Dihydrate is a natural white crystalline alkaloid having antipyretic (fever-reducing), antimalarial, analgesic (painkilling), anti-inflammatory properties and a bitter taste.Target: AntiparasiticQuinine is a natural white crystalline alkaloid having antipyretic (fever-reducing), antimalarial, analgesic (painkilling), and anti-inflammatory properties and a bitter taste. It is a stereoisomer of quinidine, which, unlike quinine, is an antiarrhythmic. Quinine contains two major fused-ring systems: the aromatic quinoline and the bicyclic quinuclidine. In patients with cerebral malaria receiving the standard dose of 10 mg/kg every eight hours, plasma quinine concentrations consistently exceeded 10 mg/liter, reaching a peak 60 ± 25 hours (mean ± 1 S.D.) after treatment was begun and then declining. Quinine total clearances (CI) and total apparent volumes of distribution (Vd) were significantly lower than in uncomplicated malaria (CI, 0.92 ± 0.42 compared with 1.35 ± 0.6 ml/min/kg, p = 0.03; Vd, 1.18 ± 0.37 compared with 1.67 ± 0.34 liter/kg, p = 0.0013) [1]. |
| Name | Quinine hydrochloride dihydrate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Quinine Hydrochloride Dihydrate is a natural white crystalline alkaloid having antipyretic (fever-reducing), antimalarial, analgesic (painkilling), anti-inflammatory properties and a bitter taste.Target: AntiparasiticQuinine is a natural white crystalline alkaloid having antipyretic (fever-reducing), antimalarial, analgesic (painkilling), and anti-inflammatory properties and a bitter taste. It is a stereoisomer of quinidine, which, unlike quinine, is an antiarrhythmic. Quinine contains two major fused-ring systems: the aromatic quinoline and the bicyclic quinuclidine. In patients with cerebral malaria receiving the standard dose of 10 mg/kg every eight hours, plasma quinine concentrations consistently exceeded 10 mg/liter, reaching a peak 60 ± 25 hours (mean ± 1 S.D.) after treatment was begun and then declining. Quinine total clearances (CI) and total apparent volumes of distribution (Vd) were significantly lower than in uncomplicated malaria (CI, 0.92 ± 0.42 compared with 1.35 ± 0.6 ml/min/kg, p = 0.03; Vd, 1.18 ± 0.37 compared with 1.67 ± 0.34 liter/kg, p = 0.0013) [1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 633ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 115-116 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C20H29ClN2O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 396.908 |
| Flash Point | 122 °C |
| Exact Mass | 396.181580 |
| PSA | 64.05000 |
| LogP | 3.78450 |
| Index of Refraction | -250 ° (C=2, EtOH) |
| InChIKey | MPQKYZPYCSTMEI-FLZPLBAKSA-N |
| SMILES | C=CC1CN2CCC1CC2C(O)c1ccnc2ccc(OC)cc12.Cl.O.O |
| Storage condition | Store at -20°C |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H317-H334 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P280-P342 + P311 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn: Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R20/21/22;R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S36/37-S45-S36/37/39-S26 |
| RIDADR | 1544 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | VA7700000 |
| HS Code | 29392000 |
| HS Code | 29392000 |
|---|
|
Photostability profiles of the experimental antimetastatic ruthenium complex NAMI-A.
J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 30(4) , 1287-96, (2002) NAMI-A is a novel ruthenium complex with selective activity against metastases currently in Phase I clinical trials in The Netherlands. The photostability of this new agent in solid state and in solut... |
|
|
Quinine blocks a calcium-activated potassium conductance in mammalian enteric neurones.
Br. J. Pharmacol. 83(1) , 3-5, (1984) Quinine (100 microM) abolished the slow calcium-dependent afterhyperpolarization which occurs after an action potential in some neurones of the guinea-pig myenteric and submucous plexus. This occurred... |
|
|
Treatment of severe malaria.
J. R. Soc. Med. 82 Suppl 17 , 44-50; discussion 50-1, (1989) In the treatment of severe Plasmodium falciparum infection antimalarial drugs should, ideally, be given by controlled rate intravenous infusion until the patient is able to swallow tablets. In cases w... |
| Quinine hydrochloride,(R)-(6-Methoxyquinolin-4-yl)((2S,4S,8R)-8-vinylquinuclidin-2-yl)methanolhydrochloride |
| EINECS 231-437-7 |
| MFCD00151248 |
| Quinine monohydrochloride dihydrate |
| Quinine Hydrochloride Dihydrate |
| Cinchonan-9-ol, 6'-methoxy-, (8α,9R)-, hydrochloride, hydrate (1:1:2) |
| (8α,9R)-6'-Methoxycinchonan-9-ol hydrochloride dihydrate |
| Quinine (hydrochloride dihydrate) |
 CAS#:4363-94-4
CAS#:4363-94-4 CAS#:121667-85-4
CAS#:121667-85-4 CAS#:121667-84-3
CAS#:121667-84-3![trimethyl 2,2',2''-(3-hydroxy-6-(hydroxy(5-vinylquinuclidin-2-yl)methyl)-8-methoxy-1-oxo-2,3,5,6-tetrahydro-1H-3a,6-methanobenzo[d]pyrrolo[2,1-b][1,3]oxazepine-3,5,5-triyl)triacetate structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/298/121667-83-2.png) CAS#:121667-83-2
CAS#:121667-83-2![5-ethenyl-1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]octane-2-carbaldehyde structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/405/35189-41-4.png) CAS#:35189-41-4
CAS#:35189-41-4
