Terazosin hydrochloride dihydrate
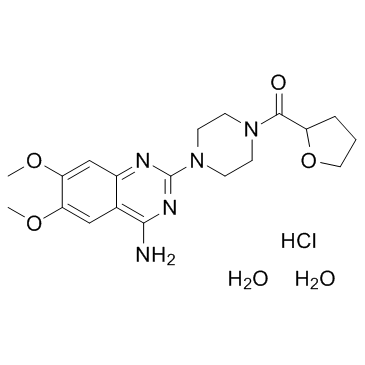
Terazosin hydrochloride dihydrate structure
|
Common Name | Terazosin hydrochloride dihydrate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 70024-40-7 | Molecular Weight | 459.924 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 664.5ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H30ClN5O6 | Melting Point | 215 - 217ºC | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Terazosin hydrochloride dihydrateTerazosin Hydrochloride dihydrate is a selective alpha1-antagonist used for treatment of symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).Target: Alpha-1 Adrenergic ReceptorTerazosin Hydrochloride dihydrate is an a1-selective blocker. Its inhibitory effect on prostate tumor growth may be the result of antiangiogenic activity. Terazosin Hydrochloride dihydrate is an inhibitor of α1A-AR, α1B-AR, α1D-AR and α2B-AR [1]. |
| Name | terazosin hydrochloride dihydrate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Terazosin Hydrochloride dihydrate is a selective alpha1-antagonist used for treatment of symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).Target: Alpha-1 Adrenergic ReceptorTerazosin Hydrochloride dihydrate is an a1-selective blocker. Its inhibitory effect on prostate tumor growth may be the result of antiangiogenic activity. Terazosin Hydrochloride dihydrate is an inhibitor of α1A-AR, α1B-AR, α1D-AR and α2B-AR [1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 664.5ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 215 - 217ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C19H30ClN5O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 459.924 |
| Exact Mass | 459.188446 |
| PSA | 121.50000 |
| LogP | 2.31430 |
| InChIKey | NZMOFYDMGFQZLS-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | COc1cc2nc(N3CCN(C(=O)C4CCCO4)CC3)nc(N)c2cc1OC.Cl.O.O |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 |
| Precautionary Statements | P301 + P312 + P330 |
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| Risk Phrases | 22 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
Noradrenergic modulation of masseter muscle activity during natural rapid eye movement sleep requires glutamatergic signalling at the trigeminal motor nucleus.
J. Physiol. 592(Pt 16) , 3597-609, (2014) Noradrenergic neurotransmission in the brainstem is closely coupled to changes in muscle activity across the sleep-wake cycle, and noradrenaline is considered to be a key excitatory neuromodulator tha... |
|
|
Efficacy of three different alpha 1-adrenergic blockers and hyoscine N-butylbromide for distal ureteral stones.
Int. Braz J Urol 37(2) , 195-200; discussion 201-2, (2011) To evaluate hyoscine N-butyl bromide (HBB) and three different alpha-1 blockers in the treatment of distal ureteral stones.A total of 140 patients with stones located in the distal tract of the ureter... |
|
|
Multiple cerebral infarctions related to famotidine-induced eosinophilia.
J. Neurol. 259(10) , 2229-31, (2012)
|
| [4-(4-Amino-6,7-dimethoxy-2-quinazolinyl)-1-piperazinyl](tetrahydro-2-furanyl)methanone hydrochloride dihydrate |
| [4-(4-Amino-6,7-dimethoxychinazolin-2-yl)piperazin-1-yl](tetrahydrofuran-2-yl)methanonhydrochloriddihydrat |
| Terazosin Hydrochloride Dihydrate |
| Terazosin monohydrochloride dihydrate |
| MFCD00941408 |
| [4-(4-amino-6,7-dimethoxyquinazolin-2-yl)piperazin-1-yl]-(oxolan-2-yl)methanone,dihydrate,hydrochloride |
| Methanone, [4-(4-amino-6,7-dimethoxy-2-quinazolinyl)-1-piperazinyl](tetrahydro-2-furanyl)-, hydrochloride, hydrate (1:1:2) |
| Terazosin HCl |