Methyl methanesulfonate
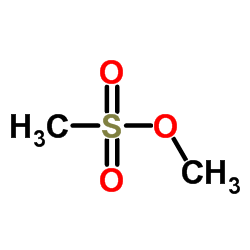
Methyl methanesulfonate structure
|
Common Name | Methyl methanesulfonate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 66-27-3 | Molecular Weight | 110.13 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 202.1±9.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C2H6O3S | Melting Point | 20ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 104.4±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of Methyl methanesulfonateMethyl methanesulfonate is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research. |
| Name | methyl methanesulfonate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Methyl methanesulfonate is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 202.1±9.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 20ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C2H6O3S |
| Molecular Weight | 110.13 |
| Flash Point | 104.4±0.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 110.003761 |
| PSA | 51.75000 |
| LogP | -0.57 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.4±0.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.406 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong acids, strong bases. |
| Water Solubility | 200 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301-H315-H319-H335-H350 |
| Precautionary Statements | P201-P261-P301 + P310-P305 + P351 + P338-P308 + P313 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US);type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | T:Toxic; |
| Risk Phrases | R22;R36/37/38;R45;R68 |
| Safety Phrases | S53-S26-S45-S36/37/39 |
| RIDADR | UN 2810 6.1/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | PB2625000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
|
Sodium fluoride promotes apoptosis by generation of reactive oxygen species in human lymphocytes.
J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 77(21) , 1269-80, (2014) Fluoride generated the attention of toxicologists due to its deleterious effects at high concentrations in human populations suffering from fluorosis and with in vivo experimental models. Interest in ... |
|
|
In vitro toxicological assessment of iron oxide, aluminium oxide and copper nanoparticles in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell types.
Drug Chem. Toxicol. 38 , 152-61, (2015) Metallic nanoparticles (NPs) have a variety of applications in different industries including pharmaceutical industry where these NPs are used mainly for image analysis and drug delivery. The increasi... |
|
|
Toxicological assessment and management options for boat pressure-washing wastewater.
Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 114 , 164-70, (2015) Boats are washed periodically for maintenance in order to remove biofoulants from hulls, which results in the generation of wastewater. This study aimed at evaluating the cyto/genotoxic and mutagenic ... |
| Methyl methansulphonate |
| methyl methane sulfonate |
| Methanesulfonic acid,methyl ester |
| Methylsulfonic acid methyl ester |
| Methanesulfonic acid, methyl ester |
| Methyl methanesulfonate |
| as-Dimethyl sulphite |
| Methyl methanesulfonic acid |
| methyl methanesulphonate |
| MFCD00007557 |
| as-Dimethyl sulfite |
| Methyl methansulfonate |
| EINECS 200-625-0 |
| methanesulphonic acid methyl ester |
| UNII-AT5C31J09G |
| Methylmethanesulfonate |
| Methyl mesylate |
 CAS#:67-56-1
CAS#:67-56-1 CAS#:124-63-0
CAS#:124-63-0 CAS#:75-75-2
CAS#:75-75-2 CAS#:35709-09-2
CAS#:35709-09-2 CAS#:861103-21-1
CAS#:861103-21-1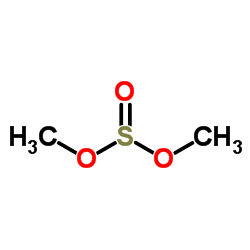 CAS#:616-42-2
CAS#:616-42-2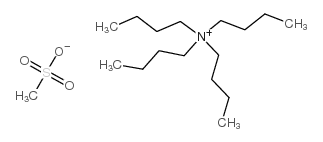 CAS#:65411-49-6
CAS#:65411-49-6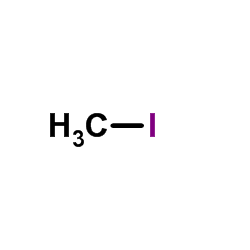 CAS#:74-88-4
CAS#:74-88-4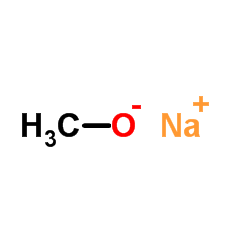 CAS#:124-41-4
CAS#:124-41-4 CAS#:102-82-9
CAS#:102-82-9 CAS#:19977-47-0
CAS#:19977-47-0 CAS#:74-87-3
CAS#:74-87-3 CAS#:115-10-6
CAS#:115-10-6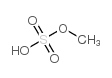 CAS#:75-93-4
CAS#:75-93-4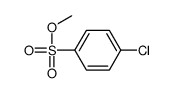 CAS#:15481-45-5
CAS#:15481-45-5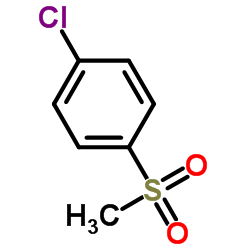 CAS#:98-57-7
CAS#:98-57-7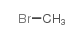 CAS#:74-83-9
CAS#:74-83-9 CAS#:5539-53-7
CAS#:5539-53-7
