D(-)-Glutamic acid
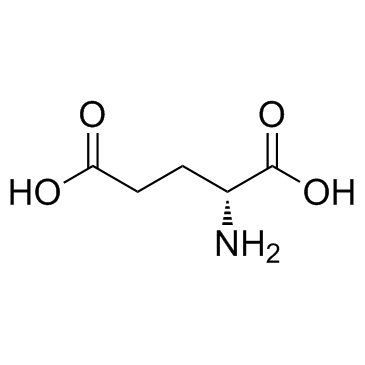
D(-)-Glutamic acid structure
|
Common Name | D(-)-Glutamic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 6893-26-1 | Molecular Weight | 147.129 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 333.8±32.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H9NO4 | Melting Point | 200-202ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 155.7±25.1 °C | |
Use of D(-)-Glutamic acidD-glutamic acid, an enantiomer of L- glutamic acid, is widely used in pharmaceuticals and foods. |
| Name | D-glutamic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | D-glutamic acid, an enantiomer of L- glutamic acid, is widely used in pharmaceuticals and foods. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Various d-amino acids, such as D-serine, D-aspartic acid (D-Asp), and D-glutamic acid (D-Glu) are widely found in mammals including human beings and they are now thought to be the candidates of novel physiologically active substances and/or biomarkers[1]. D-[Asp/Glu] (4 mg/mL) inhibits IgE binding (75%) to peanuts while D-Glu, D-Asp has no inhibitory effect. IgE is specific for D-[Asp/Glu] and may have the potential for removing IgE or reducing IgE binding to peanut allergens[2]. |
| In Vivo | D-glutamic acid is currently paid attention as a modulator of neuronal transmission and hormonal secretion. It is metabolized only by D-aspartate oxidase in mammals[1]. After intraperitoneal injection, L-glutamate is catabolized via a-ketoglutarate, whereas D-glutamate is converted to n-pyrrolidone carboxylic acid. Carbon 2 of both D- and L-glutamate is converted in the cecum to the methyl carbon of acetate. Both rat liver and kidney catalyze the conversion of D-glutamic acid to n-pyrrolidone carboxylic acid[3]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats: Male albino rats are given injections of L- or D-glutamic acid-2-C14, DL-glutamic acid-5-C14, or D-glutamic acid-5-C14. Injections by stomach tube or into the cecum are performed while the animals are under ether anesthesia. After the rats are killed, the “carcass” and liver glutamic acids are isolated, degraded, and assayed for radioactivity. “Carcass” refers to the entire animal, except liver, including the ished gastrointestinal tract[3]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 333.8±32.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 200-202ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C5H9NO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 147.129 |
| Flash Point | 155.7±25.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 147.053162 |
| PSA | 100.62000 |
| LogP | -1.43 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.522 |
| InChIKey | WHUUTDBJXJRKMK-GSVOUGTGSA-N |
| SMILES | NC(CCC(=O)O)C(=O)O |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2922499990 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS:2922499990 other amino-acids, other than those containing more than one kind of oxygen function, and their esters; salts thereof VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward) MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental... |
|
|
Low resolution X-ray structure of γ-glutamyltranspeptidase from Bacillus licheniformis: opened active site cleft and a cluster of acid residues potentially involved in the recognition of a metal ion.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1844(9) , 1523-9, (2014) γ-Glutamyltranspeptidases (γ-GTs) cleave the γ-glutamyl amide bond of glutathione and transfer the released γ-glutamyl group to water (hydrolysis) or acceptor amino acids (transpeptidation). These ubi... |
|
|
γ-glutamyl transpeptidase 1 specifically suppresses green-light avoidance via GABAA receptors in Drosophila.
J. Neurochem. 130(3) , 408-18, (2014) Drosophila larvae innately show light avoidance behavior. Compared with robust blue-light avoidance, larvae exhibit relatively weaker green-light responses. In our previous screening for genes involve... |
| H-D-Glu-OH |
| Glutamic acid, D- |
| MFCD00063112 |
| D(-)-Glutamic acid |
| glutamic acid D-form |
| EINECS 230-000-8 |
| δ-Glutamic acid |
| hydrogen D-glutamate |
| d-Glu |
| (R)-(-)-GLUTAMIC ACID |
| R-(-)-Glutamic acid |
| (2R)-2-aminopentanedioic acid |
| D-Glutamic acid |
| D(-)-Glutamicacid |
 CAS#:328-50-7
CAS#:328-50-7 CAS#:1509-35-9
CAS#:1509-35-9 CAS#:2623-91-8
CAS#:2623-91-8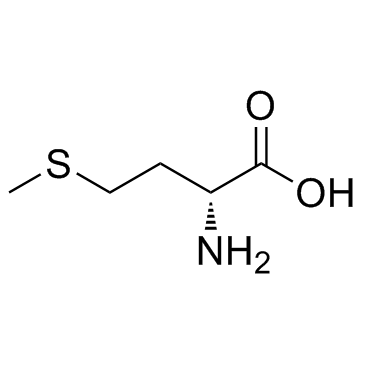 CAS#:348-67-4
CAS#:348-67-4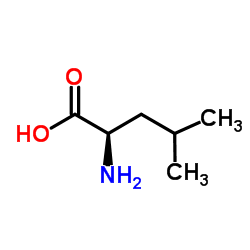 CAS#:328-38-1
CAS#:328-38-1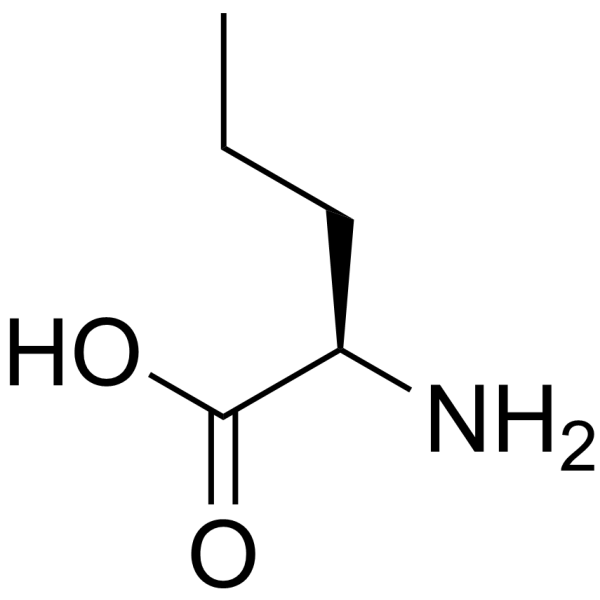 CAS#:2013-12-9
CAS#:2013-12-9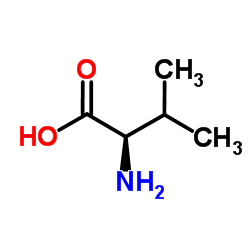 CAS#:640-68-6
CAS#:640-68-6 CAS#:351-50-8
CAS#:351-50-8 CAS#:327-56-0
CAS#:327-56-0 CAS#:617-65-2
CAS#:617-65-2 CAS#:35793-73-8
CAS#:35793-73-8 CAS#:5624-26-0
CAS#:5624-26-0 CAS#:338-69-2
CAS#:338-69-2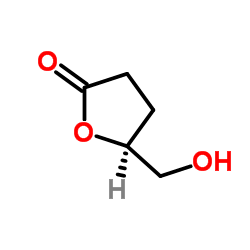 CAS#:32780-06-6
CAS#:32780-06-6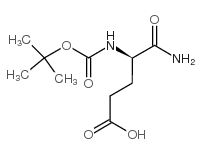 CAS#:55297-72-8
CAS#:55297-72-8 CAS#:52813-63-5
CAS#:52813-63-5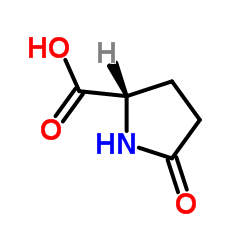 CAS#:4042-36-8
CAS#:4042-36-8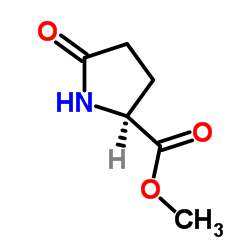 CAS#:4931-66-2
CAS#:4931-66-2 CAS#:192803-60-4
CAS#:192803-60-4
