Yeast extract
Yeast extract structure
|
Common Name | Yeast extract | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 8013-01-2 | Molecular Weight | 319.193 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 365.8±21.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | n.a. | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 175.0±22.1 °C | |
Use of Yeast extractYeast extract is a concentrate of the soluble part of yeast, especially Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The main nutritional components of yeast extract include partly hydrolyzed protein with 35-40% of free amino acid, and it also contain B vitamins and some trace elements. Yeast extract can be used as nutrients for bacterial culture media[1]. |
| Name | Ferment |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Yeast extract is a concentrate of the soluble part of yeast, especially Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The main nutritional components of yeast extract include partly hydrolyzed protein with 35-40% of free amino acid, and it also contain B vitamins and some trace elements. Yeast extract can be used as nutrients for bacterial culture media[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 365.8±21.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | n.a. |
| Molecular Weight | 319.193 |
| Flash Point | 175.0±22.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 318.025543 |
| LogP | 4.59 |
| Appearance of Characters | powder | slightly brown |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.606 |
| InChIKey | GQNBDGXKDJSVGQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
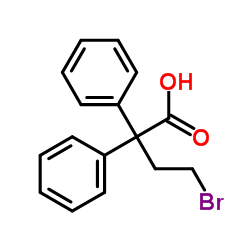
| SMILES | O=C(O)CC1c2ccccc2-c2ccc3ccccc3c21 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | H2O: 2%, turbid, yellow |
|
The mitosis-to-interphase transition is coordinated by cross talk between the SIN and MOR pathways in Schizosaccharomyces pombe.
J. Cell Biol. 190(5) , 793-805, (2010) The mechanisms that regulate cytoskeletal remodeling during the transition between mitosis and interphase are poorly understood. In fission yeast the MOR pathway promotes actin polarization to cell ti... |
|
|
LsrR quorum sensing "switch" is revealed by a bottom-up approach.
PLoS Comput. Biol. 7(9) , e1002172, (2011) Quorum sensing (QS) enables bacterial multicellularity and selective advantage for communicating populations. While genetic "switching" phenomena are a common feature, their mechanistic underpinnings ... |
|
|
Hypoxia modifies the feeding preferences of Drosophila. Consequences for diet dependent hypoxic survival.
BMC Physiol. 10 , 8, (2010) Recent attention has been given to the relationships between diet, longevity, aging and resistance to various forms of stress. Flies do not simply ingest calories. They sense different concentrations ... |
| EINECS 232-387-9 |
| 4-Bromo-2,2-diphenylbutyric acid |
| MFCD00132599 |
| Benzeneacetic acid, α-(2-bromoethyl)-α-phenyl- |
| 4-bromo-2,2-diphenylbutanoic acid |
| Yeast extract |

