Rutaecarpine
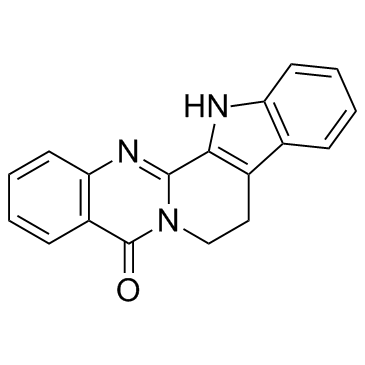
Rutaecarpine structure
|
Common Name | Rutaecarpine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 84-26-4 | Molecular Weight | 287.315 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 550.1±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H13N3O | Melting Point | 259.5 - 260ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 286.5±32.9 °C | |
Use of RutaecarpineRutaecarpine, an alkaloid of Evodia rutaecarpa, is an inhibitor of COX-2 with an IC50 value of 0.28 μM. |
| Name | Rutaecarpine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Rutaecarpine, an alkaloid of Evodia rutaecarpa, is an inhibitor of COX-2 with an IC50 value of 0.28 μM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
COX-2:0.28 μM (IC50, in BMMC) COX-1:8.7 μM (IC50, in BMMC) |
| In Vitro | Rutaecarpine has shown a variety of intriguing biological properties such as anti-thrombotic, anticancer, anti-inflammatory and analgesic, anti-obesity and thermoregulatory, vasorelaxing activity, as well as effects on the cardiovascular and endocrine systems[2]. Rutaecarpine inhibits COX-2 and COX-1 dependent phases of PGD2 generation in BMMC in a concentration-dependent manner with an IC50 of 0.28 μM and 8.7 μM, respectively. It inhibits COX-2-dependent conversion of exogenous arachidonic acid to PGE2 in a dose-dependent manner by the COX-2-transfected HEK293 cells[1]. |
| In Vivo | Rutaecarpine showed in vivo anti-inflammatory activity on rat l-carrageenan induced paw edema by intraperitoneal administration[1]. Rutaecarpine significantly decreases the number of antibody-forming cells and causes weight decrease in spleen in a dose-dependent manner. In addition, rutaecarpine administered mice exhibit reduced splenic cellularity, decreased numbers of total T cells, CD4+ cells, CD8+ cells, and B cells in spleen. IL-2, interferon and IL-10 mRNA expressions are suppressed significantly by rutaecarpine treatment. The number of CD4+IL-2+ cells is reduced significantly following administration of mice with rutaecarpine[3]. |
| Cell Assay | Rutaecarpine is dissolved in DMSO and diluted with appropriate medium before use. COX-1 and COX-2 cDNA-transfected HEK293 cells are prepared. For measuring inhibitory activity on COX-1 and COX-2 by rutaecarpine, cells in 1 mL of culture medium are seeded into each well of 24-well. After culture for 4 days, the supernatants are removed and 250 mL of fresh medium is added to the cells with or without rutaecarpine. After preincubation for 5 h at 37°C, the cells are further incubated at 37°C for 30 min with 50 mM arachidonic acid. All reactions are stopped by centrifugation at 120 g at 4°C for 5 min. Concentrations of PGE2 in the supernatant are measured[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats: Rutaecarpine is dissolved in 0.1% carboxymethyl cellulose and diluted with appropriate medium before use. Male Splague-Dawley (SD) rats (180-220 g) are used in the study. Rutaecarpine administered intraperitoneally and, 1 h later, l-carrageenan solution is injected to right hind paw of rats. Paw volumes are measured using plethysmometer 5 h after l-carrageenan injection[1]. Mice: For the antibody response to SRBCs, rutaecarpine is administered at a single dose of 10 mg/kg, 20 mg/kg, 40 mg/kg or 80 mg/kg in 10 mL of 1% povidone solution intravenously. Control animals are given 1% povidone solution at 10 mL/kg. Specific pathogen-free female BALB/c mice are used in the study[3]. |
| References |
[2]. Lee SH, et al. Progress in the studies on rutaecarpine. Molecules. 2008 Feb 6;13(2):272-300. |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 550.1±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 259.5 - 260ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C18H13N3O |
| Molecular Weight | 287.315 |
| Flash Point | 286.5±32.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 287.105865 |
| PSA | 50.68000 |
| LogP | 2.03 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.792 |
| InChIKey | ACVGWSKVRYFWRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=c1c2ccccc2nc2n1CCc1c-2[nH]c2ccccc12 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | DMSO: 18 mg/mL clear yellow solution, soluble |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933990090. heterocyclic compounds with nitrogen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Pharmacological effects of rutaecarpine as a cardiovascular protective agent.
Molecules 15(3) , 1873-81, (2010) Many studies indicate that traditional Chinese herbs are beneficial in the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Evodia rutaecarpa ('Wu-Chu-Yu') remains the most popular and multi-purpo... |
|
|
Transdermal behaviors comparisons among Evodia rutaecarpa extracts with different purity of evodiamine and rutaecarpine and the effect of topical formulation in vivo.
Fitoterapia 83(5) , 954-60, (2012) Evodiamine (EVO) and rutaecapine (RUT), the major active components from Evodia rutaecarpa extract (EE), are recognized as a depended analgesic agent. This study was designed to investigate the effect... |
|
|
Effects of rutaecarpine on the metabolism and urinary excretion of caffeine in rats.
Arch. Pharm. Res. 34(1) , 119-25, (2011) Although rutaecarpine, an alkaloid originally isolated from the unripe fruit of Evodia rutaecarpa, has been reported to reduce the systemic exposure of caffeine, the mechanism of this phenomenon is un... |
| ruteacarpine |
| Rutecarpine |
| MFCD00210551 |
| Indolo[2',3':3,4]pyrido[2,1-b]quinazolin-5(7H)-one, 8,13-dihydro- |
| RUTECARPINE 95+ |
| 8,13-Dihydroindolo[2',3':3,4]pyrido[2,1-b]quinazolin-5(7H)-one |
![6-phenylhydrazono-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-11H-pyrido[2,1-b]quinazolin-11-one Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/275/80776-66-5.png) CAS#:80776-66-5
CAS#:80776-66-5![1H-Pyrido[3,4-b]indol-1-one,2,3,4,9-tetrahydro- Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/106/17952-82-8.png) CAS#:17952-82-8
CAS#:17952-82-8 CAS#:134-20-3
CAS#:134-20-3 CAS#:118-92-3
CAS#:118-92-3![3-[2-(2-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl]quinazolin-4-one Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/136/807354-69-4.png) CAS#:807354-69-4
CAS#:807354-69-4 CAS#:1477-50-5
CAS#:1477-50-5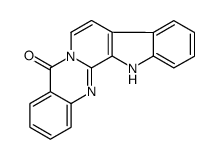 CAS#:55786-24-8
CAS#:55786-24-8
