2,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid
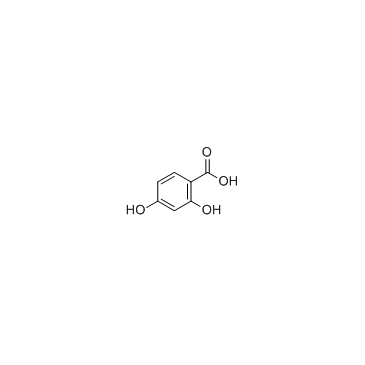
2,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid structure
|
Common Name | 2,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 89-86-1 | Molecular Weight | 154.120 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 414.8±15.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H6O4 | Melting Point | 208-211 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 218.8±16.9 °C | |
Use of 2,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid2,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid is a degradation product of cyaniding glycoside from tart cheeries in cell culture. |
| Name | 2,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 2,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid is a degradation product of cyaniding glycoside from tart cheeries in cell culture. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| References |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 414.8±15.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 208-211 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C7H6O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 154.120 |
| Flash Point | 218.8±16.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 154.026611 |
| PSA | 77.76000 |
| LogP | 1.60 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.671 |
| Water Solubility | 8 g/L (20 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36-S37/39 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | VH3708050 |
| HS Code | 2942000000 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2918290000 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS: 2918290000 other carboxylic acids with phenol function but without other oxygen function, their anhydrides, halides, peroxides, peroxyacids and their derivatives Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward) VAT:17.0% MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Identifying chelators for metalloprotein inhibitors using a fragment-based approach.
J. Med. Chem. 54 , 591-602, (2011) Fragment-based lead design (FBLD) has been used to identify new metal-binding groups for metalloenzyme inhibitors. When screened at 1 mM, a chelator fragment library (CFL-1.1) of 96 compounds produced... |
|
|
Application of Electrochemiluminescence for the Evaluation of the Antioxidant Capacity of Some Phenolic Compounds Against Superoxide Anion Radicals.
Anal. Sci. 31 , 629-34, (2015) This paper for the first time reports on novel and non-enzymatic method for studying the free radical-scavenging properties of phenolic compounds against superoxide anion radicals (O2·(-)) by using th... |
|
|
3D-QSAR and molecular docking studies of benzaldehyde thiosemicarbazone, benzaldehyde, benzoic acid, and their derivatives as phenoloxidase inhibitors.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 15 , 2006-15, (2007) Phenoloxidase (PO), also known as tyrosinase, is a key enzyme in insect development, responsible for catalyzing the hydroxylation of tyrosine into o-diphenols and the oxidation of o-diphenols into o-q... |
| p-Hydroxysalicylic acid |
| b-resorcylic acid |
| 2,4-dihydroxybenzoic_acid |
| 4-Carboxyresorcinol |
| resorcylic acid |
| 2,4-dihydroxy-benzoic acid |
| 2,4-Dihydroxy benzoic acid |
| Benzoic acid, 2,4-dihydroxy- |
| 2,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid |
| 2,4,6-TRIPHENYLPYRYLIUM TETRAFLUOROBORATE |
| Benzoic acid,2,4-dihydroxy |
| 4-Hydroxysalicylic acid |
| EINECS 201-946-9 |
| MFCD00002451 |
| 2,4-Dihydroxybenzenecarboxylic Acid |
 CAS#:108-46-3
CAS#:108-46-3 CAS#:2517-43-3
CAS#:2517-43-3 CAS#:107-98-2
CAS#:107-98-2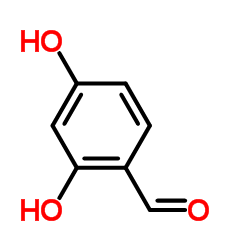 CAS#:95-01-2
CAS#:95-01-2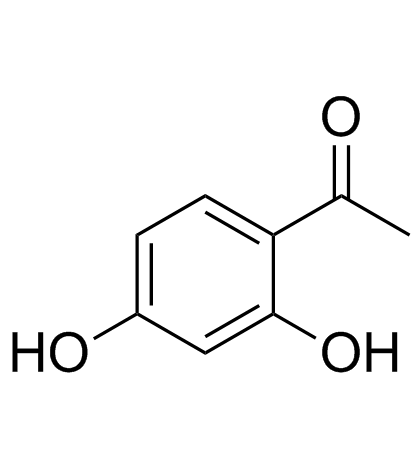 CAS#:89-84-9
CAS#:89-84-9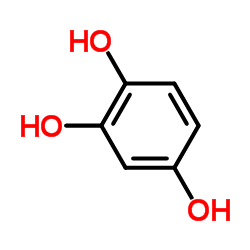 CAS#:533-73-3
CAS#:533-73-3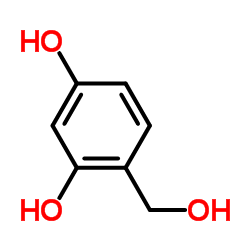 CAS#:33617-59-3
CAS#:33617-59-3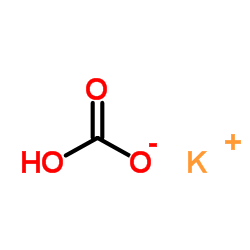 CAS#:298-14-6
CAS#:298-14-6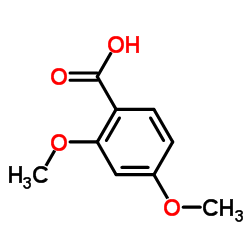 CAS#:91-52-1
CAS#:91-52-1 CAS#:69-72-7
CAS#:69-72-7 CAS#:106315-78-0
CAS#:106315-78-0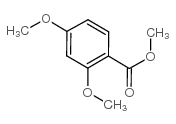 CAS#:2150-41-6
CAS#:2150-41-6 CAS#:606-45-1
CAS#:606-45-1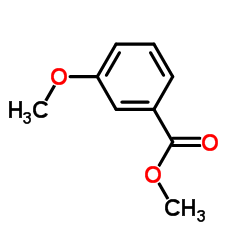 CAS#:5368-81-0
CAS#:5368-81-0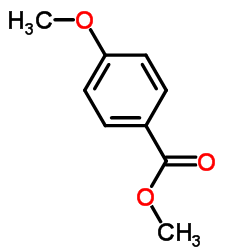 CAS#:121-98-2
CAS#:121-98-2 CAS#:2150-38-1
CAS#:2150-38-1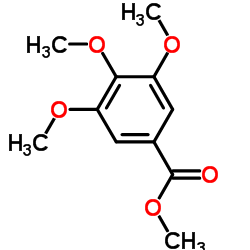 CAS#:1916-07-0
CAS#:1916-07-0 CAS#:2150-42-7
CAS#:2150-42-7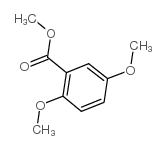 CAS#:2150-40-5
CAS#:2150-40-5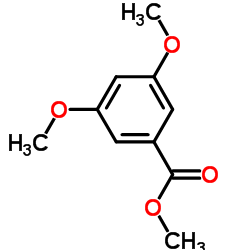 CAS#:2150-37-0
CAS#:2150-37-0
