Cholesterol esterase
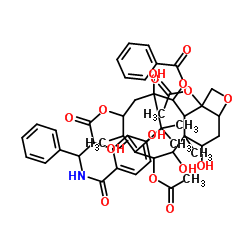
Cholesterol esterase structure
|
Common Name | Cholesterol esterase | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 9026-00-0 | Molecular Weight | 871.921 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 982.8±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C47H53NO15 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 548.2±34.3 °C | |
Use of Cholesterol esteraseCholesterol esterase is an enzyme that hydrolyzes cholesterol ester to cholesterol and free fatty acid in the intestinal lumen. Cholesterol synthesized in the acinar cells and is stored in zymogen granules. Cholesterol esterase is also known as bile salt-stimulated lipase and carboxy ester lipasea, acts function for acceleration of cholesterol absorption[1][2]. |
| Name | Esterase cholesterol |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Cholesterol esterase is an enzyme that hydrolyzes cholesterol ester to cholesterol and free fatty acid in the intestinal lumen. Cholesterol synthesized in the acinar cells and is stored in zymogen granules. Cholesterol esterase is also known as bile salt-stimulated lipase and carboxy ester lipasea, acts function for acceleration of cholesterol absorption[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 982.8±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C47H53NO15 |
| Molecular Weight | 871.921 |
| Flash Point | 548.2±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 871.341492 |
| LogP | 5.68 |
| Appearance of Characters | powder | white |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.651 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Water Solubility | Dissolve 1mg/ml in 0.1M phosphate buffer, pH 6.0 to 7.0 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Safety Phrases | 22-24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
Artificial sweeteners stimulate adipogenesis and suppress lipolysis independently of sweet taste receptors.
J. Biol. Chem. 288(45) , 32475-89, (2013) G protein-coupled receptors mediate responses to a myriad of ligands, some of which regulate adipocyte differentiation and metabolism. The sweet taste receptors T1R2 and T1R3 are G protein-coupled rec... |
|
|
Injection of phosphatidylcholine and deoxycholic acid regulates gene expression of lipolysis-related factors, pro-inflammatory cytokines, and hormones on mouse fat tissue.
Food Chem. Toxicol. 60 , 263-8, (2013) Injection of phosphatidylcholine (PC) and deoxycholic acid (DA) preparation is widely used as an alternative to liposuction for the reduction of subcutaneous fat. Nevertheless, its physiological effec... |
|
|
Modest hypoxia significantly reduces triglyceride content and lipid droplet size in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 440(1) , 43-9, (2013) A previous study has demonstrated that endurance training under hypoxia results in a greater reduction in body fat mass compared to exercise under normoxia. However, the cellular and molecular mechani... |
| Biocatalytics E3 |
| 4,10-Diacetoxy-1,7,9-trihydroxy-13-({2-hydroxy-3-[(4-hydroxybenzoyl)amino]-3-phenylpropanoyl}oxy)-5,20-epoxytax-11-en-2-yl benzoate |
| Bucelipase alfa |
| Bile salt-stimulated lipase |
| MFCD00071052 |
| Benzenepropanoic acid, α-hydroxy-β-[(4-hydroxybenzoyl)amino]-, 6,12b-bis(acetyloxy)-12-(benzoyloxy)-2a,3,4,4a,5,6,9,10,11,12,12a,12b-dodecahydro-4,5,11-trihydroxy-4a,8,13,13-tetramethyl-7,11-me thano-1H-cyclodeca[3,4]benz[1,2-b]oxet-9-yl ester |

