2-Acetonaphthone
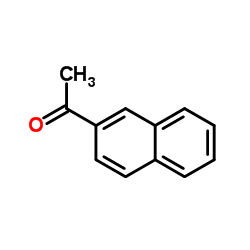
2-Acetonaphthone structure
|
Common Name | 2-Acetonaphthone | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 93-08-3 | Molecular Weight | 170.207 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 303.0±11.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C12H10O | Melting Point | 52-56 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 129.5±14.2 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of 2-Acetonaphthone2-Acetonaphthone is an endogenous metabolite. |
| Name | 2-acetylnaphthalene |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 2-Acetonaphthone is an endogenous metabolite. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 303.0±11.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 52-56 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C12H10O |
| Molecular Weight | 170.207 |
| Flash Point | 129.5±14.2 °C |
| Exact Mass | 170.073166 |
| PSA | 17.07000 |
| LogP | 2.90 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.615 |
| InChIKey | XSAYZAUNJMRRIR-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CC(=O)c1ccc2ccccc2c1 |
| Water Solubility | insoluble |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319-H335-H411 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P273-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R22;R36/37/38;R51/53 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36-S61-S24/25-S22-S36/37 |
| RIDADR | UN3077 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | DB7084000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 9 |
| HS Code | 29143900 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2914399090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2914399090. other aromatic ketones without other oxygen function. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:5.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Functional characterization of two acyltransferases from Populus trichocarpa capable of synthesizing benzyl benzoate and salicyl benzoate, potential intermediates in salicinoid phenolic glycoside biosynthesis.
Phytochemistry 113 , 149-59, (2015) Salicinoids are phenolic glycosides (PGs) characteristic of the Salicaceae and are known defenses against insect herbivory. Common examples are salicin, salicortin, tremuloidin, and tremulacin, which ... |
|
|
Organoleptic Characteristics of Flavor Materials Mosciano, G.
Perfum. Flavor. 4th ed., 28 , 104, (2003)
|
|
|
Mechanisms of Photoreactions in Solution. VI. 1 Reduction of 1-Naphthaldehyde and 2-Acetonaphthone. Hammond GS and Leermakers PA.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 84(2) , 207-211, (1962)
|
| 1-(2-Naphthyl)ethanone |
| ORANGE II |
| EINECS 202-216-2 |
| MANDARIN G |
| ORANGE P |
| 2-Acetylnaphthalene |
| ORANGE 2 |
| ORANGER |
| 1-(naphthalen-2-yl)ethanone |
| MFCD00004108 |
| ORANGE A |
| 2-Acetonaphthone |
| 1-(Naphthalen-2-yl)ethanon |
| Ethanone, 1-(2-naphthalenyl)- |
| FEMA 2723 |
| 2'-Acetonaphthone |
| 1-(2-naphthyl)-ethanone |
| β-Acetylnaphthalene |
| 1-(2-naphthyl)ethan-1-one |
| ORANGE Y |
| Ethanone, 1- (2-naphthalenyl)- |
| CI NO 5510 |
| 2-acetonaphthalene |
| methyl 2-naphthyl ketone |
| β-Acetonaphthalene |
| METHYL BETA-NAPHTHYL KETON |
 CAS#:7228-47-9
CAS#:7228-47-9 CAS#:120342-65-6
CAS#:120342-65-6 CAS#:939-27-5
CAS#:939-27-5 CAS#:613-54-7
CAS#:613-54-7 CAS#:32316-92-0
CAS#:32316-92-0 CAS#:75-05-8
CAS#:75-05-8 CAS#:827-54-3
CAS#:827-54-3 CAS#:111-34-2
CAS#:111-34-2 CAS#:580-13-2
CAS#:580-13-2 CAS#:107574-57-2
CAS#:107574-57-2 CAS#:351156-65-5
CAS#:351156-65-5 CAS#:4743-58-2
CAS#:4743-58-2![2-[(E)-2-Carboxyvinyl]benzoic acid structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/442/18454-53-0.png) CAS#:18454-53-0
CAS#:18454-53-0 CAS#:93-09-4
CAS#:93-09-4 CAS#:451-40-1
CAS#:451-40-1 CAS#:605-85-6
CAS#:605-85-6 CAS#:144371-23-3
CAS#:144371-23-3 CAS#:15914-84-8
CAS#:15914-84-8 CAS#:42177-25-3
CAS#:42177-25-3
