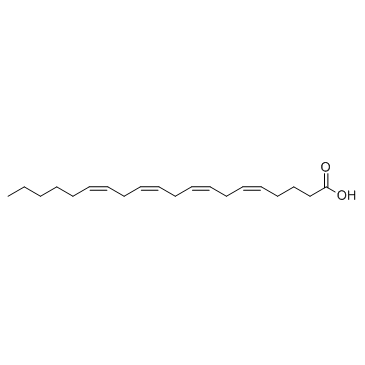
Anandamide
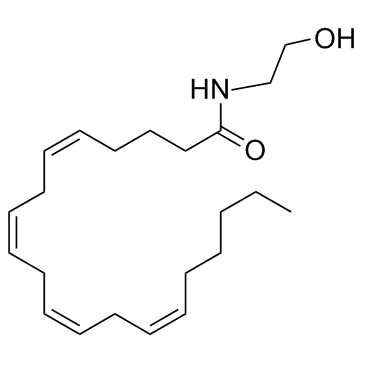
Anandamide structure
|
Common Name | Anandamide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 94421-68-8 | Molecular Weight | 347.535 | |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 522.3±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C22H37NO2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 269.7±30.1 °C | |
Use of AnandamideAnandamide is an immune modulator in the central nervous system acts via not only cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2) but also other targets (e.g., GPR18/GPR55). |
| Name | anandamide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Anandamide is an immune modulator in the central nervous system acts via not only cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2) but also other targets (e.g., GPR18/GPR55). |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
CB1 Receptor CB2 Receptor GPR18/GPR55 Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | Anandamide, acting via CB2 receptors, alleviates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced neuroinflammation in rat primary microglial cultures. The endocannabinoid system modulates both neuronal and immune functions through two protein-coupled cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2), although endocannabinoids, especially Anandamide (AEA), can activate numerous other receptors like PPARS, TRPV1, and GPR18/GPR55[1]. |
| In Vivo | Anandamide is an endocannabinoid binding both CB1R and CB2R. To evaluate the impact of CBR activation on whole-body glucose homeostasis, glucose tolerance is assessed after a single intraperitoneal Anandamide injection (10 mg/kg). The increase in glycemia in response to glucose ingestion is considerably smaller in mice treated with Anandamide compared with control, and this is associated with an improvement of glucose tolerance as illustrated by the AUC0-2h calculations[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[2] Eleven-week-old C57BL/6J male mice and global CB1R-/- mice are housed individually on a 12/12-h light/dark schedule at 22-23°C with ad libitum access to water and food. A group of mice is subject to a high-fat diet (30% lard). After 16 weeks of diet, animals with a weight gain less than +10 g compared with controls are excluded from the study. Diet-induced obesity (DIO) mice (39.1±1.1 vs. 27.3±0.9 g, DIO vs. control) are glucose intolerant and insulin resistant. On the day of each experiment, food is removed from the cages for 6 h (from 8:00 A.M. to 2:00 P.M.). Anandamide is administered intraperitoneally at 10 mg/kg. In control experiments, animals are injected with vehicle (4% DMSO/1% Tween 80)[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 522.3±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C22H37NO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 347.535 |
| Flash Point | 269.7±30.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 347.282440 |
| PSA | 49.33000 |
| LogP | 5.66 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.504 |
| InChIKey | LGEQQWMQCRIYKG-DOFZRALJSA-N |
| SMILES | CCCCCC=CCC=CCC=CCC=CCCCC(=O)NCCO |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Water Solubility | ethanol: soluble |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | F: Flammable; |
| Risk Phrases | R11 |
| Safety Phrases | 24/25-16-7 |
| RIDADR | UN 1170 3 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | JX3842500 |
| HS Code | 2924199090 |
|
~85% 
Anandamide CAS#:94421-68-8 |
| Literature: Ottria, Roberta; Casati, Silvana; Ciuffreda, Pierangela Chemistry and Physics of Lipids, 2012 , vol. 165, # 7 p. 705 - 711 |
|
~71% 
Anandamide CAS#:94421-68-8 |
| Literature: Ferreri, Carla; Anagnostopoulos, Dimitris; Lykakis, Ioannis N.; Chatgilialoglu, Chryssostomos; Siafaka-Kapadai, Athanassia Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry, 2008 , vol. 16, # 18 p. 8359 - 8365 |
|
~% 
Anandamide CAS#:94421-68-8 |
| Literature: US5925678 A1, ; |
|
~91% 
Anandamide CAS#:94421-68-8 |
| Literature: Adams, Irma B.; Ryan, William; Singer, Michael; Razdan, Raj K.; Compton, David R.; Martin, Billy R. Life Sciences, 1995 , vol. 56, # 23-24 p. 2041 - 2048 |
|
~% 
Anandamide CAS#:94421-68-8 |
| Literature: Biochemical Pharmacology, , vol. 69, # 8 p. 1187 - 1193 |
|
~% 
Anandamide CAS#:94421-68-8 |
| Literature: wyffels, Leonie; De Bruyne, Sylvie; Blanckaert, Peter; Lambert, Didier M.; De Vos, Filip Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry, 2009 , vol. 17, # 1 p. 49 - 56 |
|
~% 
Anandamide CAS#:94421-68-8 |
| Literature: Biochemical Pharmacology, , vol. 53, # 3 p. 255 - 260 |
| HS Code | 2924199090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2924199090. other acyclic amides (including acyclic carbamates) and their derivatives; salts thereof. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Gastric bypass in morbid obese patients is associated with reduction in adipose tissue inflammation via N-oleoylethanolamide (OEA)-mediated pathways.
Thromb. Haemost. 113(4) , 838-50, (2015) Paradoxically, morbid obesity was suggested to protect from cardiovascular co-morbidities as compared to overweight/obese patients. We hypothesise that this paradox could be inferred to modulation of ... |
|
|
On the effects of CP 55-940 and other cannabinoid receptor agonists in C6 and U373 cell lines.
Toxicol. In Vitro 29 , 1941-51, (2015) Cannabinoid receptor (CBs) agonists affect the growth of tumor cells via activation of deadly cascades. The spectrum of action of these agents and the precise role of the endocannabinoid system (ECS) ... |
|
|
Endocannabinoids regulate the activity of astrocytic hemichannels and the microglial response against an injury: In vivo studies.
Neurobiol. Dis. 79 , 41-50, (2015) Anandamide (AEA) is an endocannabinoid (EC) that modulates multiple functions in the CNS and that is released in areas of injury, exerting putative neuroprotective actions. In the present study, we ha... |
| arachidonic acid ethanolamide |
| MFCD00153766 |
| (5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)-N-(2-Hydroxyethyl)-5,8,11,14-icosatetraenamide |
| N-arachidonoylethanolamide |
| 5,8,11,14-Eicosatetraenamide, N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-, (5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)- |
| N-arachidonoylethanolamine |
| arachidonylethanolamide |
| 5,8,11,14-Eicosatetraenoylethanolamide |
| N-Arachidonoyl-2-hydroxyethylamide |
| N-arachidonoyl ethanolamine |
| arachidonoylethanolamide |
| Arachidonoyl-EA |
| (5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)-N-(2-Hydroxyethyl)icosa-5,8,11,14-tetraenamide |