Rotigotine
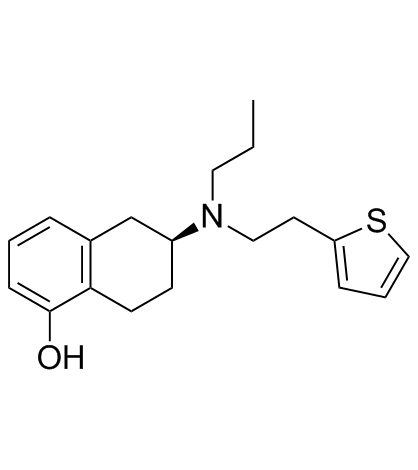
Rotigotine structure
|
Common Name | Rotigotine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 99755-59-6 | Molecular Weight | 315.473 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 470.1±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H25NOS | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 238.1±28.7 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of RotigotineRotigotine is a full agonist of dopamine receptor, a partial agonist of the 5-HT1A receptor, and an antagonist of the α2B-adrenergic receptor, with Kis of 0.71 nM, 4-15 nM, and 83 nM for the dopamine D3 receptor and D2, D5, D4 receptors, and dopamine D1 receptor. |
| Name | [14C]-Rotigotine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Rotigotine is a full agonist of dopamine receptor, a partial agonist of the 5-HT1A receptor, and an antagonist of the α2B-adrenergic receptor, with Kis of 0.71 nM, 4-15 nM, and 83 nM for the dopamine D3 receptor and D2, D5, D4 receptors, and dopamine D1 receptor. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Ki: 0.71 nM (dopamine D3 receptor), 4-15 nM (D2, D5, D4 receptors), 83 nM (dopamine D1 receptor)[1][2], 176 nM (α1A), 273 nM (α1B), 338 nM (α2A), 27 nM (α2B), 30 nM (5-HT1A), 86 nM (5-HT7)[2] |
| In Vitro | Rotigotine has a 10-fold selectivity for D3 (pKi 9.2) receptors compared with D2, D4 and D5 (pKi 8.5-8.0) and a 100-fold selectivity compared with D1 receptors (pKi 7.2). In functional studies, Rotigotine behaves as full agonist at all dopamine receptors but notably the potency for stimulation of D1 receptors is similar to that for D2 and D3 receptors (pEC50 respectively: 9.0, 9.4-8.6, 9.7)[1]. Rotigotine (10 µM) decreases the number of THir neurons by 40% in primary mesencephalic cell culture. Rotigotine (0.01 µM) slightly protects dopaminergic neurons against MPP+ toxicity, significantly protects dopaminergic neurons against rotenone-induced cell death, and significantly inhibits ROS production by rotenone[4]. |
| In Vivo | In primed rats, Rotigotine (0.035, 0.1 and 0.35 mg/kg) induces contralateral turning behavior in a dose dependent manner. In drug naive rats, the turning behavior induced by Rotigotine, either alone or in combination with SCH 39166, is reduced compared to primed rats[3]. |
| Kinase Assay | Binding assays are performed in 96-well polypropylene tubes in a final volume of 2 mL for D1 and D4 membranes and 1 mL for D2, D3 and D5 membranes containing: 50 μL radioligand, 10 μL drug/buffer/non-specific binding, buffer (final concentration 50 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.4, MgCl2 2 mM) and membranes (5 μg protein for D2 and D3 and 25 μg protein for D1 and D5). Following 120 min of incubation at 25°C, bound radioligand is determined by rapid vacuum filtration through A/C glass fibre filters presoaked in 0.1% polyethylenimine. The filters are washed four times with 2 mL ice-cold ishing buffer (Tris-HCl 50 mM, pH 7.4 at 4°C) and retained radioactivity is determined by liquid scintillation counting. |
| Animal Admin | Primed rats: Two weeks after the 6-OHDA lesions, rats are primed with apomorphine (0.5 mg/kg s.c.). Rats showing less than 150 contralateral rotations during the 1 h testing period are excluded from the study. Three days after priming, rats are divided into different experimental groups and treated with different doses of the dopamine receptor agonists (Rotigotine or pramipexole) alone or in combination with dopamine D1 (SCH 39166) or D2 (eticlopride) receptor antagonists as reported: saline+Rotigotine (0.035 mg/kg s.c., n=9; 0.1 mg/kg s.c., n=9; 0.35 mg/kg s.c., n=8); SCH 39166 (0.1 mg/kg s.c.)+Rotigotine (0.035 mg/kg s.c., n=5; 0.1 mg/kg s.c., n=7; 0.35 mg/kg s.c., n=5); eticlopride (0.1 mg/kg s.c.) + Rotigotine (0.1 mg/kg s.c., n=5; 0.35 mg/kg s.c., n=5); Saline+pramipexole (0.035 mg/kg s.c., n=5; 0.1 mg/kg s.c., n=12; 0.35 mg/kg s.c., n=7); SCH 39166 (0.1 mg/kg s.c.)+pramipexole (0.035 mg/kg s.c., n=5; 0.1 mg/kg s.c., n=6; 0.35 mg/kg s.c., n=6); eticlopride (0.1 mg/kg s.c.)+pramipexole (0.1 mg/kg s.c., n=7; 0.35 mg/kg s.c., n=5). |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 470.1±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C19H25NOS |
| Molecular Weight | 315.473 |
| Flash Point | 238.1±28.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 315.165680 |
| PSA | 51.71000 |
| LogP | 4.96 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.611 |
| Storage condition | room temp |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |
| HS Code | 2934999090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2934999090. other heterocyclic compounds. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Three-month subchronic intramuscular toxicity study of rotigotine-loaded microspheres in Cynomolgus monkeys.
Food Chem. Toxicol. 52 , 143-52, (2013) Continuous dopaminergic stimulation (CDS) is an important drug development strategy in the treatment of Parkinson's disease (PD). Rotigotine is a non-ergoline D(3)/D(2)/D(1) dopamine receptor agonist ... |
|
|
Medication update.
Nurse Pract. 37(6) , 56, (2012)
|
|
|
ADMET considerations for restless leg syndrome drug treatments.
Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 8(10) , 1247-61, (2012) Restless legs syndrome (RLS) is a common neurological disorder that might impair nocturnal rest causing decreased alertness, depressed mood, reduced job performance, and poor quality of life. In patie... |
| (S)-ROTIGOTINE |
| Rotigotine hydrochloride |
| Rotigotine |
| (6S)-6-{Propyl[2-(2-thienyl)ethyl]amino}-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-1-naphthalenol |
| (6S)-6-{propyl[2-(thiophen-2-yl)ethyl]amino}-5,6,7,8-tetrahydronaphthalen-1-ol |
| (-)-Rotigotine |
| 1-Naphthalenol, 5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-6-[propyl[2-(2-thienyl)ethyl]amino]-, (6S)- |
| (S)-5,6,7,8-TETRAHYDRO-6-(PROPYL(2-(2-THIENYL)ETHYL)AMINO)-1-NAPHTHOL |
| Neupro |
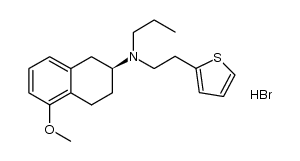 CAS#:1222074-05-6
CAS#:1222074-05-6 CAS#:125572-93-2
CAS#:125572-93-2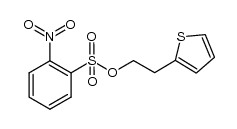 CAS#:1222074-06-7
CAS#:1222074-06-7 CAS#:101470-23-9
CAS#:101470-23-9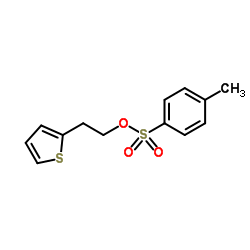 CAS#:40412-06-4
CAS#:40412-06-4 CAS#:1148154-91-9
CAS#:1148154-91-9 CAS#:1229620-82-9
CAS#:1229620-82-9 CAS#:1231158-76-1
CAS#:1231158-76-1 CAS#:1918-77-0
CAS#:1918-77-0