β-丙氨酸
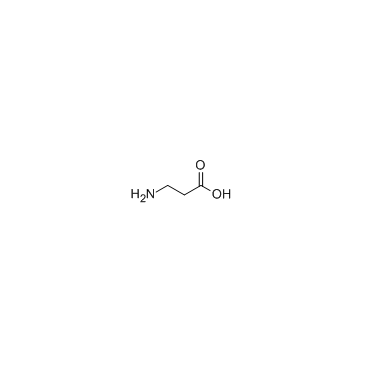
β-丙氨酸结构式

|
常用名 | β-丙氨酸 | 英文名 | beta-Alanine |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 107-95-9 | 分子量 | 89.093 | |
| 密度 | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 237.1±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C3H7NO2 | 熔点 | 202 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 97.2±22.6 °C |
|
Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine in prostate cancer progression.
Nature 457(7231) , 910-4, (2009) Multiple, complex molecular events characterize cancer development and progression. Deciphering the molecular networks that distinguish organ-confined disease from metastatic disease may lead to the identification of critical biomarkers for cancer invasion an... |
|
|
Automated screening of urine samples for carbohydrates, organic and amino acids after treatment with urease.
J. Chromatogr. A. 562(1-2) , 125-38, (1991) Eighty-five clinical urine samples and nineteen urine samples previously found by other laboratories to suggest genetic metabolic defects were prepared for trimethylsilylation by treatment with urease, followed by azeotropic dehydration. The "Target Analyte S... |
|
|
Urinary and plasma organic acids and amino acids in chronic fatigue syndrome.
Clin. Chim. Acta 361(1-2) , 150-8, (2005) Previous work by others have suggested the occurrence of one or more chemical or metabolic 'markers' for ME/CFS including specific amino acids and organic acids and a number of unidentified compounds (CFSUM1, CFSUM2). We have shown elsewhere that CFSUM1 is pa... |
|
|
Peptide dimethylation: fragmentation control via distancing the dimethylamino group.
J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 25(10) , 1694-704, (2014) Direct reductive methylation of peptides is a common method for quantitative proteomics. It is an active derivatization technique; with participation of the dimethylamino group, the derivatized peptides preferentially release intense a1 ions. The advantageous... |
|
|
Detection of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease by NMR spectroscopic fingerprinting of urine.
Kidney Int. 79(11) , 1244-53, (2011) Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is a frequent cause of kidney failure; however, urinary biomarkers for the disease are lacking. In a step towards identifying such markers, we used multidimensional-multinuclear nuclear magnetic resonance (... |
|
|
Highly sensitive GC/MS/MS method for quantitation of amino and nonamino organic acids.
Anal. Chem. 83(7) , 2705-11, (2011) Metabolite profiling methods are important tools for measurement of metabolite pools in biological systems. While most metabolite profiling methods report relative intensities or depend on a few internal standards representing all metabolites, the ultimate re... |
|
|
Subpathway-GMir: identifying miRNA-mediated metabolic subpathways by integrating condition-specific genes, microRNAs, and pathway topologies.
Oncotarget 6 , 39151-64, (2015) MicroRNAs (miRNAs) regulate disease-relevant metabolic pathways. However, most current pathway identification methods fail to consider miRNAs in addition to genes when analyzing pathways. We developed a powerful method called Subpathway-GMir to construct miRN... |
|
|
Discovery of Dap-3 polymyxin analogues for the treatment of multidrug-resistant Gram-negative nosocomial infections.
J. Med. Chem. 56(12) , 5079-93, (2013) We report novel polymyxin analogues with improved antibacterial in vitro potency against polymyxin resistant recent clinical isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa . In addition, a human renal cell in vitro assay (hRPTEC) was used to i... |
|
|
Comparative analysis and modeling of the severity of steatohepatitis in DDC-treated mouse strains.
PLoS ONE 9(10) , e111006, (2014) Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has a broad spectrum of disease states ranging from mild steatosis characterized by an abnormal retention of lipids within liver cells to steatohepatitis (NASH) showing fat accumulation, inflammation, ballooning and d... |
|
|
Human variation and CYP enzyme contribution in benfuracarb metabolism in human in vitro hepatic models.
Toxicol. Lett. 224(2) , 300-9, (2014) Human responses to the toxicological effects of chemicals are often complicated by a substantial interindividual variability in toxicokinetics, of which metabolism is often the most important factor. Therefore, we investigated human variation and the contribu... |