蔗糖酶
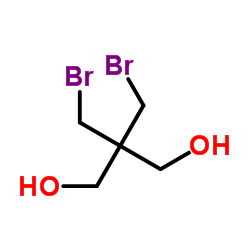
蔗糖酶结构式

|
常用名 | 蔗糖酶 | 英文名 | invertase |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 9001-57-4 | 分子量 | 261.940 | |
| 密度 | 2.0±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 370.9±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C5H10Br2O2 | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 美版 | 闪点 | 178.1±27.9 °C |
|
Physiological responses of biomass allocation, root architecture, and invertase activity to copper stress in young seedlings from two populations of Kummerowia stipulacea (maxim.) Makino.
Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 104 , 278-84, (2014) In the current study, we hypothesize that mine (metallicolous) populations of metallophytes form a trade-off between the roots and shoots when under copper (Cu) stress to adapt themselves to heavy metal contaminated habitats, and thus, differ from normal (non... |
|
|
The genetics of a putative social trait in natural populations of yeast.
Mol. Ecol. 23(20) , 5061-71, (2014) The sharing of secreted invertase by yeast cells is a well-established laboratory model for cooperation, but the only evidence that such cooperation occurs in nature is that the SUC loci, which encode invertase, vary in number and functionality. Genotypes tha... |
|
|
Production optimization of invertase by Lactobacillus brevis Mm-6 and its immobilization on alginate beads.
Carbohydr. Polym. 93(2) , 740-6, (2013) A sequential optimization strategy, based on statistical experimental designs, was employed to enhance the production of invertase by Lactobacillus brevis Mm-6 isolated from breast milk. First, a 2-level Plackett-Burman design was applied to screen the biopro... |
|
|
Cloning and characterization of acid invertase genes in the roots of the metallophyteKummerowia stipulacea(Maxim.) Makino from two populations: Differential expression under copper stress
Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 104 , 87-95, (2014) The roots of metallophytes serve as the key interface between plants and heavy metal-contaminated underground environments. It is known that the roots of metallicolous plants show a higher activity of acid invertase enzymes than those of non-metallicolous pla... |
|
|
Qualitative and event-specific real-time PCR detection methods for Bt brinjal event EE-1.
J. AOAC Int. 95(6) , 1733-9, (2012) Bt brinjal event EE-1 with cry1Ac gene, expressing insecticidal protein against fruit and shoot borer, is the first genetically modified food crop in the pipeline for commercialization in India. Qualitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) along with event-spe... |
|
|
Excess nickel modulates activities of carbohydrate metabolizing enzymes and induces accumulation of sugars by upregulating acid invertase and sucrose synthase in rice seedlings.
Biometals 26(1) , 97-111, (2013) The effects of increasing concentrations of nickel sulfate, NiSO(4) (200 and 400 μM) in the growth medium on the content of starch and sugars and activity levels of enzymes involved in starch and sugar metabolism were examined in seedlings of the two Indica r... |
|
|
The ABC transporter encoded at the pneumococcal fructooligosaccharide utilization locus determines the ability to utilize long- and short-chain fructooligosaccharides.
J. Bacteriol. 195(5) , 1031-41, (2013) Streptococcus pneumoniae is an important human pathogen that requires carbohydrates for growth. The significance of carbohydrate acquisition is highlighted by the genome encoding more than 27 predicted carbohydrate transporters. It has long been known that ab... |
|
|
Nrg1 functions as a global transcriptional repressor of glucose-repressed genes through its direct binding to the specific promoter regions.
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 439(4) , 501-5, (2013) Nrg1 is a zinc finger protein involved in the glucose repression of several glucose-repressed genes such as STA1, SUC2, and GAL1. Although the molecular details of the Nrg1-mediated repression of STA1 have been partly characterized, it still remains largely u... |
|
|
The new nucleoporin: regulator of transcriptional repression and beyond.
Nucleus 3(6) , 508-15, (2012) Transcriptional regulation is a complex process that requires the integrated action of many multi-protein complexes. The way in which a living cell coordinates the action of these complexes in time and space is still poorly understood. Recent work has shown t... |
|
|
Effect of repeated applications of buprofezin and acephate on soil cellulases, amylase, and invertase.
Environ. Monit. Assess. 186(10) , 6319-25, (2014) The impact of repeated applications of buprofezin and acephate, at concentrations ranging from 0.25 to 1.0 kg ha(-1), on activities of cellulases, amylase, and invertase in unamended and nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium (NPK) fertilizer-amended soil plant... |