叠氮化钠
一般危化品
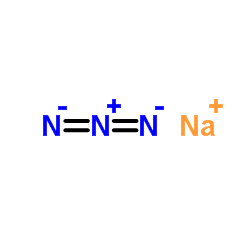
叠氮化钠结构式
|
常用名 | 叠氮化钠 | 英文名 | Sodium azide |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 26628-22-8 | 分子量 | 65.010 | |
| 密度 | 1.85 | 沸点 | 300 °C | |
| 分子式 | N3Na | 熔点 | 275 °C | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 300 °C | |
| 符号 |



GHS06, GHS08, GHS09 |
信号词 | Danger |
|
Crystal structure of the R-protein of the multisubunit ATP-dependent restriction endonuclease NgoAVII.
Nucleic Acids Res. 42(22) , 14022-30, (2014) The restriction endonuclease (REase) NgoAVII is composed of two proteins, R.NgoAVII and N.NgoAVII, and shares features of both Type II restriction enzymes and Type I/III ATP-dependent restriction enzymes (see accompanying paper Zaremba et al., 2014). Here we ... |
|
|
The dynamics of giant unilamellar vesicle oxidation probed by morphological transitions.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1838(10) , 2615-24, (2014) We have studied the dynamics of Lissamine Rhodamine B dye sensitization-induced oxidation of 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DOPC) giant unilamellar vesicles (GUVs), where the progression of the underlying chemical processes was followed via vesicle... |
|
|
Investigations on the transfer of porphyrin from o/w emulsion droplets to liposomes with two different methods.
Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 41(1) , 156-62, (2014) Due to their small particle size, colloidal fat emulsions are suitable for intravenous administration. In order to obtain information on their potential in vivo performance, it is important to find a simple and effective in vitro assay to evaluate the drug re... |
|
|
β-Amyloid1-42, HIV-1Ba-L (clade B) infection and drugs of abuse induced degeneration in human neuronal cells and protective effects of ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) and its constituent Withanolide A.
PLoS ONE 9(11) , e112818, (2014) Alzheimer's disease (AD) is characterized by progressive dysfunction of memory and higher cognitive functions with abnormal accumulation of extracellular amyloid plaques and intracellular neurofibrillary tangles throughout cortical and limbic brain regions. W... |
|
|
Coculture of peripheral blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells and endothelial progenitor cells on strontium-doped calcium polyphosphate scaffolds to generate vascularized engineered bone.
Tissue Eng. Part A 21(5-6) , 948-59, (2015) Vascularization of engineered bone tissue is critical for ensuring its survival after implantation and it is the primary factor limiting its clinical use. A promising approach is to prevascularize bone grafts in vitro using endothelial progenitor cells (EPC) ... |
|
|
pH dependence of the stress regulator DksA.
PLoS ONE 10(3) , e0120746, (2015) DksA controls transcription of genes associated with diverse stress responses, such as amino acid and carbon starvation, oxidative stress, and iron starvation. DksA binds within the secondary channel of RNA polymerase, extending its long coiled-coil domain to... |
|
|
Construction and physiochemical characterisation of a multi-composite, potential oral vaccine delivery system (VDS).
Int. J. Pharm. 468(1-2) , 264-71, (2014) An increasing human population requires a secure food supply and a cost effective, oral vaccine delivery system for livestock would help facilitate this end. Recombinant antigen adsorbed onto silica beads and coated with myristic acid, was released (∼15% (w/v... |
|
|
Local synthesis of interferon-alpha in lupus nephritis is associated with type I interferons signature and LMP7 induction in renal tubular epithelial cells.
Arthritis. Res. Ther. 17 , 72, (2015) Type I interferons are pivotal in the activation of autoimmune response in systemic lupus erythematous. However, the pathogenic role of interferon-alpha in patients affected by lupus nephritis remains uncertain. The aim of our study was to investigate the pre... |
|
|
Development and validation of a stability-indicating LC-UV method for the determination of pantethine and its degradation product based on a forced degradation study.
J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 97 , 141-50, (2014) Pantethine (d-bis-(N-pantothenyl-β-aminoethyl)-disulfide, PAN), the stable disulfide form of pantetheine, has beneficial effects in vascular diseases being able to decrease the hyperlipidaemia, moderate the platelet function and prevent the lipid peroxidation... |
|
|
Loss of SPARC dysregulates basal lamina assembly to disrupt larval fat body homeostasis in Drosophila melanogaster.
Dev. Dyn. 244(4) , 540-52, (2015) SPARC is a collagen-binding glycoprotein whose functions during early development are unknown. We previously reported that SPARC is expressed in Drosophila by hemocytes and the fat body (FB) and enriched in basal laminae (BL) surrounding tissues, including ad... |