13(s)-羟基-9z,11e-十八二烯酸
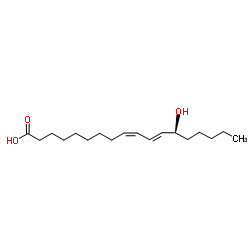
13(s)-羟基-9z,11e-十八二烯酸结构式

|
常用名 | 13(s)-羟基-9z,11e-十八二烯酸 | 英文名 | 13S-hydroxyoctadecadienoic acid |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 29623-28-7 | 分子量 | 296.445 | |
| 密度 | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 422.7±20.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C18H32O3 | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 美版 | 闪点 | 223.6±18.3 °C | |
| 符号 |


GHS02, GHS07 |
信号词 | Danger |
|
Light exposure at night disrupts host/cancer circadian regulatory dynamics: impact on the Warburg effect, lipid signaling and tumor growth prevention.
PLoS ONE 9(8) , e102776, (2014) The central circadian clock within the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) plays an important role in temporally organizing and coordinating many of the processes governing cancer cell proliferation and tumor growth in synchrony with the daily light/dark cycle whic... |
|
|
Doxorubicin resistance in breast cancer is driven by light at night-induced disruption of the circadian melatonin signal.
J. Pineal Res. 59 , 60-9, (2015) Chemotherapeutic resistance, particularly to doxorubicin (Dox), represents a major impediment to successfully treating breast cancer and is linked to elevated tumor metabolism and tumor over-expression and/or activation of various families of receptor- and no... |
|
|
Implications of chemokines, chemokine receptors, and inflammatory lipids in atherosclerosis.
J. Leukoc. Biol. 95(4) , 575-85, (2014) Chemokines are a diverse group of molecules with important implications for the development of solid tissues and normal function of the immune system. However, change of the conditions for such a complex system can have important and dangerous consequences le... |
|
|
Effect of ω-3 and ω-9 fatty acid rich oils on lipoxygenases and cyclooxygenases enzymes and on the growth of a mammary adenocarcinoma model.
Lipids Health Dis. 9 , 112, (2010) Nutritional factors play a major role in cancer initiation and development. Dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) have the ability to induce modifications in the activity of lipoxygenase (LOX) and cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes that affect tumour growth. ... |
|
|
Ligand-induced formation of transient dimers of mammalian 12/15-lipoxygenase: a key to allosteric behavior of this class of enzymes?
Proteins 80(3) , 703-12, (2012) Mammalian lipoxygenases (LOXs) have been implicated in cellular defense response and are important for physiological homeostasis. Since their discovery, LOXs have been believed to function as monomeric enzymes that exhibit allosteric properties. In aqueous so... |
|
|
Roles of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha and -gamma in the development of non-small cell lung cancer.
Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 43(6) , 674-83, (2010) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)-α and PPARγ participate in cell proliferation and apoptosis. Few studies have simultaneously investigated both PPARα and PPARγ in lung cancers in vivo. The roles of PPARα and -γ were investigated in the develo... |
|
|
Relation of blood cadmium, lead, and mercury levels to biomarkers of lipid peroxidation in premenopausal women.
Am. J. Epidemiol. 175(7) , 645-52, (2012) Exposures to cadmium, lead, and mercury are associated with adverse health effects, including cardiovascular disease, which may be promoted by lipid peroxidation. The authors examined cadmium, lead, and mercury in relation to plasma levels of F(2)-8α isoprost... |
|
|
Profiling lipoxygenase metabolism in specific steps of colorectal tumorigenesis.
Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila.) 3(7) , 829-38, (2010) Lipoxygenases (LOX) are key enzymes for the oxidative metabolism of polyunsaturated fatty acids into biologically active products. Clinical data on comparative levels of various LOX products in tumorigenesis are lacking. Therefore, we examined the profiles of... |
|
|
Circadian stage-dependent inhibition of human breast cancer metabolism and growth by the nocturnal melatonin signal: consequences of its disruption by light at night in rats and women.
Integr. Cancer Ther. 8(4) , 347-53, (2009) The circadian production of melatonin by the pineal gland during the night provides an inhibitory signal to tissue-isolated steroid receptor SR+ and - MCF-7 human breast cancer xenografts in female nude rats. A pivotal mechanism for melatonin's anticancer eff... |
|
|
12/15-lipoxygenase expressed in non-epithelial cells causes airway epithelial injury in asthma.
Sci. Rep. 3 , 1540, (2013) The mechanisms underlying asthmatic airway epithelial injury are not clear. 12/15-lipoxygenase (an ortholog of human 15-LOX-1), which is induced by IL-13, is associated with mitochondrial degradation in reticulocytes at physiological conditions. In this study... |