4-乙基苯酚
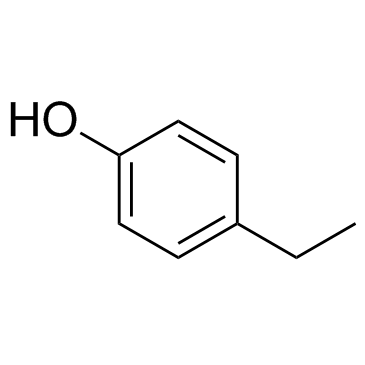
4-乙基苯酚结构式

|
常用名 | 4-乙基苯酚 | 英文名 | 4-Ethylphenol |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 123-07-9 | 分子量 | 122.164 | |
| 密度 | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 219.0±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C8H10O | 熔点 | 40-42 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 100.6±0.0 °C | |
| 符号 |

GHS05 |
信号词 | Danger |
|
Convenient QSAR model for predicting the complexation of structurally diverse compounds with β-cyclodextrins
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17 , 896-904, (2009) This paper reports a QSAR study for predicting the complexation of a large and heterogeneous variety of substances (233 organic compounds) with beta-cyclodextrins (beta-CDs). Several different theoretical molecular descriptors, calculated solely from the mole... |
|
|
Cellular apoptosis and cytotoxicity of phenolic compounds: a quantitative structure-activity relationship study.
J. Med. Chem. 48 , 7234-42, (2005) In this comprehensive study on the caspase-mediated apoptosis-inducing effect of 51 substituted phenols in a murine leukemia cell line (L1210), we determined the concentrations needed to induce caspase activity by 50% (I50) and utilized these data to develop ... |
|
|
Simple and sensitive GC/MS-method for the quantification of urinary phenol, o- and m-cresol and ethylphenols as biomarkers of exposure to industrial solvents.
J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 995-996 , 93-100, (2015) We have developed and validated a simple and sensitive method for the determination of urinary phenol as well as the urinary metabolites of toluene and ethylbenzene in one analytical run. After enzymatic hydrolysis for the cleavage of conjugates overnight, th... |
|
|
Parallel artificial membrane permeability assay: a new membrane for the fast prediction of passive human skin permeability.
J. Med. Chem. 49 , 3948-54, (2006) This work was devoted to the search for new artificial membranes allowing a rapid evaluation of passive human skin permeation of compounds with a parallel artificial membrane permeability assay (PAMPA). Effective permeability coefficients (Pe) determined for ... |
|
|
In silico and in vitro filters for the fast estimation of skin permeation and distribution of new chemical entities.
J. Med. Chem. 50 , 742-8, (2007) The development of in silico and in vitro tools to estimate or predict the passive human skin permeation and distribution of new chemical entities, useful in dermal drug delivery, in absorption studies of toxic compounds, and in the cosmetics industry, is pre... |
|
|
Characterization of Volatile Flavor Compounds in Chinese Rice Wine Fermented from Enzymatic Extruded Rice.
J. Food Sci. 80 , C1476-89, (2015) Enzymatic extrusion, instead of traditional steam cooking, to treat rice is an efficient and alternative pretreatment for Chinese rice wine fermentation. In order to determine the formation of volatiles in enzymatic extrusion-processed rice wine (EE), and to ... |
|
|
Aroma improvement by repeated freeze-thaw treatment during Tuber melanosporum fermentation.
Sci. Rep. 5 , 17120, (2015) The aroma attributes of sulfurous, mushroom and earthy are the most important characteristics of the aroma of Tuber melanosporum. However, these three aroma attributes are absent in the T. melanosporum fermentation system. To improve the quality of the aroma,... |
|
|
Oral administration of fermented probiotics improves the condition of feces in adult horses.
J. Equine. Sci. 25(4) , 65-72, (2015) The effects of probiotics on horses are still controversial. The present study was a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled crossover study designed to evaluate the ability of probiotics to improve intestinal conditions in adult horses. Fermented prob... |
|
|
Effect of experimental diabetes and insulin replacement on intestinal metabolism and excretion of 4-nitrophenol in rats.
Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 93 , 459-64, (2015) Luminal appearance of 4-nitrophenol (PNP) metabolites (4-nitrophenol-β-glucuronide (PNP-G) and 4-nitrophenol-sulfate (PNP-S)) and activity of the related metabolic enzymes have been investigated in control and experimental diabetic rats. Experimental diabetes... |
|
|
Molecularly imprinted polymers as a tool for the study of the 4-ethylphenol metabolic pathway in red wines.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1410 , 164-72, (2015) A molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) based methodology is described here for the determination of compounds that belong to the 4-ethylphenol (4EP) metabolic pathway in red wines. To this end, two MIP materials have been developed: a 4EP MIP as a class-select... |