4-甲基香豆素基-α-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷
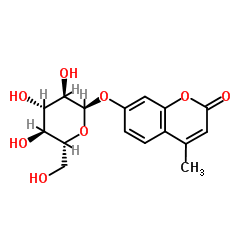
4-甲基香豆素基-α-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷结构式

|
常用名 | 4-甲基香豆素基-α-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷 | 英文名 | 7-(alpha-D-Glucopyranosyloxy)-4-methyl-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 17833-43-1 | 分子量 | 338.309 | |
| 密度 | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 626.9±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C16H18O8 | 熔点 | 171-173ºC | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 233.9±25.0 °C |
|
Glycosylation variants of a β-glucosidase secreted by a Taiwanese fungus, Chaetomella raphigera, exhibit variant-specific catalytic and biochemical properties.
PLoS ONE 9(9) , e106306, (2014) Cellulosic biomass is an abundant and promising energy source. To make cellulosic biofuels competitive against conventional fuels, conversion of rigid plant materials into sugars must become efficient and cost-effective. During cellulose degradation, cellulol... |
|
|
Scopolin-hydrolyzing beta-glucosidases in roots of Arabidopsis.
Plant Cell Physiol. 51(1) , 132-43, (2010) Three beta-glucosidases (At1g66270-BGLU21, At1g66280-BGLU22, and At3g09260-BGLU23) were purified from the roots of Arabidopsis and their cDNAs were expressed in insect cells. In addition, two beta-glucosidase binding protein cDNAs (At3g16420; PBPI and At3g164... |
|
|
Mechanism of the hydrolysis of 4-methylumbelliferyl-beta-D-glucoside by germinating and outgrowing spores of Bacillus species.
J. Appl. Microbiol. 96(6) , 1245-55, (2004) To determine the mechanism of the hydrolysis of 4-methylumbelliferyl-beta-D-glucopyranoside (beta-MUG) by germinating and outgrowing spores of Bacillus species.Spores of B. atrophaeus (formerly B. subtilis var. niger, Fritze and Pukall 2001) are used as biolo... |
|
|
The interplay of processivity, substrate inhibition and a secondary substrate binding site of an insect exo-beta-1,3-glucanase.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1774(9) , 1079-91, (2007) Abracris flavolineata midgut contains a processive exo-beta-glucanase (ALAM) with lytic activity against Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which was purified (yield, 18%; enrichment, 37 fold; specific activity, 1.89 U/mg). ALAM hydrolyses fungal cells or callose from... |
|
|
beta-Glucocerebrosidase activity in murine epidermis: characterization and localization in relation to differentiation.
J. Lipid Res. 33(8) , 1201-9, (1992) The intercellular lipids of the stratum corneum, which are highly enriched in ceramides, are critical for the mammalian epidermal permeability barrier. During the terminal stages of epidermal differentiation, the glucosylceramide content is dramatically reduc... |
|
|
Synthesis of 4-methylumbelliferyl-beta-D-glucan oligosaccharides as specific chromophoric substrates of (1-->3), (1-->4)-beta-D-glucan 4-glucanohydrolases.
Carbohydr. Res. 274 , 285-301, (1995)
|
|
|
Extracellular enzyme activities during slow sand filtration in a water recharge plant.
Water Res. 35(10) , 2484-8, (2001) Activities of the extracellular enzymes beta-glucosidase and phosphatase and bacterial densities were investigated during the filtration process at several sites in a groundwater recharge plant at the Ruhr river (Hengsen recharge plant in Schwerte. Germany). ... |
|
|
Development of sensitive chemical and immunochemical methods for detecting sulfated sialic acids and their application to glycoconjugates from sea urchin sperm and eggs.
Biochimie 89(11) , 1396-408, (2007) Sulfated sialic acid (SiaS) is a unique sialic acid (Sia) derivative in which an additional anionic group is attached to a carboxylated monosaccharide. Very little is known about the occurrence and biologic function of SiaS, due to the limitations of analytic... |
|
|
Study of beta-glucosidase production by wine-related yeasts during alcoholic fermentation. A new rapid fluorimetric method to determine enzymatic activity.
J. Appl. Microbiol. 99(3) , 509-17, (2005) The beta-glucosidase activity is involved in the hydrolysis of several important compounds for the development of varietal wine flavour. The aim of the present study was to investigate the production of beta-glucosidase in a number of wine-related yeast strai... |
|
|
Endoplasmic reticulum stress underlying the pro-apoptotic effect of epigallocatechin gallate in mouse hepatoma cells
Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 41(3) , 694-700, (2009) It has been recently reported that tea flavanols, including epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), efficiently inhibit glucosidase II in liver microsomes. Since glucosidase II plays a central role in glycoprotein processing and quality control in the endoplasmic re... |