甘露醇
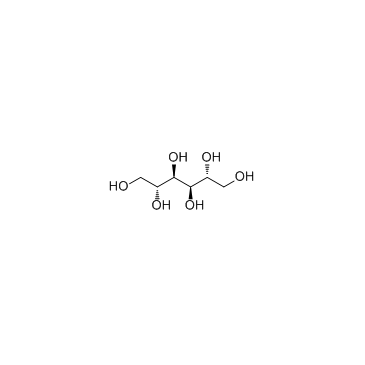
甘露醇结构式

|
常用名 | 甘露醇 | 英文名 | D-Mannitol |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 69-65-8 | 分子量 | 182.172 | |
| 密度 | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 494.9±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C6H14O6 | 熔点 | 167-170ºC | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 292.5±23.3 °C |
|
Urinary metabolic fingerprinting of mice with diet-induced metabolic derangements by parallel dual secondary column-dual detection two-dimensional comprehensive gas chromatography.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1361 , 265-76, (2014) This study investigates the potential of a parallel dual secondary column-dual detection two-dimensional comprehensive GC platform (GC×2GC-MS/FID) for metabolic profiling and fingerprinting of mouse urine. Samples were obtained from a murine model that mimics... |
|
|
Evidence of oxidative stress and mitochondrial respiratory chain dysfunction in an in vitro model of sepsis-induced kidney injury.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1837(10) , 1790-800, (2014) To investigate the role of oxidative stress and/or mitochondrial impairment in the occurrence of acute kidney injury (AKI) during sepsis, we developed a sepsis-induced in vitro model using proximal tubular epithelial cells exposed to a bacterial endotoxin (li... |
|
|
Rapid detection of sugar alcohol precursors and corresponding nitrate ester explosives using direct analysis in real time mass spectrometry.
Analyst 140(8) , 2785-96, (2015) This work highlights the rapid detection of nitrate ester explosives and their sugar alcohol precursors by direct analysis in real time mass spectrometry (DART-MS) using an off-axis geometry. Demonstration of the effect of various parameters, such as ion pola... |
|
|
AS101 prevents diabetic nephropathy progression and mesangial cell dysfunction: regulation of the AKT downstream pathway.
PLoS ONE 9(12) , e114287, (2014) Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is characterized by proliferation of mesangial cells, mesangial expansion, hypertrophy and extracellular matrix accumulation. Previous data have cross-linked PKB (AKT) to TGFβ induced matrix modulation. The non-toxic compound AS101 h... |
|
|
Mitochondrial targeting of bilirubin regulatory enzymes: An adaptive response to oxidative stress.
Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 282(1) , 77-89, (2015) The intracellular level of bilirubin (BR), an endogenous antioxidant that is cytotoxic at high concentrations, is tightly controlled within the optimal therapeutic range. We have recently described a concerted intracellular BR regulation by two microsomal enz... |
|
|
Molecular markers in ambient aerosol in the Mahanadi Riverside Basin of eastern central India during winter.
Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 22(2) , 1220-31, (2015) Organic molecular markers are important atmospheric constituents. Their formation and sources are important aspects of the study of urban and rural air quality. We collected PM10 aerosol samples from the Mahanadi Riverside Basin (MRB), a rural part of eastern... |
|
|
Toxicity of copper on isolated liver mitochondria: impairment at complexes I, II, and IV leads to increased ROS production.
Cell Biochem. Biophys. 70(1) , 367-81, (2014) Oxidative damage has been implicated in disorders associated with abnormal copper metabolism and also Cu(2+) overloading states. Besides, mitochondria are one of the most important targets for Cu(2+), an essential redox transition metal, induced hepatotoxicit... |
|
|
Glassy-state stabilization of a dominant negative inhibitor anthrax vaccine containing aluminum hydroxide and glycopyranoside lipid A adjuvants.
J. Pharm. Sci. 104(2) , 627-39, (2015) During transport and storage, vaccines may be exposed to temperatures outside of the range recommended for storage, potentially causing efficacy losses. To better understand and prevent such losses, dominant negative inhibitor (DNI), a recombinant protein ant... |
|
|
Progressive dopaminergic alterations and mitochondrial abnormalities in LRRK2 G2019S knock-in mice.
Neurobiol. Dis. 78 , 172-95, (2015) Mutations in the LRRK2 gene represent the most common genetic cause of late onset Parkinson's disease. The physiological and pathological roles of LRRK2 are yet to be fully determined but evidence points towards LRRK2 mutations causing a gain in kinase functi... |
|
|
Antisense Oligonucleotide-mediated Suppression of Muscle Glycogen Synthase 1 Synthesis as an Approach for Substrate Reduction Therapy of Pompe Disease.
Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 3 , e206, (2014) Pompe disease is an autosomal recessive disorder caused by a deficiency of acid α-glucosidase (GAA; EC 3.2.1.20) and the resultant progressive lysosomal accumulation of glycogen in skeletal and cardiac muscles. Enzyme replacement therapy using recombinant hum... |