巴氯芬
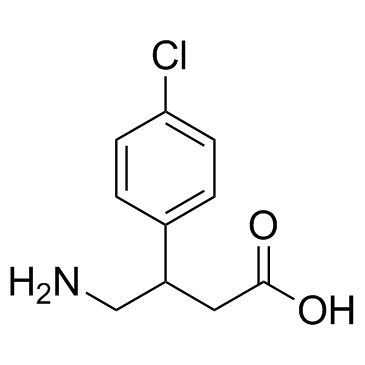
巴氯芬结构式

|
常用名 | 巴氯芬 | 英文名 | Baclofen |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 1134-47-0 | 分子量 | 213.661 | |
| 密度 | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 364.3±32.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C10H12ClNO2 | 熔点 | 208-210°C | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 174.1±25.1 °C | |
| 符号 |


GHS06, GHS08 |
信号词 | Danger |
|
GABA and its B-receptor are present at the node of Ranvier in a small population of sensory fibers, implicating a role in myelination.
J. Neurosci. Res. 93(2) , 285-95, (2014) The γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) type B receptor has been implicated in glial cell development in the peripheral nervous system (PNS), although the exact function of GABA signaling is not known. To investigate GABA and its B receptor in PNS development and dege... |
|
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental drug discovery projects toward safer medicines. In this st... |
|
|
Translating clinical findings into knowledge in drug safety evaluation--drug induced liver injury prediction system (DILIps).
J. Sci. Ind. Res. 65(10) , 808, (2006) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a significant concern in drug development due to the poor concordance between preclinical and clinical findings of liver toxicity. We hypothesized that the DILI types (hepatotoxic side effects) seen in the clinic can be tra... |
|
|
Chemical genetics reveals a complex functional ground state of neural stem cells.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 3(5) , 268-273, (2007) The identification of self-renewing and multipotent neural stem cells (NSCs) in the mammalian brain holds promise for the treatment of neurological diseases and has yielded new insight into brain cancer. However, the complete repertoire of signaling pathways ... |
|
|
Structural requirements for drug inhibition of the liver specific human organic cation transport protein 1.
J. Med. Chem. 51 , 5932-42, (2008) The liver-specific organic cation transport protein (OCT1; SLC22A1) transports several cationic drugs including the antidiabetic drug metformin and the anticancer agents oxaliplatin and imatinib. In this study, we explored the chemical space of registered ora... |
|
|
GABAB receptors are expressed in human aortic smooth muscle cells and regulate the intracellular Ca(2+) concentration.
Heart Vessels 30(2) , 249-57, (2015) The aim of this study was to investigate the expression of GABAB receptors, a subclass of receptors to the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABAB), in human aortic smooth muscle cells (HASMCs), and to explore if altering receptor activatio... |
|
|
Gingival pain: an unusual side effect of ziprasidone.
BMJ Case Rep. 2013 , doi:10.1136/bcr-2012-007577, (2013) The patient is a 52-year-old man with schizophrenia who developed severe, unremitting gingival pain after his ziprasidone dosage was increased from 80 to 120 mg. His physical examination and laboratory findings were unremarkable. He did not have any extra-pyr... |
|
|
Pharmacological characterization of GABAB receptor subtypes assembled with auxiliary KCTD subunits.
Neuropharmacology 88 , 145-54, (2014) GABAB receptors (GABABRs) are considered promising drug targets for the treatment of mental health disorders. GABABRs are obligate heteromers of principal GABAB1 and GABAB2 subunits. GABABRs can additionally associate with auxiliary KCTD8, 12, 12b and 16 subu... |
|
|
Molecular modifications on carboxylic acid derivatives as potent histone deacetylase inhibitors: Activity and docking studies.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17 , 5219-28, (2009) In the light of known HDAC inhibitors, 33 carboxylic acid derivatives were tested to understand the structural requirements for HDAC inhibition activity. Several modifications were applied to develop the structure-activity relationships of carboxylic acid HDA... |
|
|
Single-Molecule Imaging of PSD-95 mRNA Translation in Dendrites and Its Dysregulation in a Mouse Model of Fragile X Syndrome.
J. Neurosci. 35 , 7116-30, (2015) Fragile X syndrome (FXS) is caused by the loss of the fragile X mental retardation protein (FMRP), an RNA binding protein that regulates translation of numerous target mRNAs, some of which are dendritically localized. Our previous biochemical studies using sy... |