四甲基罗丹明乙酯高氯酸盐
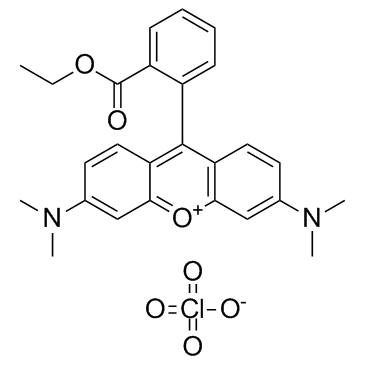
四甲基罗丹明乙酯高氯酸盐结构式

|
常用名 | 四甲基罗丹明乙酯高氯酸盐 | 英文名 | TMRE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 115532-52-0 | 分子量 | 514.955 | |
| 密度 | N/A | 沸点 | N/A | |
| 分子式 | C26H27ClN2O7 | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | N/A | |
| 符号 |

GHS07 |
信号词 | Warning |
|
Synergism of arsenic trioxide and MG132 in Raji cells attained by targeting BNIP3, autophagy, and mitochondria with low doses of valproic acid and vincristine.
Eur. J. Cancer 50(18) , 3243-61, (2014) We previously demonstrated that arsenic trioxide (ATO) and proteasome inhibitor MG132 synergistically induced cell death in promonocytic leukaemia cell line U937 but were antagonistic in Burkitt's lymphoma cell line Raji. Here we explore the role of autophagy... |
|
|
Mutations in the Corneal Endothelial Dystrophy-Associated Gene SLC4A11 Render the Cells More Vulnerable to Oxidative Insults.
Cornea 34 , 668-74, (2015) To investigate the effect of mutations in SLC4A11 on cellular localization of the protein, mitochondrial function, and apoptosis due to oxidative stress. Mutations in SLC4A11 have been associated with 2 different forms of corneal endothelial dystrophy that le... |
|
|
Cyclophilin-D: a resident regulator of mitochondrial gene expression.
FASEB J. 29(7) , 2734-48, (2015) Cyclophilin-D (Cyp-D) is a mitochondrial matrix peptidyl-prolyl isomerase. Because cyclophilins can regulate nuclear gene expression, we examined whether Cyp-D could regulate mitochondrial gene expression. We demonstrated in HEK 293T cells that transfected Cy... |
|
|
Destabilisation of dimeric 14-3-3 proteins as a novel approach to anti-cancer therapeutics.
Oncotarget 6 , 14522-36, (2015) 14-3-3 proteins play a pivotal role in controlling cell proliferation and survival, two commonly dysregulated hallmarks of cancers. 14-3-3 protein expression is enhanced in many human cancers and correlates with more aggressive tumors and poor prognosis, sugg... |
|
|
Aminopeptidase P3, a new member of the TNF-TNFR2 signaling complex, induces phosphorylation of JNK1 and JNK2.
J. Cell Sci. 128(4) , 656-69, (2015) Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is an important mediator that triggers onset of autoimmune diseases and exerts its biological effects by interacting through two receptors, TNFR1 (also known as TNFRSF1A) and TNFR2 (also known as TNFRSF1B). TNFR2 signaling has sign... |
|
|
Plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase isoforms composition regulates cellular pH homeostasis in differentiating PC12 cells in a manner dependent on cytosolic Ca2+ elevations.
PLoS ONE 9(7) , e102352, (2014) Plasma membrane Ca(2+)-ATPase (PMCA) by extruding Ca(2+) outside the cell, actively participates in the regulation of intracellular Ca(2+) concentration. Acting as Ca(2+)/H(+) counter-transporter, PMCA transports large quantities of protons which may affect o... |
|
|
Low abundance of mitochondrial DNA changes mitochondrial status and renders cells resistant to serum starvation and sodium nitroprusside insult.
Cell Biol. Int. 39 , 865-72, (2015) Mutation or depletion of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) can cause severe mitochondrial malfunction, originating from the mitochondrion itself, or from the crosstalk between nuclei and mitochondria. However, the changes that would occur if the amount of mtDNA is di... |
|
|
HBCDD-induced sustained reduction in mitochondrial membrane potential, ATP and steroidogenesis in peripubertal rat Leydig cells.
Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 282(1) , 20-9, (2015) Hexabromocyclododecane (HBCDD), a brominated flame retardant added to various consumer products, is a ubiquitous environmental contaminant. We have previously shown that 6-hour exposure to HBCDD disturbs basal and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)-induced st... |
|
|
HAX-1 regulates cyclophilin-D levels and mitochondria permeability transition pore in the heart.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 112 , E6466-75, (2015) The major underpinning of massive cell death associated with myocardial infarction involves opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP), resulting in disruption of mitochondria membrane integrity and programmed necrosis. Studies in human ... |
|
|
Controlled sumoylation of the mevalonate pathway enzyme HMGS-1 regulates metabolism during aging.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 111(37) , E3880-9, (2014) Many metabolic pathways are critically regulated during development and aging but little is known about the molecular mechanisms underlying this regulation. One key metabolic cascade in eukaryotes is the mevalonate pathway. It catalyzes the synthesis of stero... |