DAPT (GSI-IX)
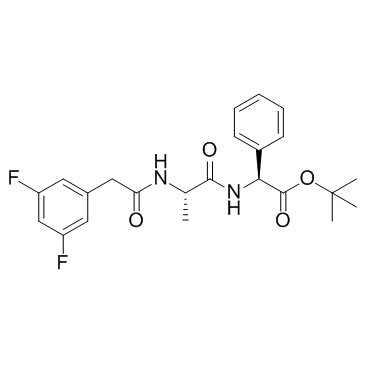
DAPT (GSI-IX)结构式

|
常用名 | DAPT (GSI-IX) | 英文名 | DAPT (GSI-IX) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 208255-80-5 | 分子量 | 432.460 | |
| 密度 | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 612.2±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C23H26F2N2O4 | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 美版 | 闪点 | 324.1±31.5 °C |
|
A small molecule targeting ALK1 prevents Notch cooperativity and inhibits functional angiogenesis.
Angiogenesis 18(2) , 209-17, (2015) Activin receptor-like kinase 1 (ALK1, encoded by the gene ACVRL1) is a type I BMP/TGF-β receptor that mediates signalling in endothelial cells via phosphorylation of SMAD1/5/8. During angiogenesis, sprouting endothelial cells specialise into tip cells and sta... |
|
|
Relaxin protects cardiac muscle cells from hypoxia/reoxygenation injury: involvement of the Notch-1 pathway.
FASEB J. 29(1) , 239-49, (2015) In animal models, the cardiotropic hormone relaxin has been shown to protect the heart against ischemia and reperfusion-induced damage, acting by multiple mechanisms that primarily involve the coronary vessels. This in vitro study evaluates whether relaxin al... |
|
|
Loss of the Notch effector RBPJ promotes tumorigenesis.
J. Exp. Med. 212(1) , 37-52, (2015) Aberrant Notch activity is oncogenic in several malignancies, but it is unclear how expression or function of downstream elements in the Notch pathway affects tumor growth. Transcriptional regulation by Notch is dependent on interaction with the DNA-binding t... |
|
|
Notch signaling promotes osteoclast maturation and resorptive activity.
J. Cell. Biochem. 116 , 2598-609, (2015) The role of Notch signaling in osteoclast differentiation is controversial with conflicting experimental evidence indicating both stimulatory and inhibitory roles. Differences in experimental protocols and in vivo versus in vitro models may explain the discre... |
|
|
In vitro expansion of single Lgr5+ liver stem cells induced by Wnt-driven regeneration.
Nature 494 , 247-50, (2013) The Wnt target gene Lgr5 (leucine-rich-repeat-containing G-protein-coupled receptor 5) marks actively dividing stem cells in Wnt-driven, self-renewing tissues such as small intestine and colon, stomach and hair follicles. A three-dimensional culture system al... |
|
|
Outcome of patients on oral anticoagulation undergoing coronary artery stenting: data from discharge to 12 months in the Warfarin and Coronary Stenting (WAR-STENT) Registry.
J. Invasive Cardiol. 26(11) , 563-9, (2014) To obtain further, and more focused, information on the efficacy and safety of the antithrombotic regimens, including triple therapy (TT) of warfarin, aspirin, and clopidogrel; dual therapy (DT) of warfarin and single antiplatelet agent (aspirin or clopidogre... |
|
|
Alk1 and Alk5 inhibition by Nrp1 controls vascular sprouting downstream of Notch.
Nat. Commun. 6 , 7264, (2015) Sprouting angiogenesis drives blood vessel growth in healthy and diseased tissues. Vegf and Dll4/Notch signalling cooperate in a negative feedback loop that specifies endothelial tip and stalk cells to ensure adequate vessel branching and function. Current co... |
|
|
Inside-out Regulation of Ectodomain Cleavage of Cluster-of-Differentiation-44 (CD44) and of Neuregulin-1 Requires Substrate Dimerization.
J. Biol. Chem. 290 , 17041-54, (2015) Ectodomain shedding of transmembrane precursor proteins generates numerous life-essential molecules, such as epidermal growth factor receptor ligands. This cleavage not only releases the regulatory growth factor, but it is also the required first step for the... |
|
|
Shedding of glycan-modifying enzymes by signal peptide peptidase-like 3 (SPPL3) regulates cellular N-glycosylation.
EMBO J. 33(24) , 2890-905, (2014) Protein N-glycosylation is involved in a variety of physiological and pathophysiological processes such as autoimmunity, tumour progression and metastasis. Signal peptide peptidase-like 3 (SPPL3) is an intramembrane-cleaving aspartyl protease of the GxGD type... |
|
|
Loss of endophilin-B1 exacerbates Alzheimer's disease pathology.
Brain 138 , 2005-19, (2015) Endophilin-B1, also known as Bax-interacting factor 1 (Bif-1, and encoded by SH3GLB1), is a multifunctional protein involved in apoptosis, autophagy and mitochondrial function. We recently described a unique neuroprotective role for neuron-specific alternativ... |