铬酸钠,四水合物
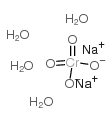
铬酸钠,四水合物结构式

|
常用名 | 铬酸钠,四水合物 | 英文名 | Sodium chromate tetrahydrate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 10034-82-9 | 分子量 | 234.03400 | |
| 密度 | 2.73 | 沸点 | N/A | |
| 分子式 | CrH8Na2O8 | 熔点 | 792ºC | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | N/A | |
| 符号 |




GHS05, GHS06, GHS08, GHS09 |
信号词 | Danger |
|
Particulate and soluble hexavalent chromium are cytotoxic and genotoxic to human lung epithelial cells.
Mutat. Res. 610(1-2) , 2-7, (2006) Particulate hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI)) is a well-established human lung carcinogen. It is currently a major public health concern, there is widespread exposure to it in occupational settings and to the general public. However, despite the potential widespre... |
|
|
Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of hexavalent chromium in human and North Atlantic right whale (Eubalaena glacialis) lung cells
Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 150(4) , 487-94, (2009) Humans and cetaceans are exposed to a wide range of contaminants. In this study, we compared the cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of a metal pollutant, hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)], which has been shown to cause damage in lung cells from both humans and North ... |
|
|
The clastogenic effects of chronic exposure to particulate and soluble Cr(VI) in human lung cells.
Mutat. Res. 610(1-2) , 8-13, (2006) Hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI)) is a well-designated human lung carcinogen, with solubility playing an important role in its carcinogenic potential. Although it is known that particulate or water-insoluble Cr(VI) compounds are more potent than the soluble specie... |
|
|
Human lung cell growth is not stimulated by lead ions after lead chromate-induced genotoxicity.
Mol. Cell Biochem. 279(1-2) , 75-84, (2005) Chromate compounds are known human lung carcinogens. Water solubility is an important factor in the carcinogenicity of these compounds with the most potent carcinogenic compounds being water-insoluble or 'particulate'. Previously we have shown that particulat... |
|
|
Comparative cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of particulate and soluble hexavalent chromium in human and sperm whale (Physeter macrocephalus) skin cells.
Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 155(1) , 143-50, (2012) Chromium (Cr) is a global marine pollutant, present in marine mammal tissues. Hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)] is a known human carcinogen. In this study, we compare the cytotoxic and clastogenic effects of Cr(VI) in human (Homo sapiens) and sperm whale (Physeter... |
|
|
Chromium oxidation state imaging in mammalian cells exposed in vitro to soluble or particulate chromate compounds.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 18(10) , 1512-9, (2005) Hexavalent chromium compounds are known carcinogens for the respiratory tract in humans. The mechanism of cell transformation by hexavalent chromium compounds is not fully understood although a role for intracellular reduction is sought. The aim of this study... |
|
|
Carcinogenic lead chromate induces DNA double-strand breaks in human lung cells.
Mutat. Res. 586(2) , 160-72, (2005) Hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI)) is a widespread environmental contaminant and a known human carcinogen, generally causing bronchial cancer. Recent studies have shown that the particulate forms of Cr(VI) are the potent carcinogens. Particulate Cr(VI) is known to ... |
|
|
Chromium-induced genotoxicity and interference in human lymphoblastoid cell (TK6) repair processes.
J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 74(15-16) , 1030-9, (2011) Two model chromium (Cr) compounds, one hexavalent (sodium chromate) and one trivalent (chromium chloride), were investigated in a human lymphoblastoid cell line (TK6) to increase our knowledge regarding Cr-induced genotoxicity mechanisms. Both selected compou... |
|
|
Comparison between acetic acid and landfill leachates for the leaching of Pb(II), Cd(II), As(V), and Cr(VI) from cementitious wastes.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 38(14) , 3977-83, (2004) The Toxicity Characteristic Leaching Procedure (TCLP) has been widely used to characterize the suitability of solid wastes for disposal in landfills. However, the widespread application of this test for the assessment of wastes disposed in different landfill ... |
|
|
Elucidation of the percutaneous absorption of chromium compounds by functional proteomics.
Proteomics 9(22) , 5120-31, (2009) Chromium compounds are known to be associated with cytotoxicity and carcinogenicity when applied via a skin route. The aim of this study was to evaluate the skin permeability and toxicological profiles of four chromium species. Chromium permeation across the ... |