Erastin
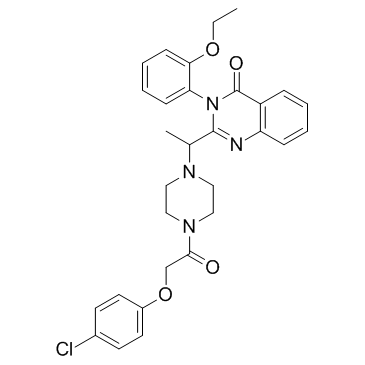
Erastin结构式

|
常用名 | Erastin | 英文名 | Erastin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 571203-78-6 | 分子量 | 547.044 | |
| 密度 | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 721.9±70.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C30H31ClN4O4 | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 390.4±35.7 °C | |
| 符号 |

GHS06 |
信号词 | Danger |
|
HSPB1 as a novel regulator of ferroptotic cancer cell death.
Oncogene 34(45) , 5617-25, (2015) Ferroptosis is an iron-dependent form of non-apoptotic cell death, but its molecular mechanism remains largely unknown. Here, we demonstrate that heat shock protein beta-1 (HSPB1) is a negative regulator of ferroptotic cancer cell death. Erastin, a specific f... |
|
|
Sensitization of acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells for LCL161-induced cell death by targeting redox homeostasis.
Biochem. Pharmacol. 105 , 14-22, (2016) Disturbed redox homeostasis with both elevated reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels and antioxidant defense mechanisms has been reported in acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). We therefore hypothesized that inhibition of pathways responsible for ROS detoxific... |
|
|
Glutathione peroxidase 4 prevents necroptosis in mouse erythroid precursors.
Blood 127 , 139-48, (2016) Maintaining cellular redox balance is vital for cell survival and tissue homoeostasis because imbalanced production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) may lead to oxidative stress and cell death. The antioxidant enzyme glutathione peroxidase 4 (Gpx4) is a key r... |
|
|
The 5-Lipoxygenase Inhibitor Zileuton Confers Neuroprotection against Glutamate Oxidative Damage by Inhibiting Ferroptosis.
Biol. Pharm. Bull. 38 , 1234-9, (2015) 5-Lipoxygenase (5-LOX) inhibitors have been shown to be protective in several neurodegenerative disease models; however, the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. We investigated whether 5-LOX inhibitor zileuton conferred direct neuroprotection against glutam... |
|
|
Activation of the p62-Keap1-NRF2 pathway protects against ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
Hepatology 63 , 173-84, (2015) Ferroptosis is a recently recognized form of regulated cell death caused by an iron-dependent accumulation of lipid reactive oxygen species. However, the molecular mechanisms regulating ferroptosis remain obscure. Here, we report that nuclear factor erythroid... |
|
|
Discovery of small-molecule enhancers of reactive oxygen species that are nontoxic or cause genotype-selective cell death.
ACS Chem. Biol. 8(5) , 923-9, (2013) Elevation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels has been observed in many cancer cells relative to nontransformed cells, and recent reports have suggested that small-molecule enhancers of ROS may selectively kill cancer cells in various in vitro and in vivo... |
|
|
RAS-RAF-MEK-dependent oxidative cell death involving voltage-dependent anion channels.
Nature 447 , 864-868, (2007) Therapeutics that discriminate between the genetic makeup of normal cells and tumour cells are valuable for treating and understanding cancer. Small molecules with oncogene-selective lethality may reveal novel functions of oncoproteins and enable the creation... |
|
|
Identification of genotype-selective antitumor agents using synthetic lethal chemical screening in engineered human tumor cells.
Cancer Cell 3 , 285-296 , (2003) We used synthetic lethal high-throughput screening to interrogate 23,550 compounds for their ability to kill engineered tumorigenic cells but not their isogenic normal cell counterparts. We identified known and novel compounds with genotype-selective activity... |
|
|
Chemical genetic approaches to probing cell death.
Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 11 , 83-87, (2007) Chemical genetics has arisen as a tool for the discovery of pathways and proteins in mammalian systems. This approach, comprising small-molecule screening combined with biochemical and genomic target identification methods, enables one to assess which protein... |
|
|
Antifungal drug itraconazole targets VDAC1 to modulate the AMPK/mTOR signaling axis in endothelial cells.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 112 , E7276-85, (2015) Itraconazole, a clinically used antifungal drug, was found to possess potent antiangiogenic and anticancer activity that is unique among the azole antifungals. Previous mechanistic studies have shown that itraconazole inhibits the mechanistic target of rapamy... |