4-环己烷丁酸
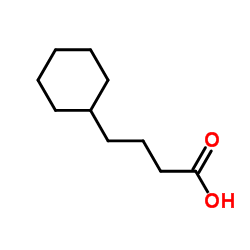
4-环己烷丁酸结构式

|
常用名 | 4-环己烷丁酸 | 英文名 | Cyclohexanebutyric acid |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 4441-63-8 | 分子量 | 170.249 | |
| 密度 | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 283.3±8.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C10H18O2 | 熔点 | 30-32 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 138.9±9.8 °C | |
| 符号 |

GHS07 |
信号词 | Warning |
|
Biosynthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoate copolyester containing cyclohexyl groups by Pseudomonas oleovorans.
Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 29(3) , 145-50, (2001) Production of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) substituted with cyclohexyl groups by Pseudomonas oleovorans grown with 4-cyclohexylbutyric acid (4-CHB) and its mixtures with nonanoic acid (NA) was investigated. Addition of NA to medium gave rise to an increase in... |
|
|
Metabolism of cyclohexaneacetic acid and cyclohexanebutyric acid by Arthrobacter sp. strain CA1.
J. Bacteriol. 150(3) , 1172-82, (1982) A strain of Arthrobacter was isolated by enrichment culture with cyclohexaneacetate as the sole source of carbon and grew with a doubling time of 4.2 h. In addition to growing with cyclohexaneacetate, the organism also grew with cyclohexanebutyrate at concent... |
|
|
Naphthenic acid biodegradation by the unicellular alga Dunaliella tertiolecta.
Chemosphere 84(4) , 504-11, (2011) Naphthenic acids (NAs) are a major contributor to toxicity in tailings waste generated from bitumen production in the Athabasca Oil Sands region. While investigations have shown that bacteria can biodegrade NAs and reduce tailings toxicity, the potential of a... |