对羟基苯甲酸钠
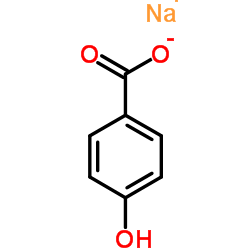
对羟基苯甲酸钠结构式

|
常用名 | 对羟基苯甲酸钠 | 英文名 | Sodium 4-hydroxybenzoate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 114-63-6 | 分子量 | 160.103 | |
| 密度 | 1.375g/cm3 | 沸点 | 336.2ºC at 760mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C7H5NaO3 | 熔点 | >300 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 171.3ºC | |
| 符号 |

GHS07 |
信号词 | Warning |
|
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Inhibition of the β-class enzymes from the fungal pathogens Candida albicans and Cryptococcus neoformans with branched aliphatic/aromatic carboxylates and their derivatives.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 21 , 2521-6, (2011) The inhibition of the β-carbonic anhydrases (CAs, EC 4.2.1.1) from the pathogenic fungi Cryptococcus neoformans (Can2) and Candida albicans (Nce103) with a series of 25 branched aliphatic and aromatic carboxylates has been investigated. Human isoforms hCA I a... |
|
|
Enzyme-catalyzed modification of PES surfaces: Reduction in adsorption of BSA, dextrin and tannin
J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 378(1) , 191-200, (2012) Graphical abstract |
|
|
p-Hydroxybenzoate esters metabolism in MCF7 breast cancer cells.
Food Chem. Toxicol. 50(11) , 4109-14, (2012) Parabens are among the most frequently used preservatives to inhibit microbial growth and extend the shelf life of a range of consumer products. The objective of the present study was to gain insight into the metabolism of parabens in breast cancer cells (MCF... |
|
|
Genomic and functional analyses of the gentisate and protocatechuate ring-cleavage pathways and related 3-hydroxybenzoate and 4-hydroxybenzoate peripheral pathways in Burkholderia xenovorans LB400.
PLoS ONE 8(2) , e56038, (2013) In this study, the gentisate and protocatechuate pathways in Burkholderia xenovorans LB400 were analyzed by genomic and functional approaches, and their role in 3-hydroxybenzoate (3-HBA) and 4-hydroxybenzoate (4-HBA) degradation was proposed. The LB400 genome... |
|
|
The rice bacterial pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae produces 3-hydroxybenzoic acid and 4-hydroxybenzoic acid via XanB2 for use in xanthomonadin, ubiquinone, and exopolysaccharide biosynthesis.
Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 26(10) , 1239-48, (2013) Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae, the causal agent of rice bacterial blight, produces membrane-bound yellow pigments, referred to as xanthomonadins. Xanthomonadins protect the pathogen from photodamage and host-induced perioxidation damage. They are also require... |
|
|
Antiproliferative and proapoptotic activities of 4-hydroxybenzoic acid-based inhibitors of histone deacetylases.
Cancer Lett. 343(1) , 134-46, (2014) Histone acetyltransferases (HATs) and histone deacetylases (HDACs) regulate cellular processes by modifying the acetylation status of many proteins. Pathologically altered HDAC activity contributes to cancer development and thus characterization of novel acet... |
|
|
Antioxidant capacities, phenolic compounds and polysaccharide contents of 49 edible macro-fungi.
Food Funct. 3(11) , 1195-205, (2012) Edible macro-fungi are widely consumed as food sources for their flavors and culinary features. In order to explore the potential of macro-fungi as a natural resource of bioactive compounds, the antioxidant properties and polysaccharide contents of 49 edible ... |
|
|
Mixed ligand-silver(I) complexes with anti-inflammatory agents which can bind to lipoxygenase and calf-thymus DNA, modulating their function and inducing apoptosis.
Metallomics 4(6) , 545-60, (2012) A new mixed ligand-silver(I) complex of formula [Ag(tpp)(2)(p-Hbza)] (1) (p-HbzaH = 4-hydroxybenzoic acid and tpp = triphenylphosphine) has been synthesized and characterized by elemental analysis, mp, vibrational spectroscopy (mid- and far-FT-IR), (1)H-NMR, ... |
|
|
Development of magnetic multiwalled carbon nanotubes as solid-phase extraction technique for the determination of p-hydroxybenzoates in beverage.
J. Sep. Sci. 35(13) , 1667-74, (2012) In this work, magnetic multiwalled carbon nanotubes were synthesized through a facile hydrothermal process, and then successfully used as magnetic solid-phase extraction sorbents for the determination of p-hydroxybenzoates in beverage. The prepared magnetic m... |
|
|
Erythrolic acids A-E, meroterpenoids from a marine-derived Erythrobacter sp.
J. Org. Chem. 77(7) , 3401-7, (2012) Erythrolic acids A-E (1-5) are five unusual meroterpenoids isolated from the bacterium Erythrobacter sp. derived from a marine sediment sample collected in Galveston, TX. The structures were elucidated by means of detailed spectroscopic analysis and chemical ... |