3-羟基肉桂酸
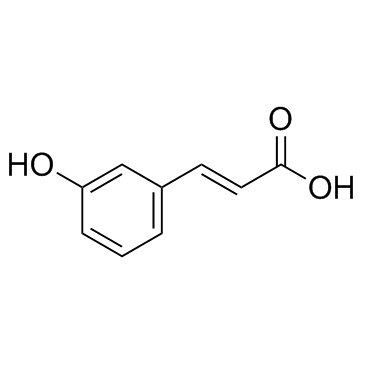
3-羟基肉桂酸结构式

|
常用名 | 3-羟基肉桂酸 | 英文名 | 3-Hydroxycinnamic acid |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 588-30-7 | 分子量 | 164.158 | |
| 密度 | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 373.2±25.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C9H8O3 | 熔点 | 193-195ºC(lit.) | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 193.7±19.7 °C | |
| 符号 |

GHS07 |
信号词 | Warning |
|
Antimicrobial activity of natural products from the flora of Northern Ontario, Canada.
Pharm. Biol. 53(6) , 800-6, (2015) The number of multidrug resistant (MDR) microorganisms is increasing and the antimicrobial resistance expressed by these pathogens is generating a rising global health crisis. In fact, there are only a few antimicrobial agents left that can be used against MD... |
|
|
The tomato sauce making process affects the bioaccessibility and bioavailability of tomato phenolics: a pharmacokinetic study.
Food Chem. 173 , 864-72, (2014) Tomato sauce is the most commonly consumed processed tomato product worldwide, but very little is known about how the manufacturing process may affect the phenolic composition and bioavailability after consumption. In a prospective randomised, cross-over inte... |
|
|
Development of a targeted method for twenty-three metabolites related to polyphenol gut microbial metabolism in biological samples, using SPE and UHPLC-ESI-MS/MS.
Talanta 128 , 221-30, (2014) An increasing number of studies have concerned the profiling of polyphenol microbial metabolites, especially in urine or plasma, but only a few have regarded their accurate quantification. This study reports on a new ultra-performance liquid chromatography ta... |
|
|
Dietary supplementation with cocoa flavanols does not alter colon tissue profiles of native flavanols and their microbial metabolites established during habitual dietary exposure in C57BL/6J mice.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 62(46) , 11190-9, (2014) Metabolism of flavanols (catechins, procyanidins) by gut microbiota has been extensively characterized. Comparatively little is known about accumulation of flavanols and their metabolites in the colon tissues, particularly during chronic exposure to low doses... |
|
|
Assessment of the anti-invasion potential and mechanism of select cinnamic acid derivatives on human lung adenocarcinoma cells.
Mol. Pharm. 10(5) , 1890-900, (2013) Patients with lung adenocarcinoma are often diagnosed with metastasizing symptoms and die of early and distal metastasis. Metastasis is made up of a cascade of interrelated and sequential steps, including cell adhesion, extracellular matrix degradation, cell ... |
|
|
Microbial metabolites of ingested caffeic acid are absorbed by the monocarboxylic acid transporter (MCT) in intestinal Caco-2 cell monolayers.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 52(21) , 6418-24, (2004) It was previously reported that m-coumaric acid, m-hydroxyphenylpropionic acid (mHPP), and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylpropionic acid (DHPP) are major metabolites of ingested caffeic acid formed by gut microflora and would be transported by the monocarboxylic acid tra... |
|
|
Kinetic study on the slow inhibition of epidermis tyrosinase by m-coumaric acid.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 790(2) , 101-7, (1984) The inhibition by m-coumaric acid of oxidation of L-dopa by epidermis tyrosinase (monophenol,dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine:oxygen oxidoreductase, EC 1.14.18.1) is characterized by a prolonged transient phase. Kinetic data correspond to that for a postulated mecha... |
|
|
Orally administered rosmarinic acid is present as the conjugated and/or methylated forms in plasma, and is degraded and metabolized to conjugated forms of caffeic acid, ferulic acid and m-coumaric acid.
Life Sci. 75(2) , 165-78, (2004) Rosmarinic acid (RA) is contained in various Lamiaceae herbs used commonly as culinary herbs. Although RA has various potent physiological actions, little is known on its bioavailability. We therefore investigated the absorption and metabolism of orally admin... |
|
|
Antimicrobial activity and phenolic content of natural site and micropropagated Limonium avei (De Not.) Brullo & Erben plant extracts.
Nat. Prod. Res. 26(22) , 2132-6, (2012) This study reported the antimicrobial activity and phenolic content of natural site and micropropagated Limonium avei (De Not.) Brullo & Erben inflorescences. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) of ethanolic... |