13-Methyltetradecanoic acid
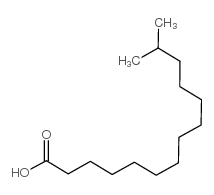
13-Methyltetradecanoic acid structure
|
Common Name | 13-Methyltetradecanoic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2485-71-4 | Molecular Weight | 242.40 | |
| Density | 0.894 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 355.5ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H30O2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 197.4ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Melanogenesis of methyl myristate loaded niosomes in B16F10 melanoma cells.
J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 9(4) , 626-38, (2013) The objective of this study was to compare the charge effect of methyl myristate loaded in neutral (Brij 72/cholesterol at 7:3), cationic (Brij 72/cholesterol/dimethyl dioctadecyl ammonium bromide at 7:3:0.65) and anionic niosomes (Brij 72/cholesterol/dicetyl... |
|
|
Methyl-branched poly(hydroxyalkanoate) biosynthesis from 13-methyltetradecanoic acid and mixed isostearic acid isomer substrates.
Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 85 , 359-370, (2009) Pseudomonas resinovorans, a known medium-chain-length (mcl-) poly(hydroxyalkanoate) (PHA) producer, was grown on 13-methyltetradecanoic acid (13-MTDA) and a mixture of isostearic acid (IA) isomers to produce methyl-branched mcl-PHA polymers. Shake-flask exper... |
|
|
13-Methyltetradecanoic acid induces mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis in human bladder cancer cells.
Urol. Oncol. 30(3) , 339-45, (2010) 13-Methyltetradecanoic acid (13-MTD), a saturated branched-chain fatty acid purified from soy fermentation products, is known to induce apoptosis in many types of human cancer cells. This study was designed to investigate the molecular mechanisms involved in ... |
|
|
Induction of apoptotic cell death and in vivo growth inhibition of human cancer cells by a saturated branched-chain fatty acid, 13-methyltetradecanoic acid.
Cancer Res. 60 , 505-509, (2000) A saturated branched-chain fatty acid, 13-methyltetradecanoic acid (13-MTD), was purified from a soy fermentation product, which was used by many cancer patients as a treatment supplement. Our preliminary study indicated that 13-MTD could induce cell death in... |
|
|
Biosynthesis of iso-fatty acids in myxobacteria.
Org. Biomol. Chem. 3 , 2824-2831, (2005) The fatty acid (FA) profiles of the myxobacteria Stigmatella aurantiaca and Myxococcus xanthus were investigated by acidic methanolysis of total cell extracts and GC or GC-MS analysis. The main components were 13-methyltetradecanoic acid (iso-15:0) and (Z)-he... |
|
|
Incorporation of branched-chain fatty acid into cellular lipids and caspase-independent apoptosis in human breast cancer cell line, SKBR-3.
Lipids Health Dis. 4 , 29, (2005) 13-Methyltetradecanoic acid (13-MTD), an iso-C15 branched- chain saturated fatty acid, has been shown to induce apoptotic cell death of numerous human cancer cells. However, the mechanism for the induction of apoptosis has not been fully understood. This stud... |
|
|
The fatty acid bimodal action on superoxide anion production by human adherent monocytes under phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate or diacylglycerol activation can be explained by the modulation of protein kinase C and p47phox translocation.
J. Biol. Chem. 270(25) , 15111-8, (1995) We studied the translocation of protein kinase C (PKC), the endogenous phosphorylation and presence in the membrane fraction of p47phox (the 47-kDa cytosolic component of the phagocyte NADPH oxidase), and the O-.2 production in human adherent monocytes (HAMs)... |
|
|
Novel iso-branched ether lipids as specific markers of developmental sporulation in the myxobacterium Myxococcus xanthus.
J. Biol. Chem. 281(48) , 36691-700, (2006) Iso-fatty acids (FAs) are the dominant FA family in all myxobacteria analyzed. Furthermore, it was postulated that iso-FAs or compounds derived thereof are involved in fruiting body formation in Myxococcus xanthus, since mutants with a reduced level of iso-FA... |
|
|
Adipose tissue labelling in man, using a structurally-labelled fatty acid as tracer.
Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 53(1) , 115-9, (1983) Three healthy male subjects had their adipose tissue enriched with a structurally-labelled fatty acid, 13-methyltetradecanoic acid (13-MTD), occurring naturally only in trace amounts. Needle biopsies from femoral, gluteal and abdominal adipose tissue were obt... |
|
|
Impact on lipid membrane organization by free branched-chain fatty acids.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 8(41) , 4792-7, (2006) Here, we exploit the non-invasive techniques of solid-state NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) to study the effect of free iso and ante-iso branched chain fatty acids (BCFAs) on the physicochemical properties of lipid... |