9-(2,2-Dicyanovinyl)julolidine
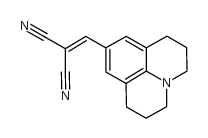
9-(2,2-Dicyanovinyl)julolidine structure
|
Common Name | 9-(2,2-Dicyanovinyl)julolidine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 58293-56-4 | Molecular Weight | 249.31000 | |
| Density | 1.23 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 470.7ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C16H15N3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 214.6ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Fluorescent molecular rotors: a new class of probes for tubulin structure and assembly.
Biochemistry 28 , 6678, (1989) 9-(Dicyanovinyl)julolidine (DCVJ) is a fluorescent dye whose intramolecular rotational relaxation is solvent dependent. Since its quantum yield increases with decreasing free volume, this molecule has been very useful in monitoring synthetic polymer reactions... |
|
|
9-(Dicyanovinyl)julolidine binding to bovine brain calmodulin.
J. Biochem. 109 , 499, (1991) A molecular rotor, 9-(dicyanovinyl)julolidine (DCVJ), is a fluorescent dye whose intramolecular rotation determines its fluorescence yield [Kung, C.E. & Reed, J.K. (1989) Biochemistry 28, 6678-6686]. DCVJ binds to bovine brain calmodulin and emits strong fluo... |
|
|
Antibodies for fluorescent molecular rotors.
Biochemistry 32 , 7589, (1993) We have prepared monoclonal antibodies for the fluorescent molecular rotors 9-(2-carboxy-2-cyanovinyl)julolidine (CCVJ) and 9-(dicyanovinyl)julolidine (DCVJ). Mouse monoclonal antibody (IgG2b) prepared against CCVJ-conjugated bovine serum albumin strongly bou... |
|
|
Conformational Dynamics of Specific Aβ Oligomers Govern Their Ability To Replicate and Induce Neuronal Apoptosis.
Biochemistry 55 , 2238-50, (2016) Oligomers of amyloid-β (Aβ) have emerged as the primary toxic agents responsible for early synaptic dysfunction and neuronal death in Alzheimer's disease (AD). Characterization of oligomers is an important step in the progress toward delineating the complex m... |
|
|
Characterization and Higher-Order Structure Assessment of an Interchain Cysteine-Based ADC: Impact of Drug Loading and Distribution on the Mechanism of Aggregation.
Bioconjug. Chem. 27 , 604-15, (2016) The impact of drug loading and distribution on higher order structure and physical stability of an interchain cysteine-based antibody drug conjugate (ADC) has been studied. An IgG1 mAb was conjugated with a cytotoxic auristatin payload following the reduction... |
|
|
Fluorescent molecular rotors as dyes to characterize polysorbate-containing IgG formulations.
Pharm. Res. 27 , 314-26, (2010) The aim was to evaluate fluorescent molecular rotors (DCVJ and CCVJ), which are mainly sensitive to viscosity, for the characterization of polysorbate-containing IgG formulations and compare them to the polarity-sensitive dyes ANS, Bis-ANS and Nile Red.IgG fo... |
|
|
Assessment of physical stability of an antibody drug conjugate by higher order structure analysis: impact of thiol- maleimide chemistry.
Pharm. Res. 31(7) , 1710-23, (2014) To provide a systematic biophysical approach towards a better understanding of impact of conjugation chemistry on higher order structure and physical stability of an antibody drug conjugate (ADC).ADC was prepared using thiol-maleimide chemistry. Physical stab... |
|
|
A Flow-Cytometry-Based Approach to Facilitate Quantification, Size Estimation and Characterization of Sub-visible Particles in Protein Solutions.
Pharm. Res. 32 , 2863-76, (2015) Sub-visible particles were shown to facilitate unwanted immunogenicity of protein therapeutics. To understand the root cause of this phenomenon, a comprehensive analysis of these particles is required. We aimed at establishing a flow-cytometry-based technolog... |
|
|
Fluid shear stress increases membrane fluidity in endothelial cells: a study with DCVJ fluorescence.
Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 278(4) , H1401-6, (2000) Fluid shear stress (FSS) has been shown to be an ubiquitous stimulator of mammalian cell metabolism. Although many of the intracellular signal transduction pathways have been characterized, the primary mechanoreceptor for FSS remains unknown. One hypothesis i... |
|
|
Fluorescence anisotropy of molecular rotors.
ChemPhysChem 12(3) , 662-72, (2011) We present polarization-resolved fluorescence measurements of fluorescent molecular rotors 9-(2-carboxy-2-cyanovinyl)julolidine (CCVJ), 9-(2,2-dicyanovinyl)julolidine (DCVJ), and a meso-substituted boron dipyrromethene (BODIPY-C(12)). The photophysical proper... |