3,4-Dichlorophenol
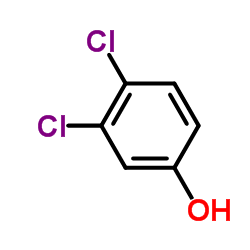
3,4-Dichlorophenol structure
|
Common Name | 3,4-Dichlorophenol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 95-77-2 | Molecular Weight | 163.001 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 247.1±20.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H4Cl2O | Melting Point | 65-67 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 109.1±15.8 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS07 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Microbial degradation of xenobiotic, aromatic pollutants in humic water.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 54(7) , 1864-7, (1988) The microbial degradation of a number of 14C-labeled, recalcitrant, aromatic pollutants, including trichloroguaiacol and di-, tri-, and pentachlorophenol, was investigated in aquatic model systems in the laboratory. Natural, mixed cultures of microorganisms i... |
|
|
Oxidation of 2,4-dichlorophenol and 3,4-dichlorophenol by means of Fe(III)-homogeneous photocatalysis and algal toxicity assessment of the treated solutions.
Water Res. 45(5) , 2038-48, (2011) Chlorophenols are used worldwide as broad-spectrum biocides and fungicides. They have half-life times in water from 0.6 to 550 h and in sediments up to 1700 h and, due to their numerous origins, they can be found in wastewaters, groundwaters or soils. Moreove... |
|
|
Regiospecific dechlorination of pentachlorophenol by dichlorophenol-adapted microorganisms in freshwater, anaerobic sediment slurries.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 57(8) , 2293-301, (1991) The reductive dechlorination of pentachlorophenol (PCP) was investigated in anaerobic sediments that contained nonadapted or 2,4- or 3,4-dichlorophenol (DCP)-adapted microbial communities. Adaptation of sediment communities increased the rate of conversion of... |
|
|
In Silico Improvement of beta3-peptide inhibitors of p53 x hDM2 and p53 x hDMX.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131(18) , 6356-7, (2009) There is great interest in molecules capable of inhibiting the interactions between p53 and its negative regulators hDM2 and hDMX, as these molecules have validated potential against cancers in which one or both oncoproteins are overexpressed. We reported pre... |
|
|
Effect of ambient oxygen concentration upon the acute toxicity of chlorophenols and heavy metals to the groundwater copepod Parastenocaris germanica (Crustacea).
Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 24(2) , 131-43, (1992) Acute static toxicity experiments have been performed under normoxic and hypoxic conditions. The test animals used were adults of the groundwater-adapted copepod Parastenocaris germanica. The animals originated from a sandy, gravelly phreatic aquifer of the M... |
|
|
Degradation of chlorophenols by Phanerochaete chrysosporium: effect of 3,4-dichlorophenol on extracellular peroxidase activities.
Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 59(2-3) , 284-8, (2002) Extracellular peroxidases play an important role in the degradation of chlorophenols by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Depending on the moment of 3,4-dichlorophenol addition, the production of lignin peroxidase and manganese peroxidase in C-limited agitated cul... |
|
|
Disappearance kinetics of 2,4- and 3,4-dichlorophenol in a fluvial system.
Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 62(8) , 971-5, (1984) The disappearance rates of 2,4- and 3,4-dichlorophenol in a small stream were studied and were shown to be first order with respect to either distance or time of flow. Both chlorophenols disappeared at approximately the same rate with average half-lives in th... |