N(G)-Nitroarginine-4-nitroanilide
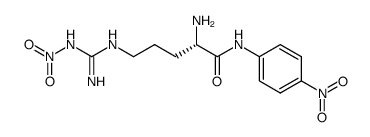
N(G)-Nitroarginine-4-nitroanilide structure
|
Common Name | N(G)-Nitroarginine-4-nitroanilide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 85697-89-8 | Molecular Weight | 339.30700 | |
| Density | 1.59g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C12H17N7O5 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Monitoring nitric oxide (NO) in rat locus coeruleus: differential effects of NO synthase inhibitors.
Neuroreport 8 , 1321-1325, (1997) A porphyrinic microsensor combined with in vivo voltammetry was used to monitor extracellular nitric oxide (NO) in the locus coeruleus (LC) of anaesthetized rats. Administration of N omega-nitro-L-arginine p-nitro-anilide (100 mg/kg, i.p) or 7-nitro indazole ... |
|
|
Effect of phosphodiesterase inhibitors on human arteries in vitro.
Br. J. Anaesth. 76(1) , 122-9, (1996) In the present study, we investigated if the relaxant effects of phosphodiesterase (PDE) III inhibitors on human vessels could be inhibited by a nitric oxide synthase blocker, L-NAME, or by a blocker of ATP-sensitive potassium channels (KATP), glibenclamide. ... |
|
|
Endogenous nitric oxide in the rat pons promotes sleep.
Brain Res. 816(1) , 209-19, (1999) Pontine cholinergic structures are known to play a key role in the regulation of vigilance states associated with desynchronised EEG, i. e., wakefulness and paradoxical sleep. As the cholinergic cells of these nuclei, the pedunculopontine tegmentum (PPT) and ... |
|
|
Stimulation of bradykinin B(1) receptors induces vasodilation in conductance and resistance coronary vessels in conscious dogs: comparison with B(2) receptor stimulation.
Circulation 101(15) , 1848-53, (2000) Constitutive bradykinin B(1) receptors have been identified in dogs; however, their physiological implications involving the coronary circulation remain to be determined. This study examined, in conscious dogs, the coronary response to des-Arg(9)-bradykinin (... |
|
|
NO in the caudal NTS modulates the increase in respiratory frequency in response to chemoreflex activation in awake rats.
Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 166(1) , 32-40, (2009) The role of nitric oxide (NO) in the caudal NTS (cNTS) on baseline cardiovascular and respiratory parameters and on changes in respiratory frequency (fR) and cardiovascular responses to chemoreflex activation was evaluated in awake rats. Bilateral microinject... |
|
|
The role of nitric oxide in inhibitory neurotransmission in the middle cerebral artery of the sheep.
Gen. Pharmacol. 28(3) , 393-7, (1997) 1. The involvement of nitric oxide (NO) as a mediator of inhibitory neurotransmission and its potential release mechanism in sheep isolated middle cerebral artery rings was investigated using NO synthase inhibitors, haemolysate, superoxide dismutase (SOD) and... |
|
|
Nitric oxide and liver microcirculation during autoregulation and haemorrhagic shock in rabbit model.
Br. J. Anaesth. 97(2) , 137-46, (2006) Direct evidence of nitric oxide (NO) involvement in the regulation of hepatic microcirculation is not yet available under physiological conditions nor in haemorrhagic shock.A laser Doppler flowmetry was used to measure liver perfusion index and a specific NO-... |
|
|
Voltammetric detection of nitric oxide (NO) in the rat brain: its variations throughout the sleep-wake cycle.
Neurosci. Lett. 226(2) , 131-5, (1997) A sensor allowing the specific detection of nitric oxide (NO) is reported. Together with differential pulsed voltammetry, it allows the detection of a 650 mV signal either in NO solutions or in the rat frontal cortex. The intraperitoneal (i.p.) administration... |
|
|
Nitric oxide (NO): in vivo electrochemical monitoring in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord of the rat.
Brain Res. 773(1-2) , 66-75, (1997) NO synthase (NOS) is largely distributed in the superficial and deep laminae of the dorsal horn as well as in dorsal root ganglion cells. It has been proposed that nitric oxide (NO) participates in the transmission of sustained, and possibly brief, nociceptiv... |
|
|
Interaction between neurotransmitter antagonists and effects of sacral neuromodulation in rats with chronically hyperactive bladder.
BJU Int. 96(6) , 900-8, (2005) To investigate to what extent antagonists of spinal neurotransmitters interact with the effects of sacral neuromodulation in a rat model of a chronically hyperactive urinary bladder.In female rats the urinary bladder was instilled with turpentine oil 2.5% to ... |