LY-294,002 hydrochloride
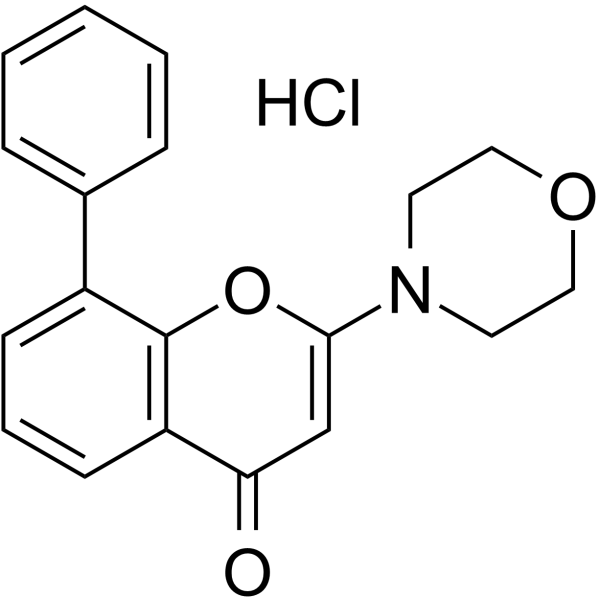
LY-294,002 hydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | LY-294,002 hydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 934389-88-5 | Molecular Weight | 343.80400 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H18ClNO3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
Alpha-lipoic acid activates eNOS through activation of PI3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway.
Vascul. Pharmacol. 64 , 28-35, (2015) Lipoic acid (LA) exerts therapeutic effects on cardiovascular diseases. However, the mechanisms underlying these therapeutic effects remain elusive. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) plays a critical role in cardiovascular homeostasis. LA was shown to ... |
|
|
Neuritogenic Activity of Tetradecyl 2,3-Dihydroxybenzoate Is Mediated through the Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 Receptor/Phosphatidylinositol 3 Kinase/Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Pathway.
Mol. Pharmacol. 88 , 326-34, (2015) Tetradecyl 2,3-dihydroxybenzoate (ABG-001) is a lead compound derived from neuritogenic gentisides. In the present study, we investigated the mechanism by which ABG-001 induces neurite outgrowth in a rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cell line (PC12). Inhibitors o... |
|
|
Deficiency of Factor VII activating protease alters the outcome of ischemic stroke in mice.
Eur. J. Neurosci. 41(7) , 965-75, (2015) Factor VII activating protease (FSAP) is a circulating protease with a putative role in hemostasis, remodeling and inflammation. A polymorphism giving rise to low proteolytic activity has been associated with an increased risk of stroke and carotid stenosis. ... |
|
|
Urocortin 2 stimulates nitric oxide production in ventricular myocytes via Akt- and PKA-mediated phosphorylation of eNOS at serine 1177.
Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 307(5) , H689-700, (2014) Urocortin 2 (Ucn2) is a cardioactive peptide exhibiting beneficial effects in normal and failing heart. In cardiomyocytes, it elicits cAMP- and Ca(2+)-dependent positive inotropic and lusitropic effects. We tested the hypothesis that, in addition, Ucn2 activa... |
|
|
Deciphering combinations of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway drugs augmenting anti-angiogenic efficacy in vivo.
PLoS ONE 9(8) , e105280, (2014) Ocular neovascularization is a common pathology associated with human eye diseases e.g. age-related macular degeneration and proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Blindness represents one of the most feared disabilities and remains a major burden to health-care... |
|
|
Heme oxygenase-1 dysregulates macrophage polarization and the immune response to Helicobacter pylori.
J. Immunol. 193(6) , 3013-22, (2014) Helicobacter pylori incites a futile inflammatory response, which is the key feature of its immunopathogenesis. This leads to the ability of this bacterial pathogen to survive in the stomach and cause peptic ulcers and gastric cancer. Myeloid cells recruited ... |
|
|
Insulin augments serotonin-induced contraction via activation of the IR/PI3K/PDK1 pathway in the rat carotid artery.
Pflugers Arch. 468 , 667-77, (2016) Hyperinsulinemia associated with type 2 diabetes may contribute to the development of vascular diseases. Although we recently reported that enhanced contractile responses to serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT) are observed in the arteries of type 2 diabetes... |
|
|
YB-1 regulates Sox2 to coordinately sustain stemness and tumorigenic properties in a phenotypically distinct subset of breast cancer cells.
BMC Cancer 14 , 328, (2014) Sox2, a transcription factor and an embryonic stem cell marker, has been implicated in the pathogenesis of breast cancer (BC). YB-1 is another transcription factor that has been shown to promote stemness in BC cells.Western blotting, quantitative PCR, and siR... |
|
|
Ketamine affects the neurogenesis of rat fetal neural stem progenitor cells via the PI3K/Akt-p27 signaling pathway.
Birth Defects Res. B Dev. Reprod. Toxicol. 101(5) , 355-63, (2014) Ketamine is widely used as an anesthetic, analgesic, or sedative in pediatric patients. We reported that ketamine alters the normal neurogenesis of rat fetal neural stem progenitor cells (NSPCs) in the developing brain, but the underlying mechanisms remain un... |
|
|
Direct inhibition of the signaling functions of the mammalian target of rapamycin by the phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitors, wortmannin and LY294002.
EMBO J. 15 , 5256-5267, (1996) The immunosuppressant, rapamycin, inhibits cell growth by interfering with the function of a novel kinase, termed mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR). The putative catalytic domain of mTOR is similar to those of mammalian and yeast phosphatidylinositol (PI) ... |