4-(4-Nitrobenzyl)pyridine
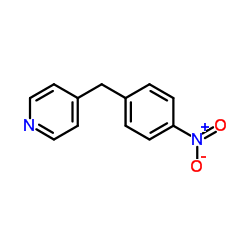
4-(4-Nitrobenzyl)pyridine structure
|
Common Name | 4-(4-Nitrobenzyl)pyridine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1083-48-3 | Molecular Weight | 214.220 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 383.4±22.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C12H10N2O2 | Melting Point | 69-71 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 185.6±22.3 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Colorimetric assays for quantitative analysis and screening of epoxide hydrolase activity.
Biotechnol. Lett. 27(23-24) , 1921-7, (2005) Focusing on directed evolution to tailor enzymes as usable biocatalysts for fine chemistry, we have studied in detail several colorimetric assays for quantitative analysis of epoxide hydrolase (EH) activity. In particular, two assays have been optimized to ch... |
|
|
2,4-dihydroxy-7-methoxy-2H-1,4-benzoxazin-3(4H)-one (DIMBOA) inhibits trichothecene production by Fusarium graminearum through suppression of Tri6 expression.
Int. J. Food Microbiol. 214 , 123-8, (2015) Fusarium head blight (FHB) is a devastating disease of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) caused by a mycotoxigenic fungus Fusarium graminearum resulting in significantly decreased yields and accumulation of toxic trichothecenes in grains. We tested 7 major seconda... |
|
|
The relationship between reactivity of metabolites of pyrrolizidine alkaloids and extrahepatic toxicity.
Proc. West. Pharmacol. Soc. 42 , 13-6, (1999) Pyrrolizidine alkaloids (PAs) are a large group of structurally similar toxins. In animals, including man, they are hepatotoxic and in some cases pneumo- and neurotoxic. PAs are metabolized by the liver P450 system to reactive dehydroalkaloid (DHA) intermedia... |
|
|
Clinical pharmacokinetics of cyclophosphamide and metabolites with and without SR-2508.
Cancer Res. 54(24) , 6421-9, (1994) The pharmacokinetics of cyclophosphamide (CP) and several important metabolites was studied in detail in six patients receiving CP alone and with a radio- and chemosensitizing agent, SR-2508. CP at 1000 mg/m2 was either infused in 20 min alone or given 2 h be... |
|
|
Mutagenicity of bisphenol A (4,4'-isopropylidenediphenol) in vitro: effects of nitrosylation.
Teratog. Carcinog. Mutagen. 22(6) , 425-41, (2002) Bisphenol A (4,4'-isopropylidenediphenol) is a common component of polycarbonate plastics and epoxy resins. Since bisphenol A-containing plastics and resins have found uses in food-contact items, its potential migration into foodstuffs and possible health con... |
|
|
On-resin real-time reaction monitoring of solid-phase oligosaccharide synthesis.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124(43) , 12638-9, (2002) On-resin real-time monitoring by a combination of a color test of (p-nitrobenzyl)pyridine and Disperse Red was developed for oligosaccharide synthesis. |
|
|
DNA-damaging disinfection byproducts: alkylation mechanism of mutagenic mucohalic acids.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 45(20) , 9009-16, (2011) Hydroxyhalofuranones form a group of genotoxic disinfection byproduct (DBP) of increasing interest. Among them, mucohalic acids (3,4-dihalo-5-hydroxyfuran-2(5H)-one, MXA) are known mutagens that react with nucleotides, affording etheno, oxaloetheno, and halop... |
|
|
Sorbate-nitrite interactions: acetonitrile oxide as an alkylating agent.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 22(7) , 1320-4, (2009) Because chemical species with DNA-damaging and mutagenic activity are formed in sorbate-nitrite mixtures and because sorbic acid sometimes coexists with nitrite occurring naturally or incorporated as a food additive, the study of sorbate-nitrite interactions ... |
|
|
Connecting the chemical and biological reactivity of epoxides.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 25(12) , 2755-62, (2012) The chemical reactivity of the mutagenic epoxides (EP) propylene oxide (PO), 1,2-epoxybutane (1,2-EB), and cis- and trans-2,3-epoxybutane (cis- and trans-2,3-EB) with 4-(p-nitrobenzyl)pyridine (NBP), a bionucleophile model for S(N)2 alkylating agents with hig... |
|
|
Gas-phase ion-molecule reactions: a model for the determination of biologically reactive electrophilic contaminants in the environment.
Anal. Chem. 66(11) , 1902-10, (1994) A promising instrumental technique has been investigated to rapidly screen complex environmental samples for chemical contaminants having the propensity to covalently bond to biomacromolecules such as DNA. Radical molecular ions of pyridine, a model compound ... |