Propachlor
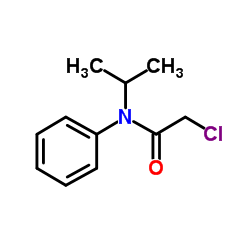
Propachlor structure
|
Common Name | Propachlor | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1918-16-7 | Molecular Weight | 211.688 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 290.4±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C11H14ClNO | Melting Point | 67-76°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 129.4±22.6 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Glutathione-dependent cytotoxicity of the chloroacetanilide herbicides alachlor, metolachlor, and propachlor in rat and human hepatoma-derived cultured cells.
Cell Biol. Toxicol. 15(5) , 325-32, (1999) Alachlor, metolachlor, and propachlor are widely used chloroacetanilide herbicides. Their cytotoxicity in rat (Fa32) and human (Hep G2) hepatoma-derived cells was investigated, in connection with their influence on the endogenous glutathione (GSH) content, on... |
|
|
Kinetics and mechanism of propachlor reductive transformation through nucleophilic substitution by dithionite
Chemosphere 85(9) , 1438-43, (2011) Highlights ► The reductive dechlorination of propachlor was efficiently achieved by dithionite. ► The transformation of propachlor initiated by dithionite follows second-order kinetics. ► Dechlorination was found to be the first and necessary step of propachl... |
|
|
Characterization of glutathione conjugates of chloroacetanilide pesticides using ultra-performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry and liquid chromatography/ion trap mass spectrometry.
Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 21(24) , 4017-22, (2007) Glutathione S-transferases (GSTs) isolated from maize were used to catalyze the conjugation of glutathione (GSH) with chloroacetanilide herbicides, producing stable conjugates that were structurally characterized using ultra-performance liquid chromatography/... |
|
|
Correlation analyses for bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reactions of chloroacetanilide herbicides and their structural analogs with environmentally relevant nucleophiles.
Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 24(10) , 2401-9, (2005) Second-order rate constants (kNuc) for aqueous-phase bimolecular nucleophilic substitution (SN2) reactions of a range of anionic nucleophiles with alachlor, propachlor, and two analogs of propachlor (a thioacetanilide and a beta-anilide) were fit to the Swain... |
|
|
Comparison of rat olfactory mucosal responses to carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic chloracetanilides.
Food Chem. Toxicol. 47(6) , 1051-7, (2009) Alachlor and butachlor are chloracetanilide herbicides that induce olfactory tumors in rats, whereas propachlor does not. The mechanism by which alachlor induces tumors is distinct from many other nasal carcinogens, in that alachlor induces a gradual de-diffe... |
|
|
Pesticide retention in an experimental wetland treating non-point source pollution from agriculture runoff.
Water Sci. Technol. 55(3) , 37-44, (2007) Pesticide losses to the environment are unwanted due to possible environmental and health hazards. An experimental wetland is established to study the efficiency with respect to retention of sediments, nutrients and pesticides. Pesticides were applied on an a... |
|
|
Development of EPA method 535 for the determination of chloroacetanilide and other acetamide herbicide degradates in drinking water by solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry.
J. AOAC Int. 89(1) , 201-9, (2006) U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Method 535 has been developed in order to provide a method for the analysis of "Alachlor ESA and other acetanilide degradation products," which are listed on EPA's 1998 Drinking Water Contaminant Candidate List. Meth... |
|
|
Comparative metabolism and elimination of acetanilide compounds by rat.
Xenobiotica 24(10) , 1003-12, (1994) 1. 14C-labelled propachlor, alachlor, butachlor, metolachlor, methoxypropachlor and some of their mercapturic acid pathway metabolites (MAP) were given to rat either by gavage or by perfusion into a renal artery. MAP metabolites were isolated from bile and ur... |
|
|
Effect of AT-125 on the metabolism of propachlor and the glutathione conjugates of propachlor and bromobenzene in rat.
Xenobiotica 24(9) , 909-19, (1994) 1. Dosing rats with the gamma-glutamyl-transpeptidase inhibitor AT-125 results in the excretion of free glutathione in the urine of rat: this treatment did not lead to the excretion of glutathione conjugates of orally dosed xenobiotics, neither did AT-125 inc... |
|
|
Metabolism of N-isopropylacetanilide in rat.
Xenobiotica 30(12) , 1153-7, (2000) 1. Radioactivity from oral doses of N-isopropyl[1-14C]acetanilide was excreted in urine (53.5%), faeces (8.1%) and expired air (17.0%) of rat. 2. Enterohepatic circulation occurred during formation of approximately 34% of the metabolites. N-isopropylacetanili... |